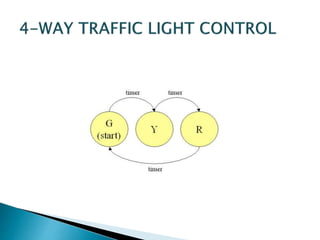
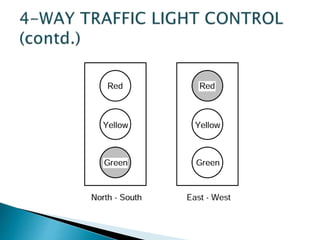
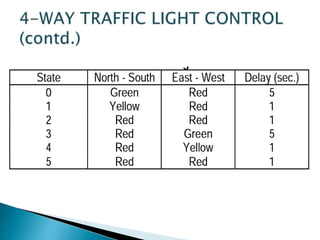
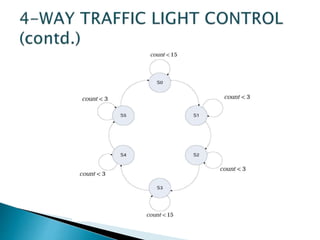
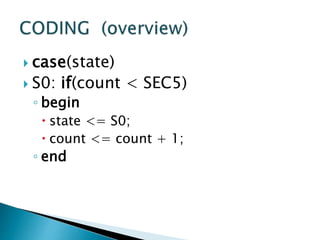
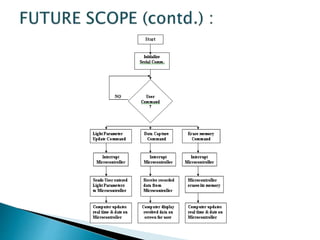
This presentation summarizes the history and development of traffic lights. It discusses how the first traffic light was installed in London in 1868 [1]. It then provides details on the typical light sequences of red, yellow, and green [2]. The presentation goes on to describe how a basic four-way traffic light system can be modeled using a state diagram and Verilog code [3]. It concludes by discussing how more advanced traffic light controllers can help improve urban traffic flow.