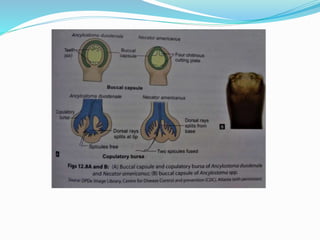
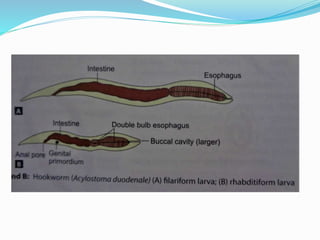
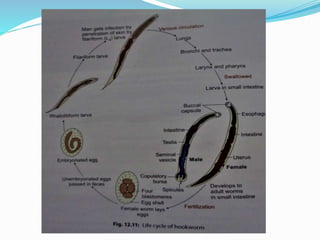
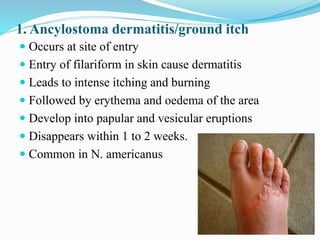
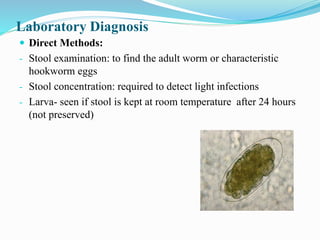
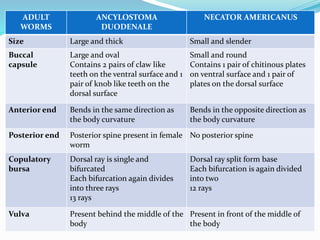
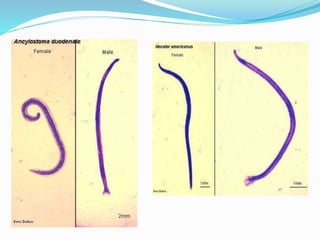
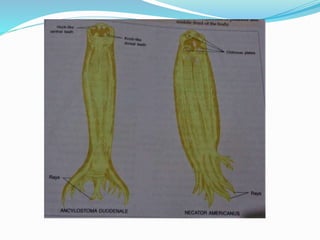
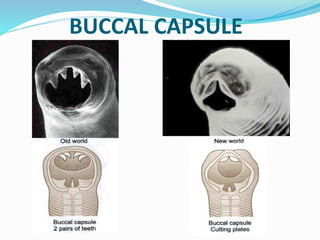
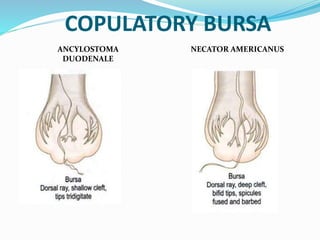
Hookworm is a parasitic nematode that infects the small intestine and is a major cause of iron-deficiency anemia globally. Two species infect humans - Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. The worms attach to the small intestine where the female lays thousands of eggs daily that are passed in feces. If soil contaminated with feces comes into contact with human skin, larvae can penetrate and migrate through tissues before reaching the intestine. This causes a rash and eosinophilia. In the intestine, the worms feed on blood, causing microcytic anemia. Over 900 million people are infected worldwide, especially in tropical areas with