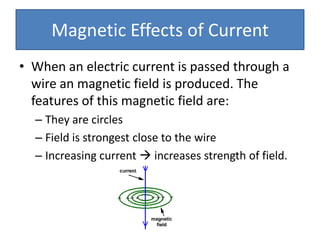
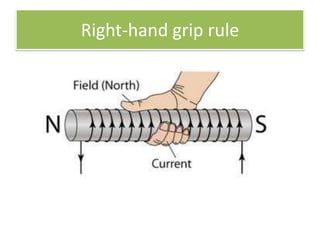
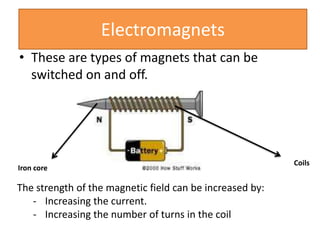
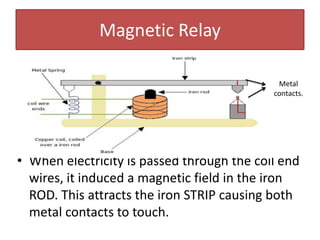
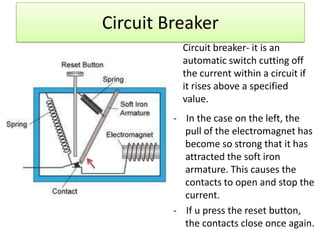
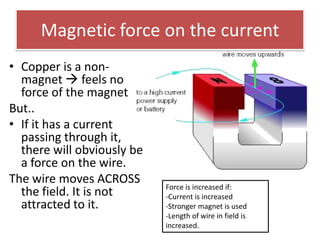
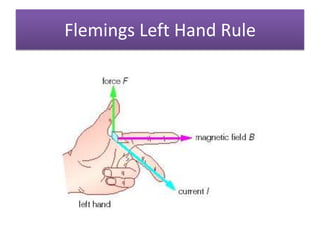
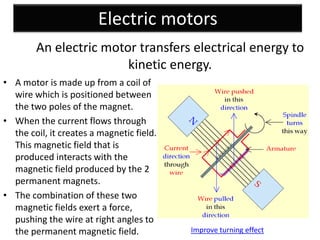
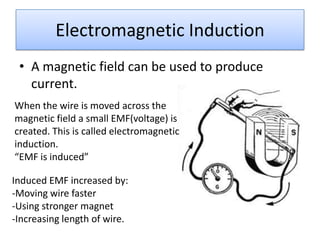
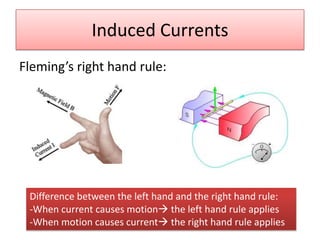
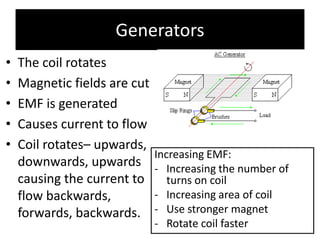
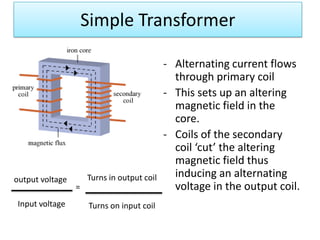
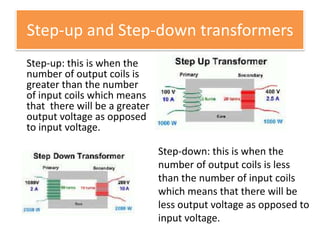
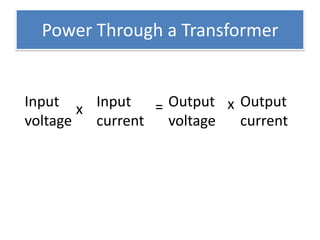
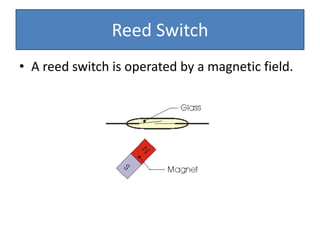
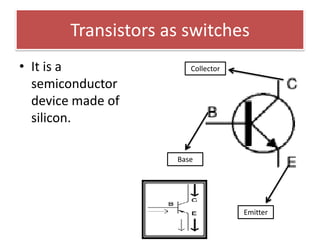
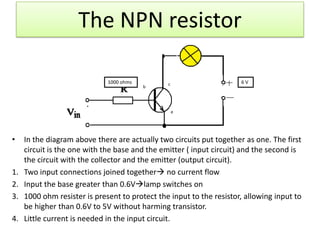
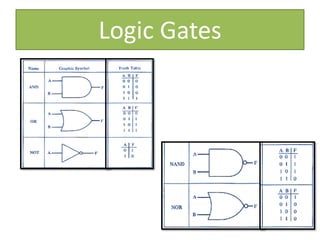
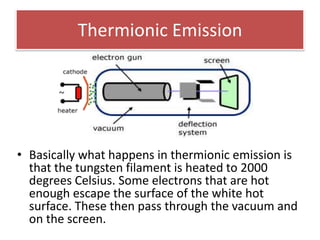
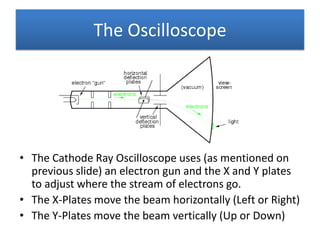
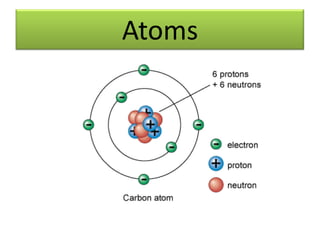
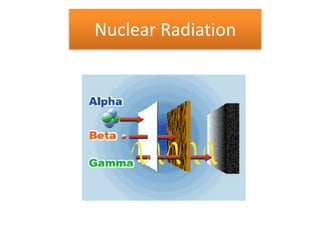
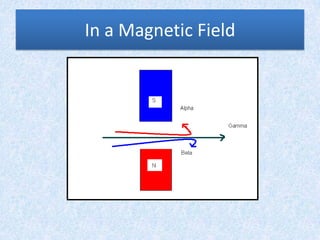
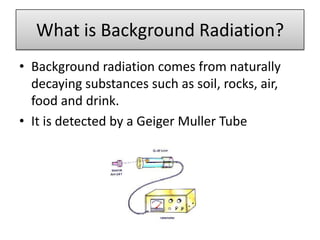
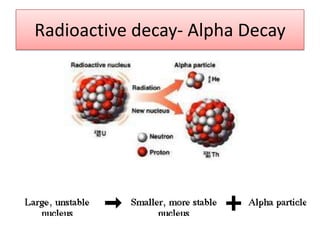
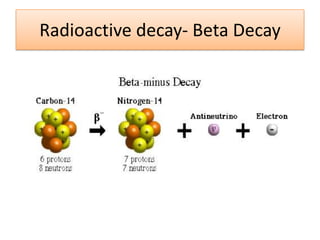
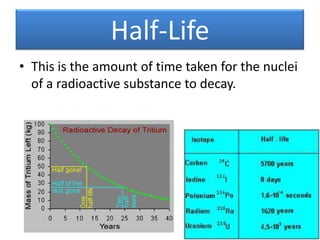
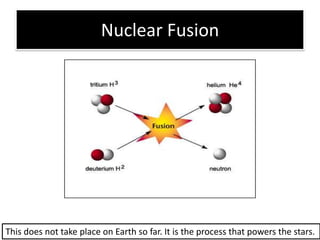
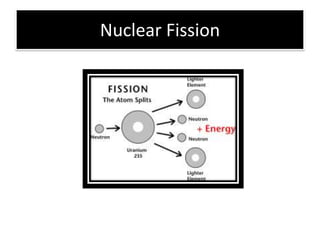
The document provides information about physics concepts related to magnets, electromagnetism, and nuclear radiation. It discusses the properties of magnetic materials and magnets, induced magnetism, magnetic effects of current, electromagnets, and magnetic force. It also covers electromagnetic induction, generators, transformers, diodes, transistors, logic gates, thermionic emission, and the oscilloscope. Finally, it briefly discusses atoms and the types of nuclear radiation such as alpha particles.