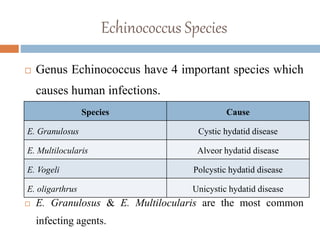
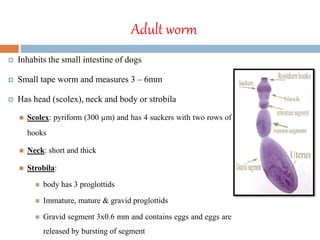
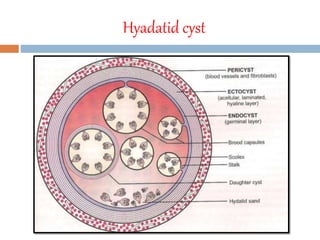
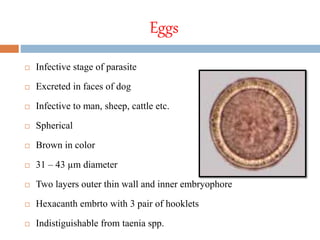
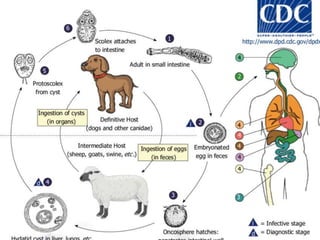
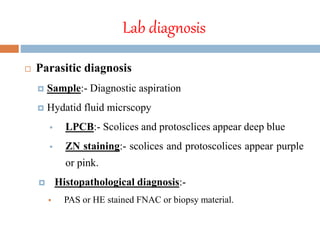
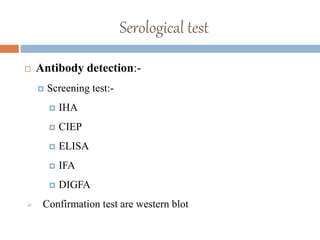
Echinococcus granulosus is a tapeworm that causes cystic hydatid disease in humans, with dogs as the definitive host and sheep or goats as intermediate hosts. The life cycle involves eggs being excreted in dog feces, which can contaminate food and water, leading to infection in accidental hosts like humans. Diagnosis can be made through various lab techniques, and treatment primarily involves surgical intervention, complemented by chemotherapy.