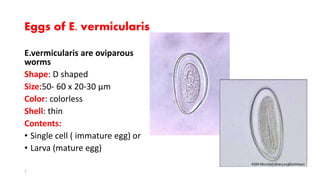
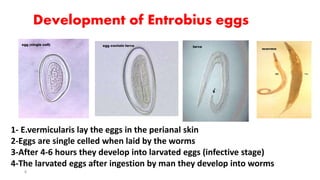
Enterobius vermicularis, commonly known as pinworm, is a nematode that primarily infects the human large intestine, causing enterobiasis characterized by symptoms such as anal itching and irritability, particularly in children. The infection spreads as the female lays thousands of eggs around the anus at night, which can survive for up to two weeks in the environment. Diagnosis is typically made via perianal swabs, and treatment includes medications like mebendazole, with emphasis on hygiene practices to prevent reinfection.