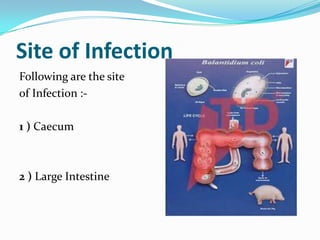
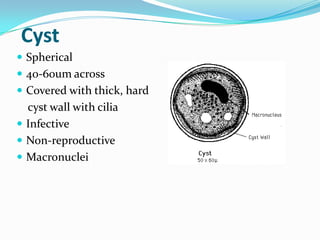
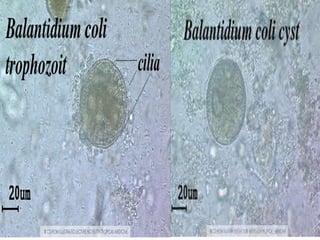
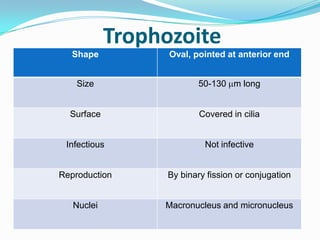
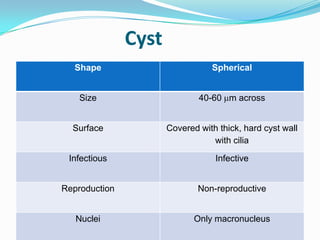
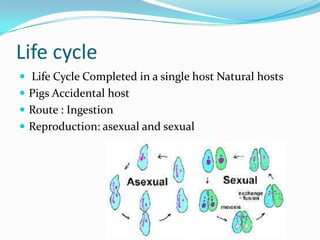
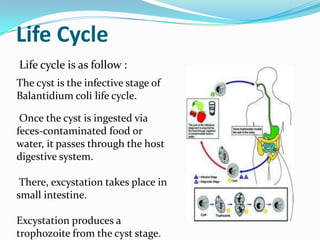
Balantidium coli is a protozoan parasite that causes the disease balantidiasis in humans. It has two stages - a trophozoite stage where it reproduces and feeds, and an infective cyst stage. Humans typically become infected through ingesting cysts from fecally contaminated food or water. The cysts excyst in the small intestine and trophozoites take up residence in the large intestine, where they can cause symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and dysentery. Diagnosis is via stool examination or biopsy. Treatment involves antibiotics like tetracycline, metronidazole, or iodoquinol. Prevention focuses on sanitary disposal of human and pig feces to avoid