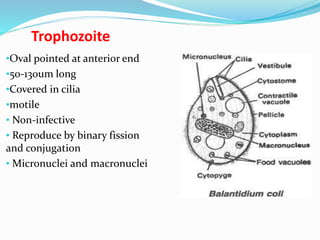
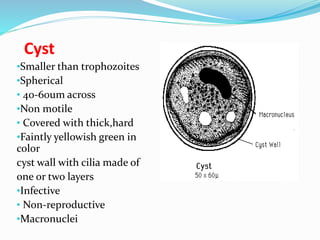
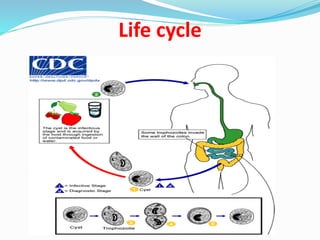
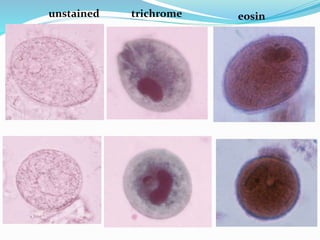
This document discusses Balantidium coli, a ciliated protozoan parasite that causes the disease balantidiasis in humans. It has two life stages, a motile trophozoite stage that inhabits the large intestine and reproduces, and an infective cyst stage that is transmitted through fecal contamination. Symptoms include diarrhea, dysentery, abdominal pain and ulceration of the intestinal wall. Diagnosis is made by examining stool samples under a microscope. Treatment involves oral antibiotics such as tetracycline or metronidazole.