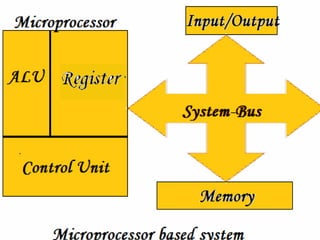
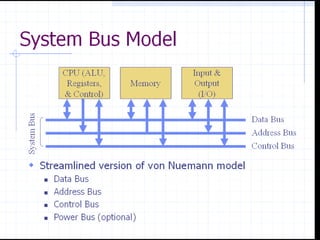
This document discusses microprocessors and networking. It provides details on microprocessors such as their components like the ALU, registers and control unit. It describes early microprocessors like the 4004 and 8085. It also discusses microprocessor memory, buses and different types of integrated circuits. The document also defines what a computer network is and the different ways of physically connecting computers through guided media like coaxial cable, twisted pair and fiber optic cable. It explains wireless connections using infrared, radio frequency and microwave communications.