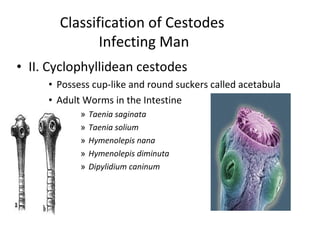
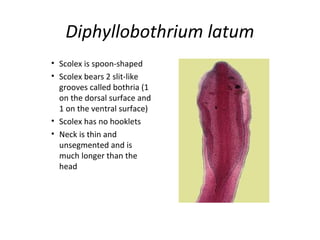
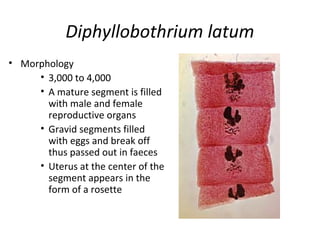
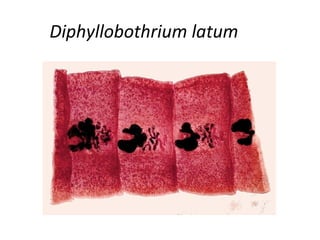
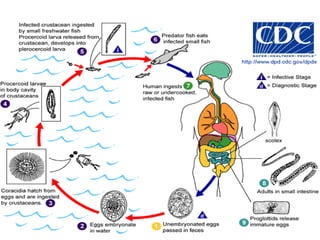
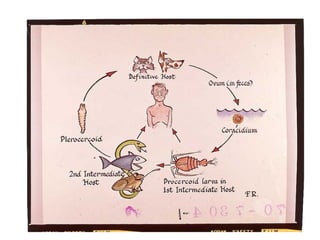
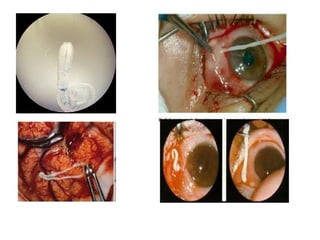
Tapeworms are flat, segmented parasitic worms that infect the intestines. There are two main types: pseudophyllideans and cyclophyllideans. Pseudophyllideans like Diphyllobothrium latum (the fish tapeworm) have two slit-like grooves and develop through two intermediate hosts. Cyclophyllideans like Taenia saginata have four cup-like suckers and do not require intermediate hosts. Symptoms of infection depend on the tapeworm species and location. Diagnosis involves finding eggs or proglottid segments in stool or removing the worm surgically.