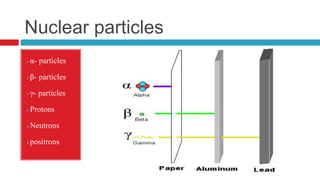
Nuclear radiation detectors detect nuclear particles and radiation. They work by exciting or ionizing the atoms in the material they pass through. There are different types of radiation including charged particles like alpha and beta particles, uncharged neutrons, and electromagnetic gamma rays and x-rays. Detection methods are based on the radiation interacting with the detector's base material, often ionizing or exciting its atoms. Detectors are classified as gas filled, ionization chambers, Geiger-Muller counters, semiconductors, Wilson cloud chambers or bubble chambers. Their workings exploit the properties of ionization, fluorescence, or exposing photographic plates.