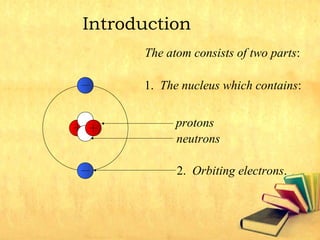
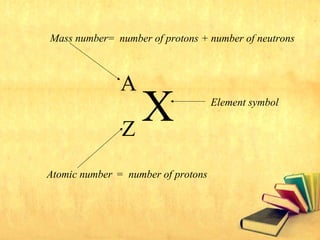
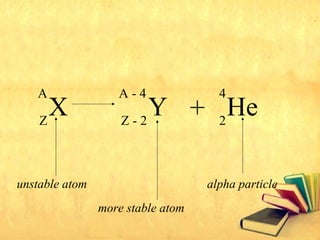
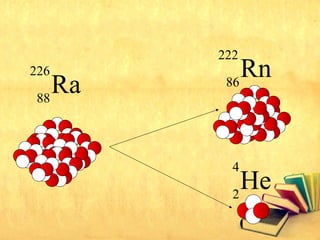
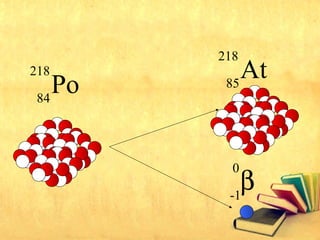
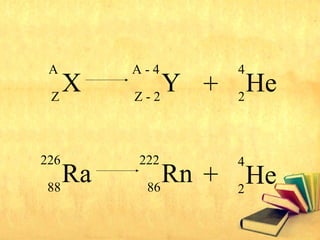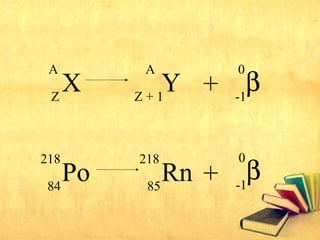Radioactive decay occurs through three main types: alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay. Alpha decay involves emitting an alpha particle, which is identical to a helium nucleus containing two protons and two neutrons. Beta decay results in one less neutron but one extra proton. Gamma decay occurs when atoms are still energetic after alpha or beta decay and emit gamma rays to become stable. These decays are important applications in areas like nuclear medicine, nuclear reactors, and sterilization.