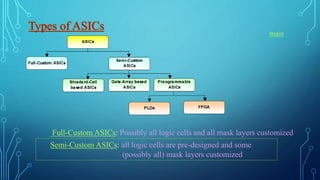
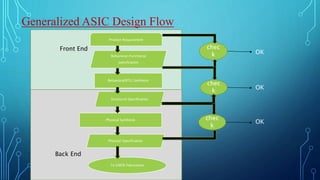
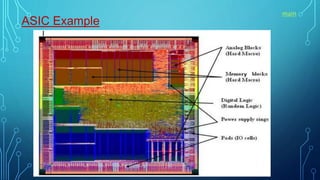
Application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are microchips designed for special applications. There are two types: full-custom ASICs where all logic cells and mask layers are customized, and semi-custom where pre-designed logic cells have some customizable mask layers. ASICs have advantages over FPGAs like lower costs, higher speeds, and lower power usage, but have higher design costs and longer development times. Common applications of ASICs include aerospace systems, high-performance processors, and specialized consumer electronics.