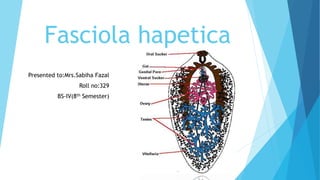
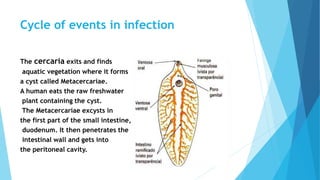
Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke, is a parasitic flatworm that infects the livers of sheep and cattle. Its complex life cycle involves freshwater snails acting as intermediate hosts. Humans can become accidentally infected by consuming raw freshwater plants containing the fluke larvae. The flukes mature and reproduce in the bile ducts of the liver, causing a disease called fascioliasis. Symptoms range from asymptomatic to abdominal pain and liver damage. Diagnosis involves examining stool samples for fluke eggs or conducting imaging tests and antibody tests. Treatment primarily involves administering deworming medications like triclabendazole or bithionol.