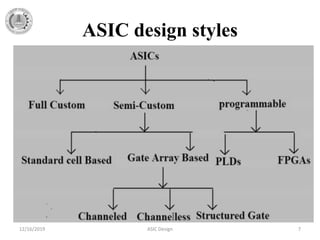
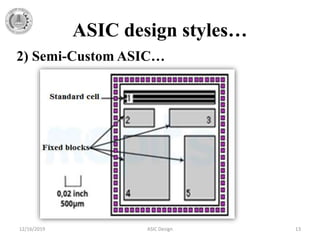
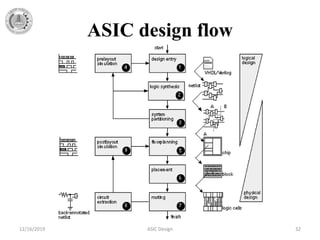
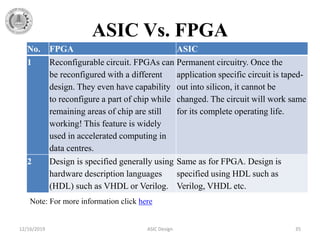
The document provides a detailed overview of Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), including their definition, design styles, flow, and comparison with FPGAs. It discusses various types of ASICs such as full-custom, semi-custom, and programmable ASICs, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, the document outlines the ASIC design process and important design considerations.