Embed presentation
Downloaded 30 times


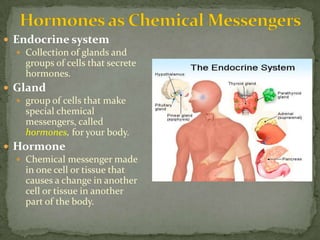

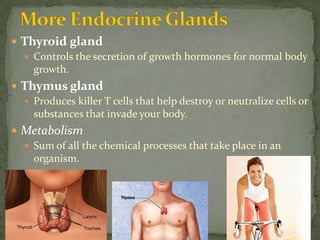
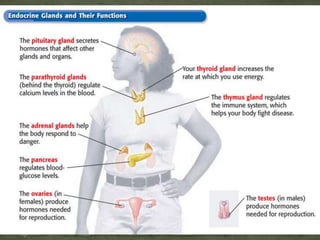

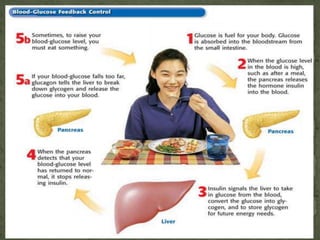
The endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones to regulate various bodily functions. The main glands include the adrenal glands, which release epinephrine during the fight or flight response; the thyroid gland, which controls growth hormone secretion; and the thymus gland, which produces immune cells. These glands utilize feedback mechanisms to control hormone release and ensure balance, though imbalances can occur if a gland produces too much or too little of a certain hormone.







