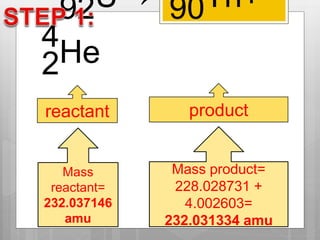
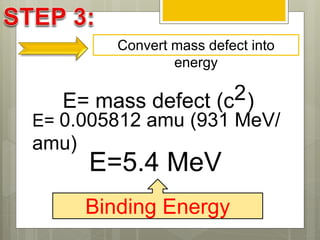
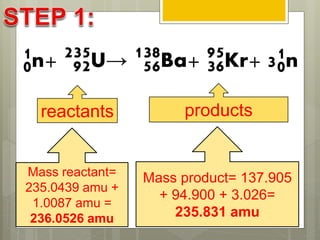
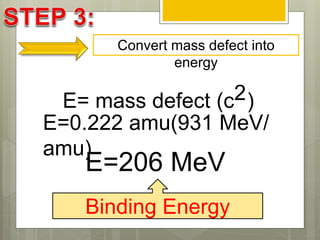
The document discusses binding energy and mass defect, explaining that binding energy is the energy required to break a system into its components, while mass defect refers to the difference in mass between a nucleus and the sum of its individual nucleons. It provides examples of alpha decay and fission of uranium, calculating the mass defects and their corresponding energy conversions. The binding energy for alpha decay is 5.4 MeV, while for fission it is significantly higher at 206 MeV.