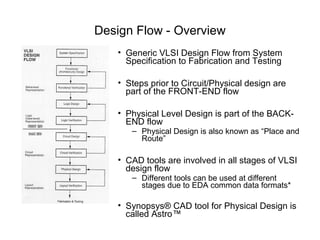
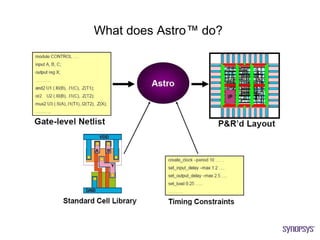
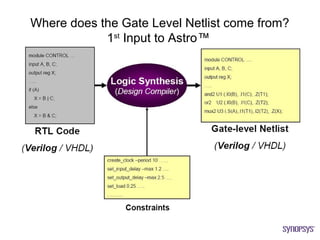
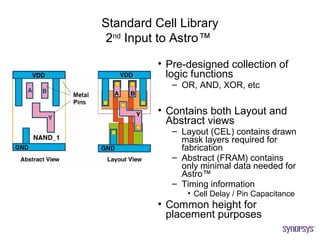
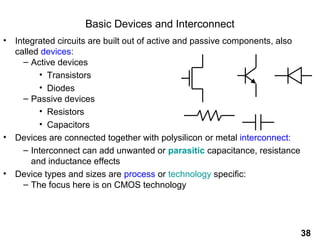
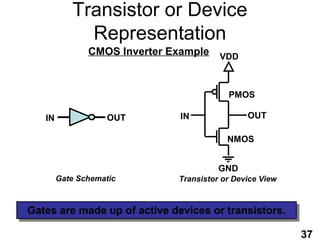
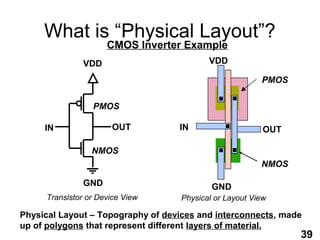
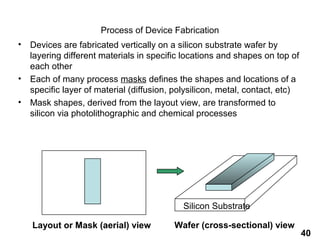
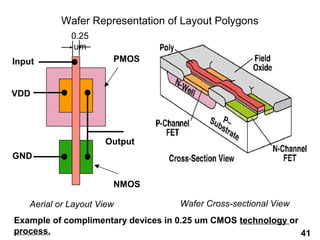
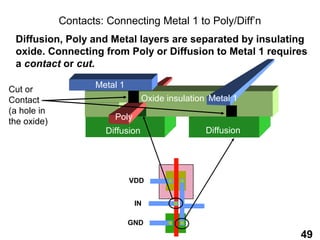
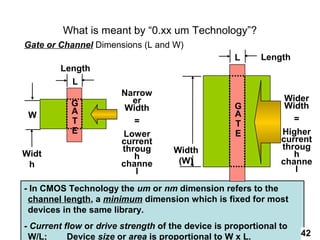
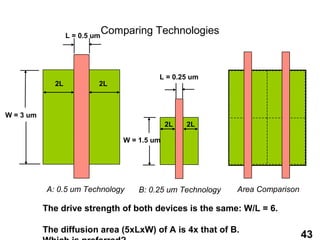
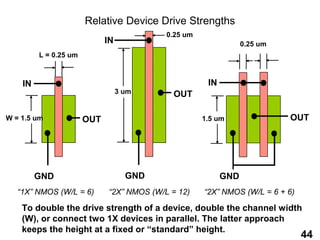
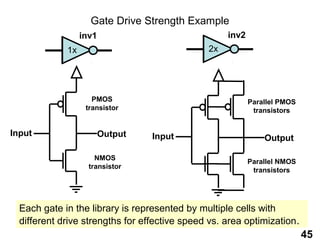
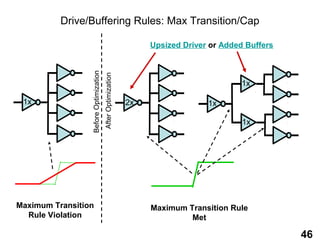
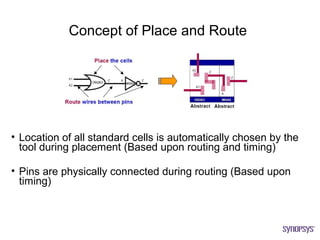
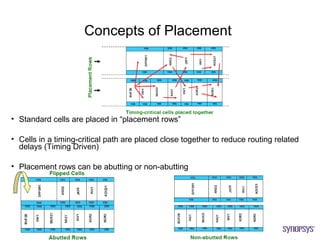
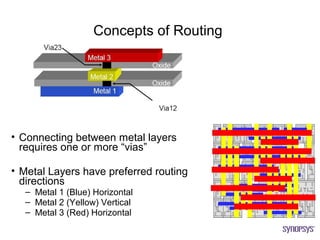
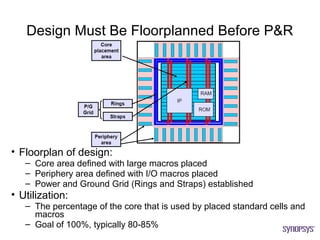
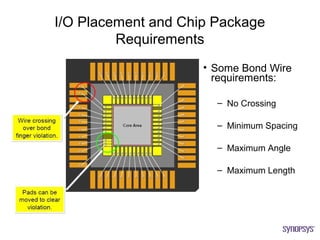
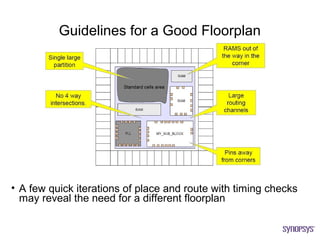
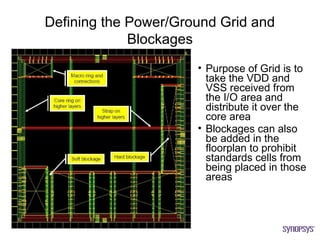
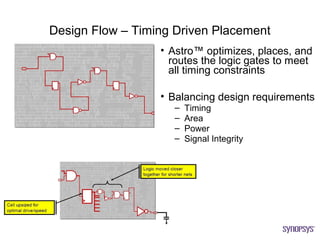
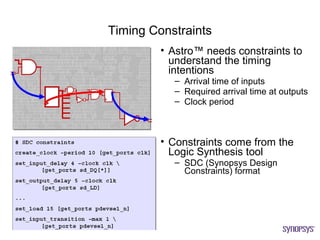
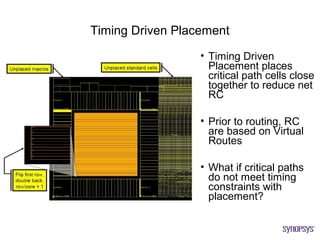
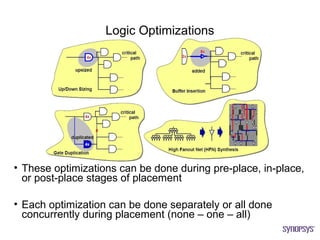
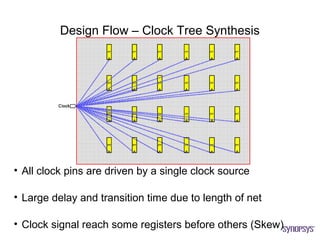
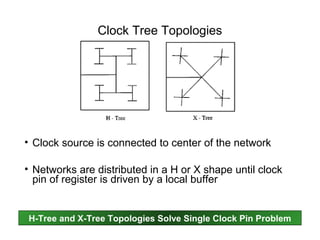
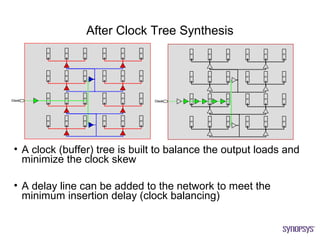
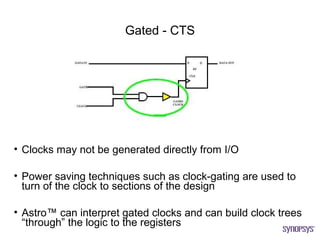
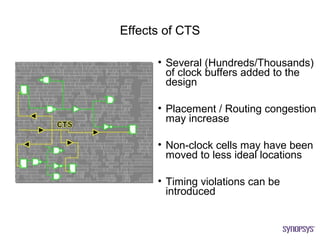
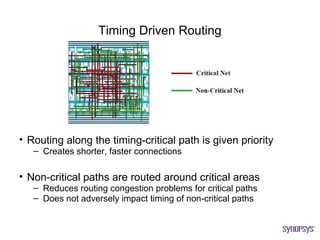
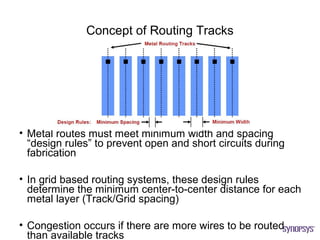
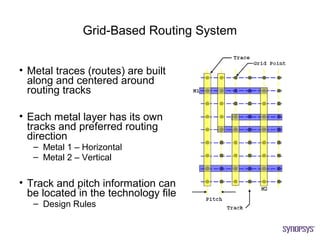
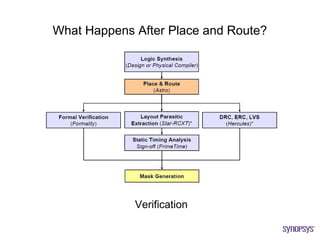
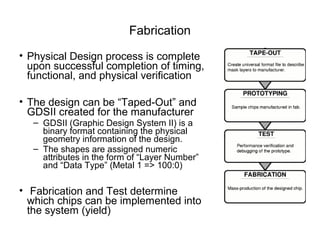
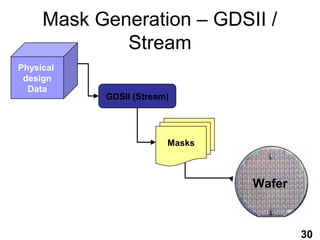
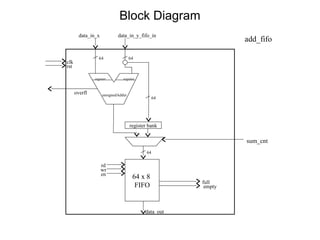
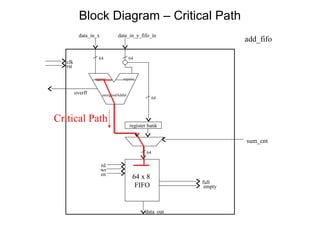
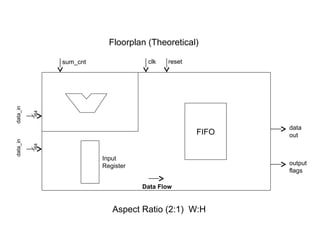
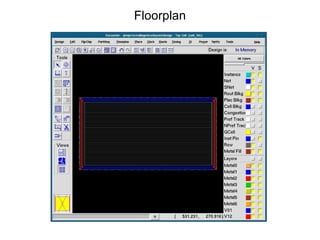
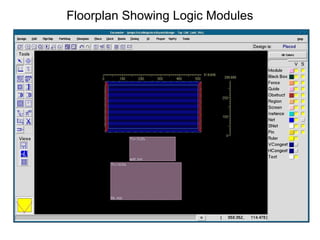
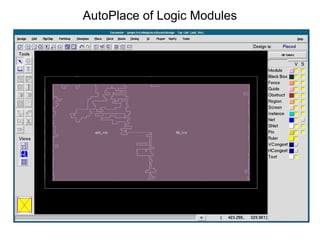
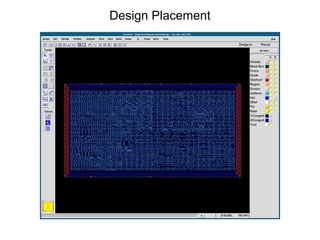
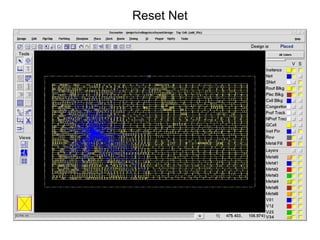
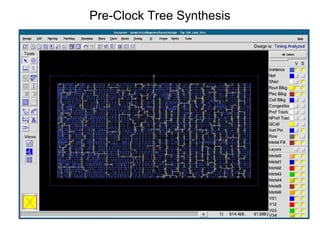
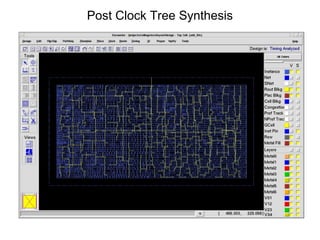
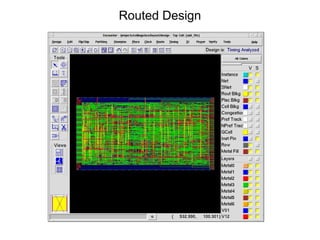
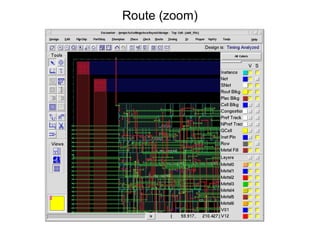
The document provides an overview of the ASIC back-end design flow, including physical design steps like floorplanning, timing driven placement, clock tree synthesis, and routing. It explains key concepts in physical design like standard cell libraries, placement, routing grids and tracks, and timing driven optimization. The document also discusses verification steps after physical design like formal verification to check logic equivalence and timing analysis using RC extraction and static timing analysis to check design constraints.