Embed presentation
Downloaded 29 times



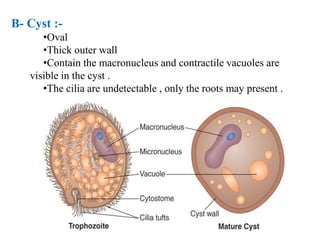

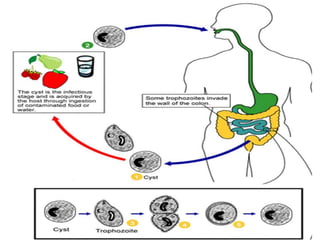



Balantidium coli is the largest protozoan parasite that inhabits the large intestines of humans and other primates like pigs and monkeys. It exists in two stages - the trophozoite, which is the invasive stage, and the cyst, which is the infective transmission stage. Balantidium coli is found worldwide and can be transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food, water, or undercooked meat containing the cysts. In the intestines, the cysts excyst into trophozoites that colonize and cause damage to the large intestine mucosa through enzyme production, potentially resulting in ulcers, diarrhea, dysentery, and other gastrointestinal symptoms. Diagnosis involves stool examination and treatment focuses on hy








