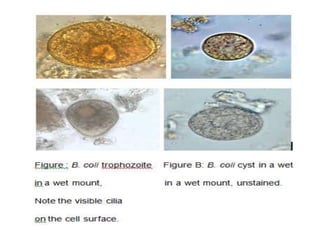
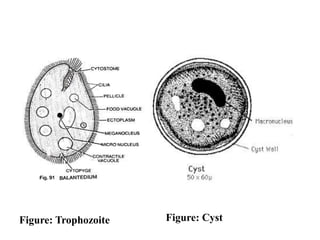
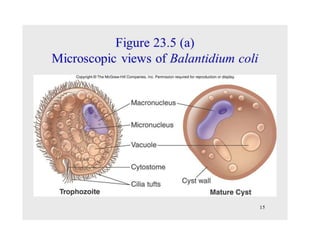
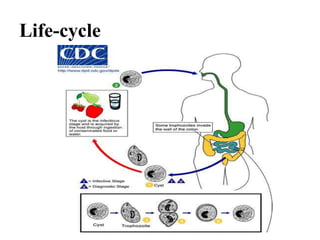
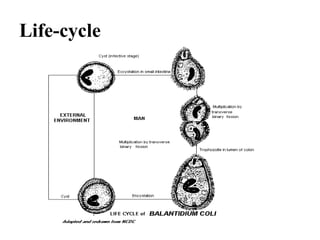
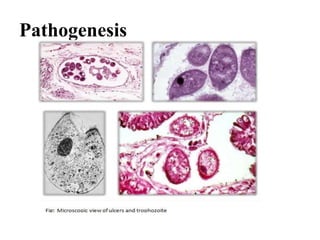
Balantidium coli is the largest protozoan parasite that infects humans. It has two stages - the trophozoite stage, which is actively motile, and the cyst stage, which is the infective stage found in feces. B. coli's natural host is pigs, but it can infect humans through ingestion of contaminated food or water containing cysts. In humans, it causes the disease balantidiasis through invasion and ulceration of the large intestine. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloody stool. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of stool samples for trophozoites or cysts. Treatment involves antibiotics like tetracycline or metronidazole.