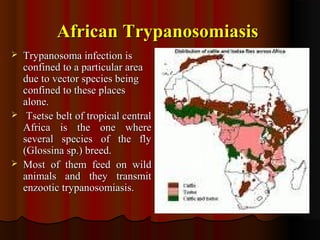
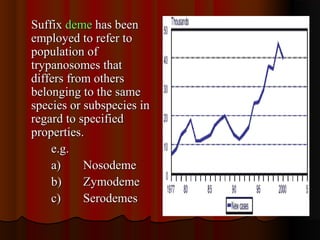
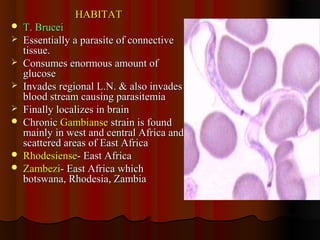
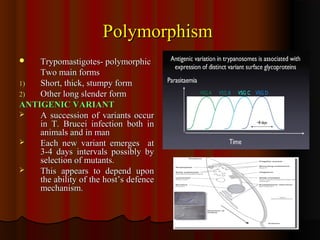
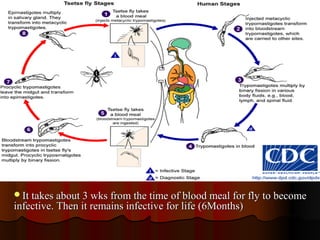
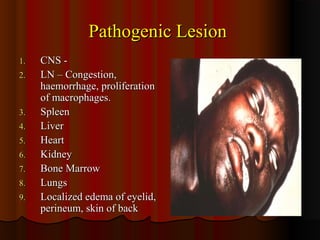
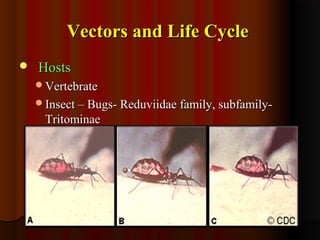
Trypanosomiasis is caused by pathogenic Trypanosoma and is endemic in Africa and South America. It is transmitted between hosts by blood-sucking insects. Trypanosoma brucei causes African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) and exists in the vertebrate host as trypomastigotes, passing between hosts via the tsetse fly vector. The disease occurs in two stages with initial symptoms of fever and swelling followed by neurological involvement if untreated. Diagnosis involves blood, lymph node aspirate, or CSF examination to detect the parasites.