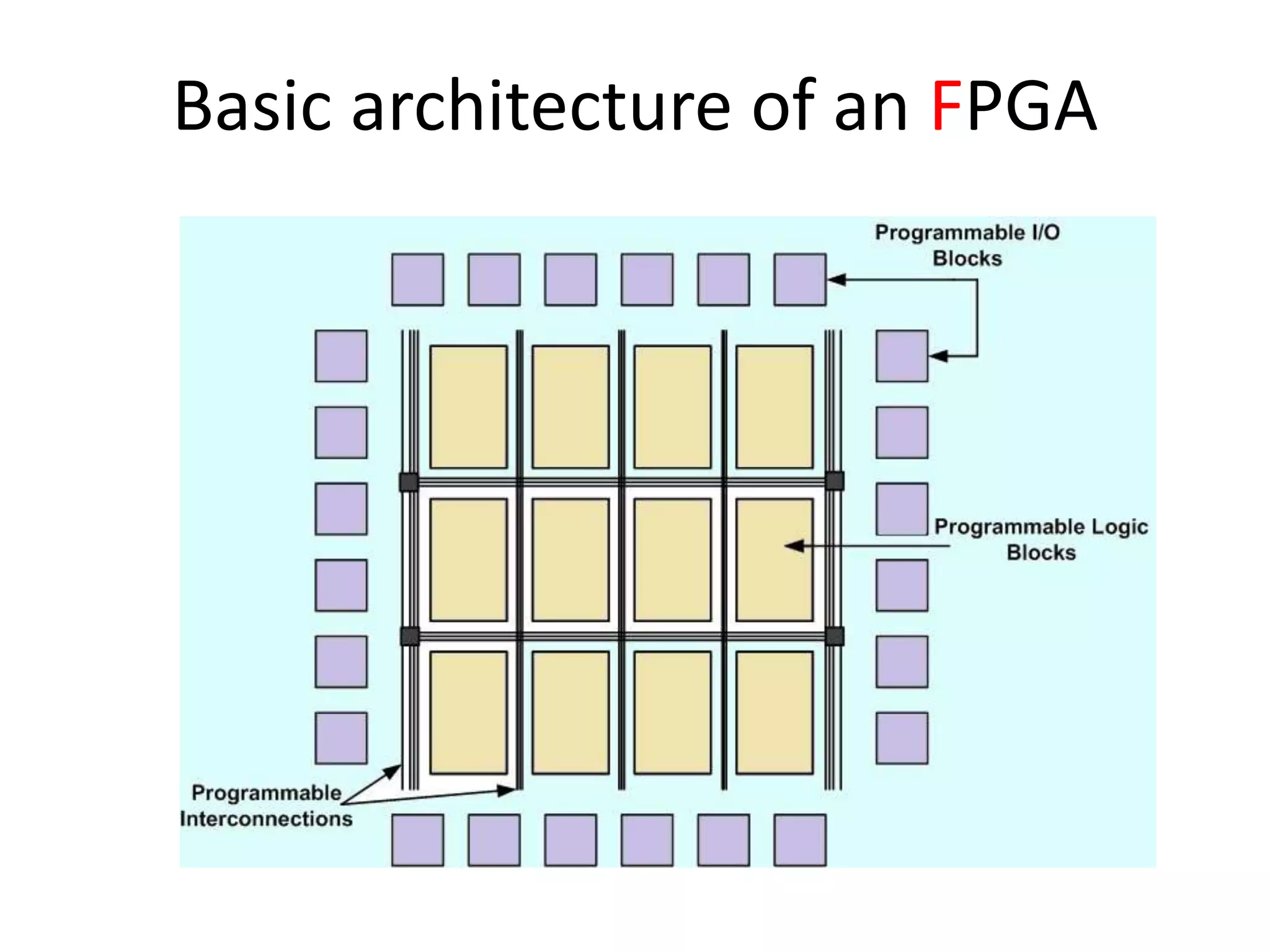
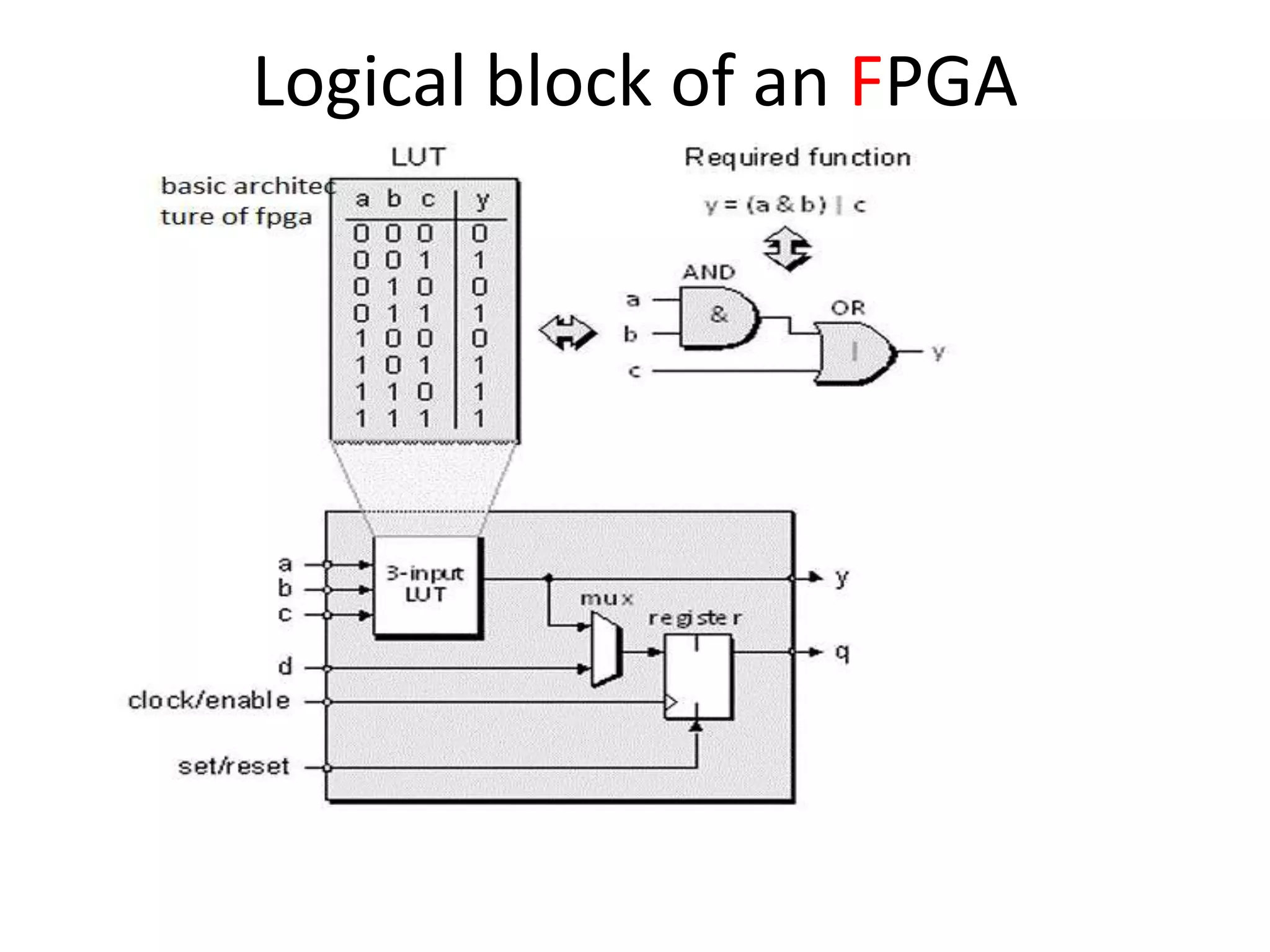
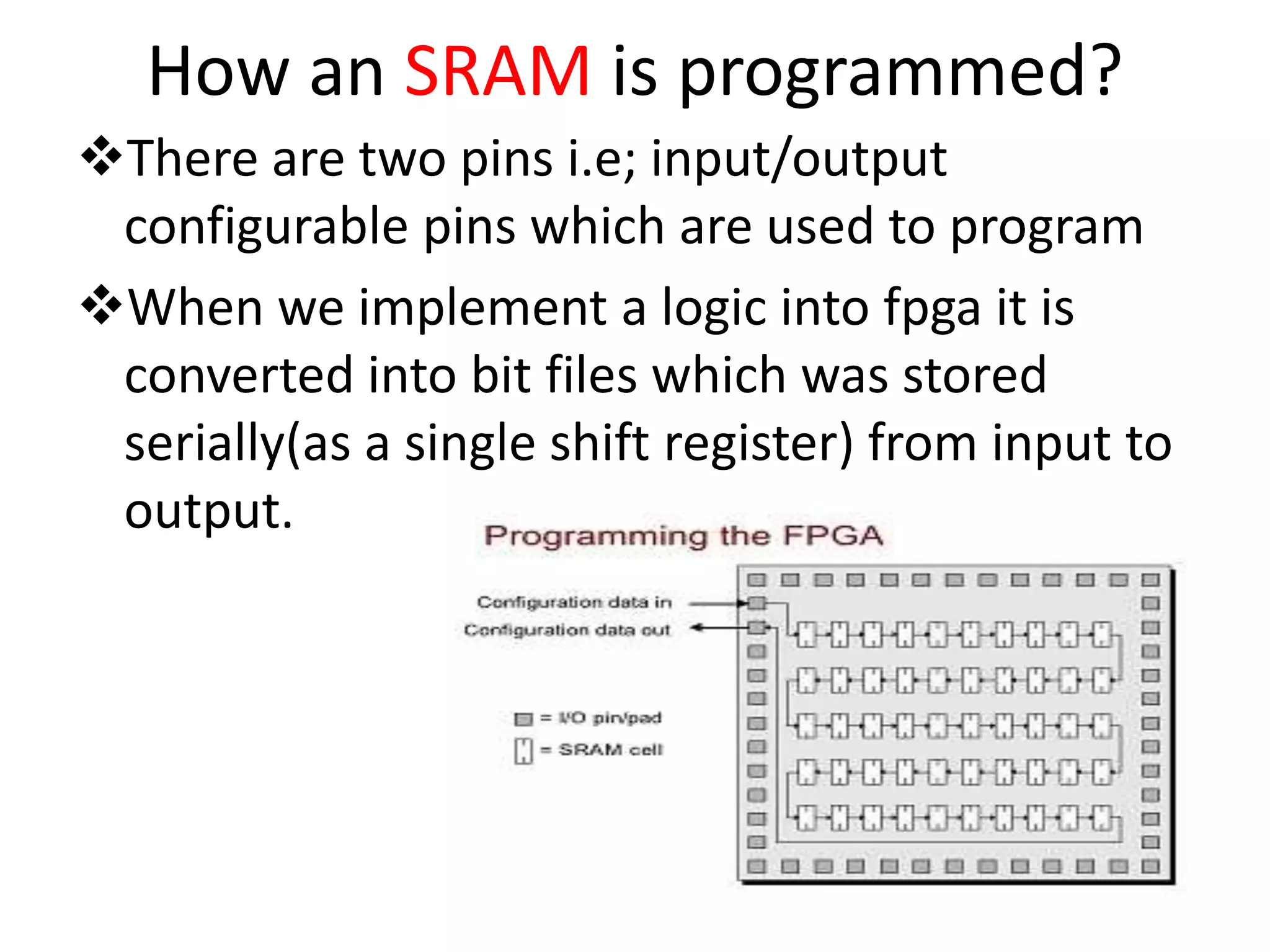
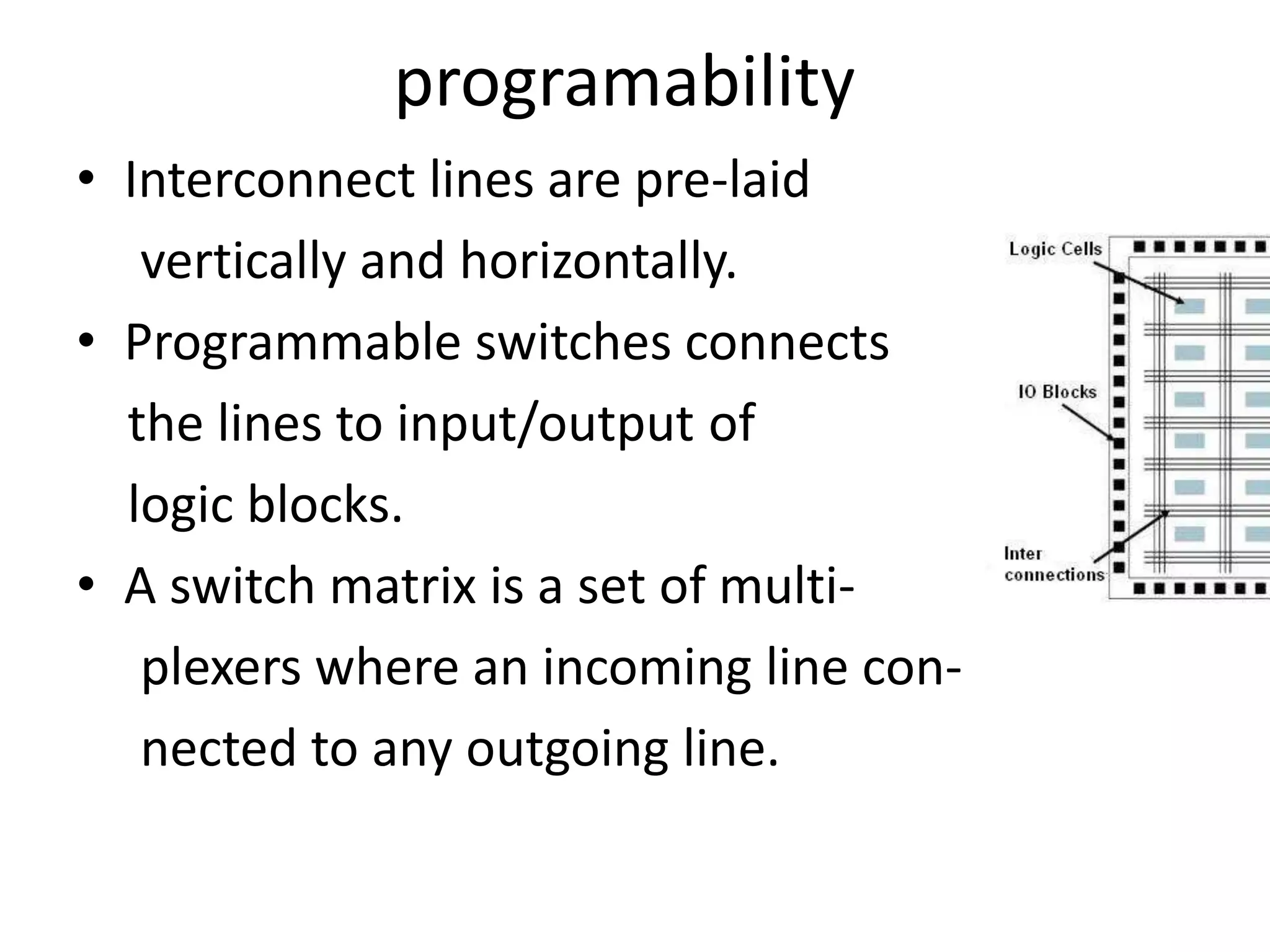
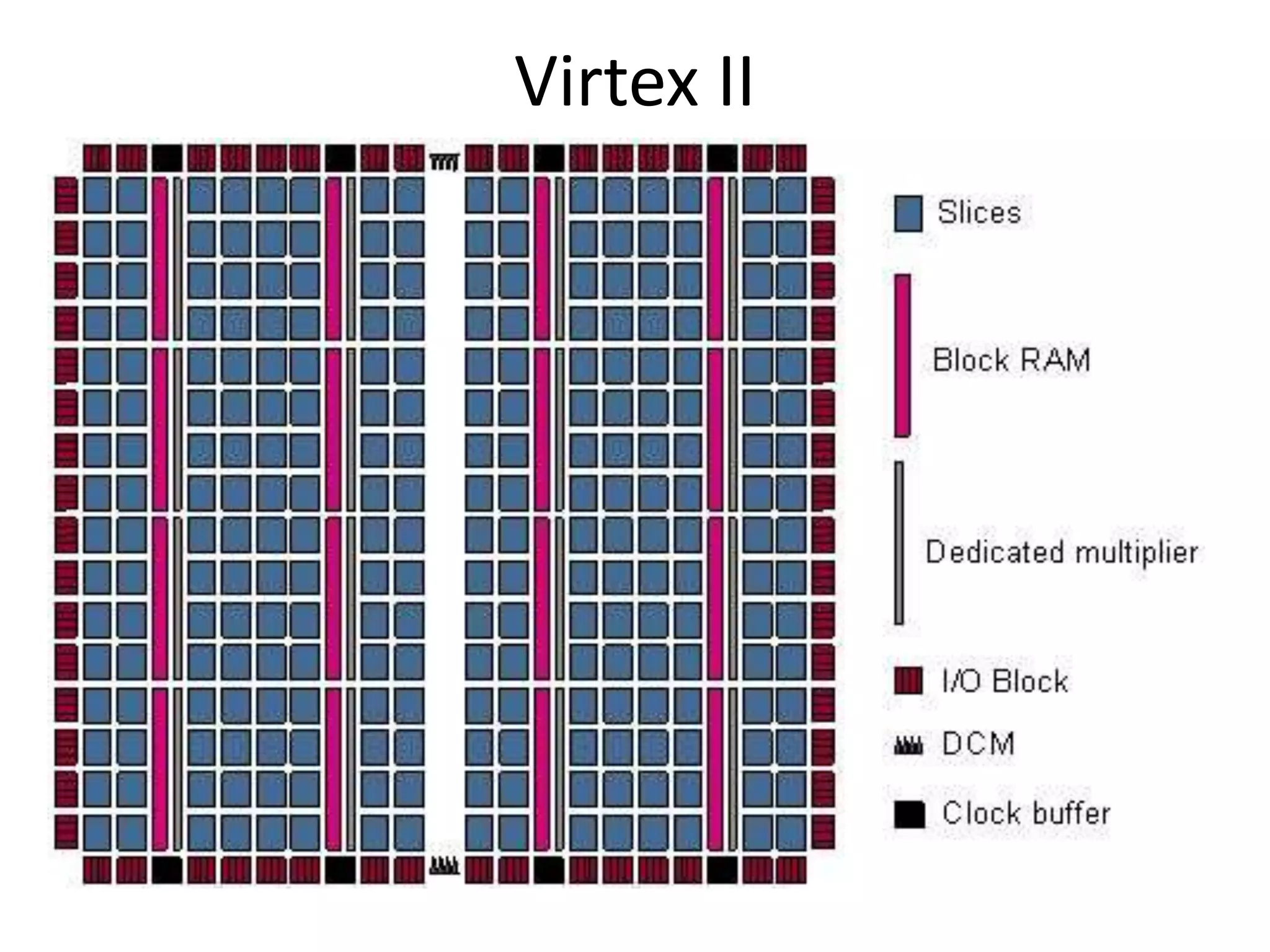
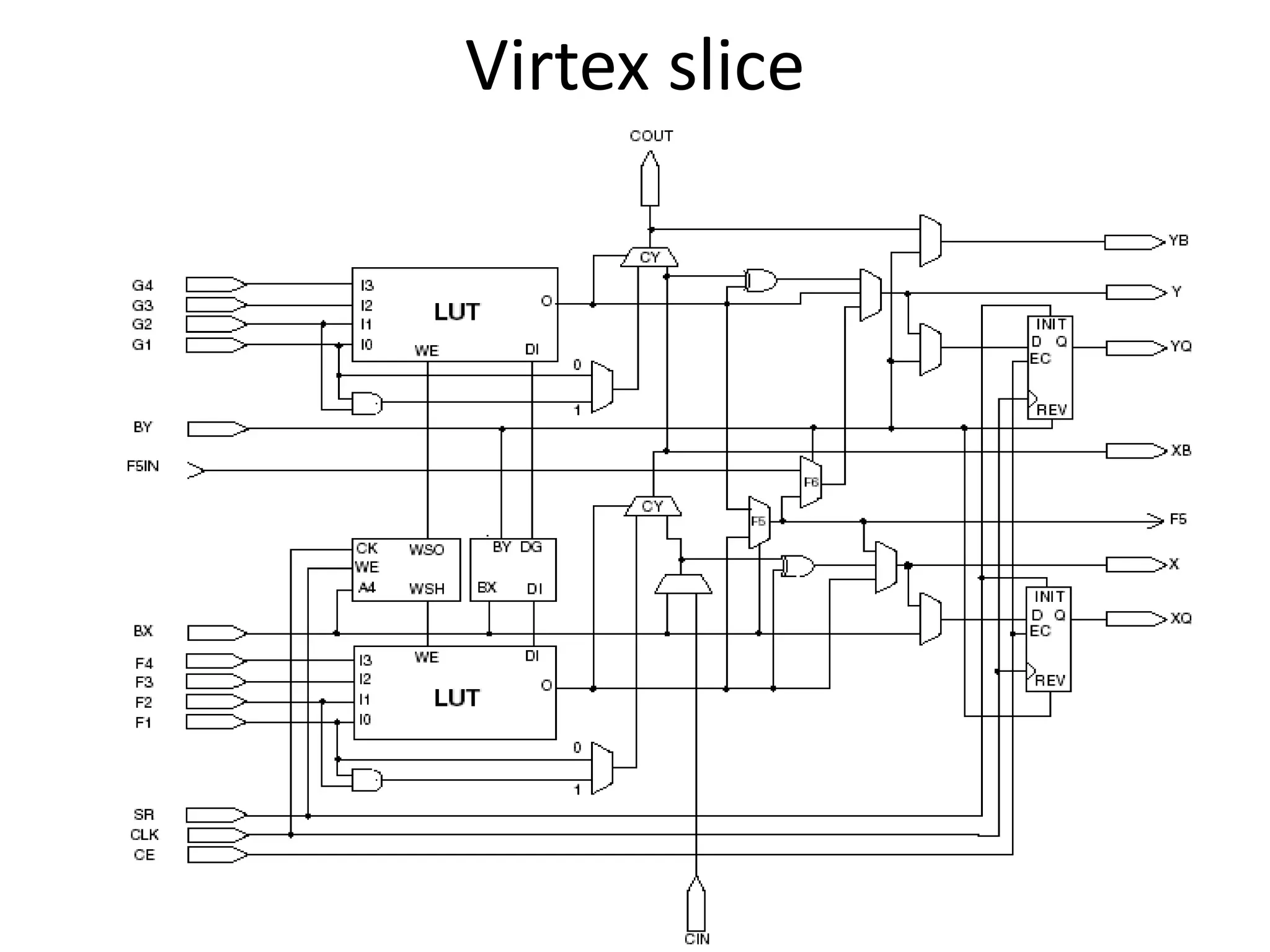
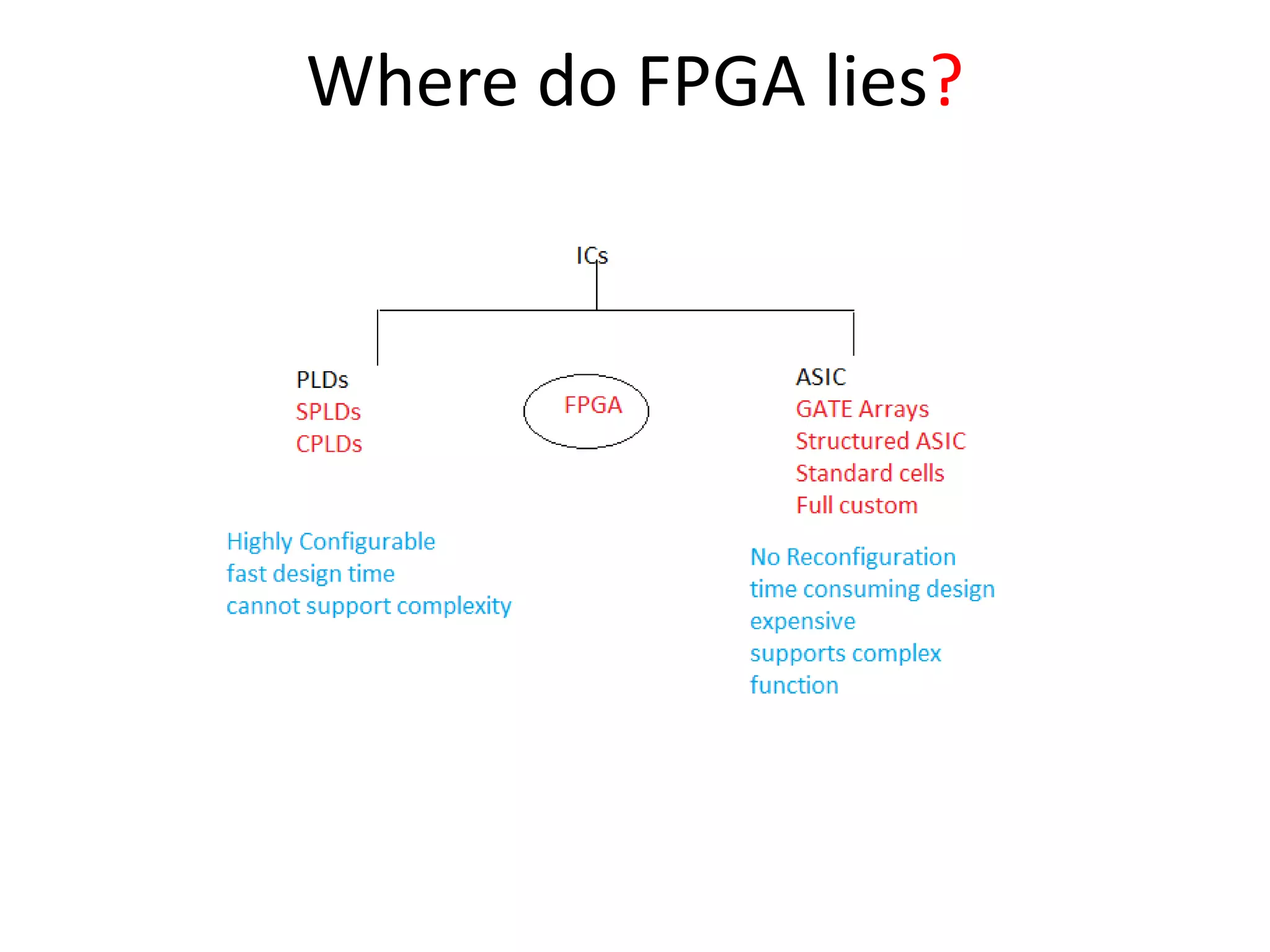
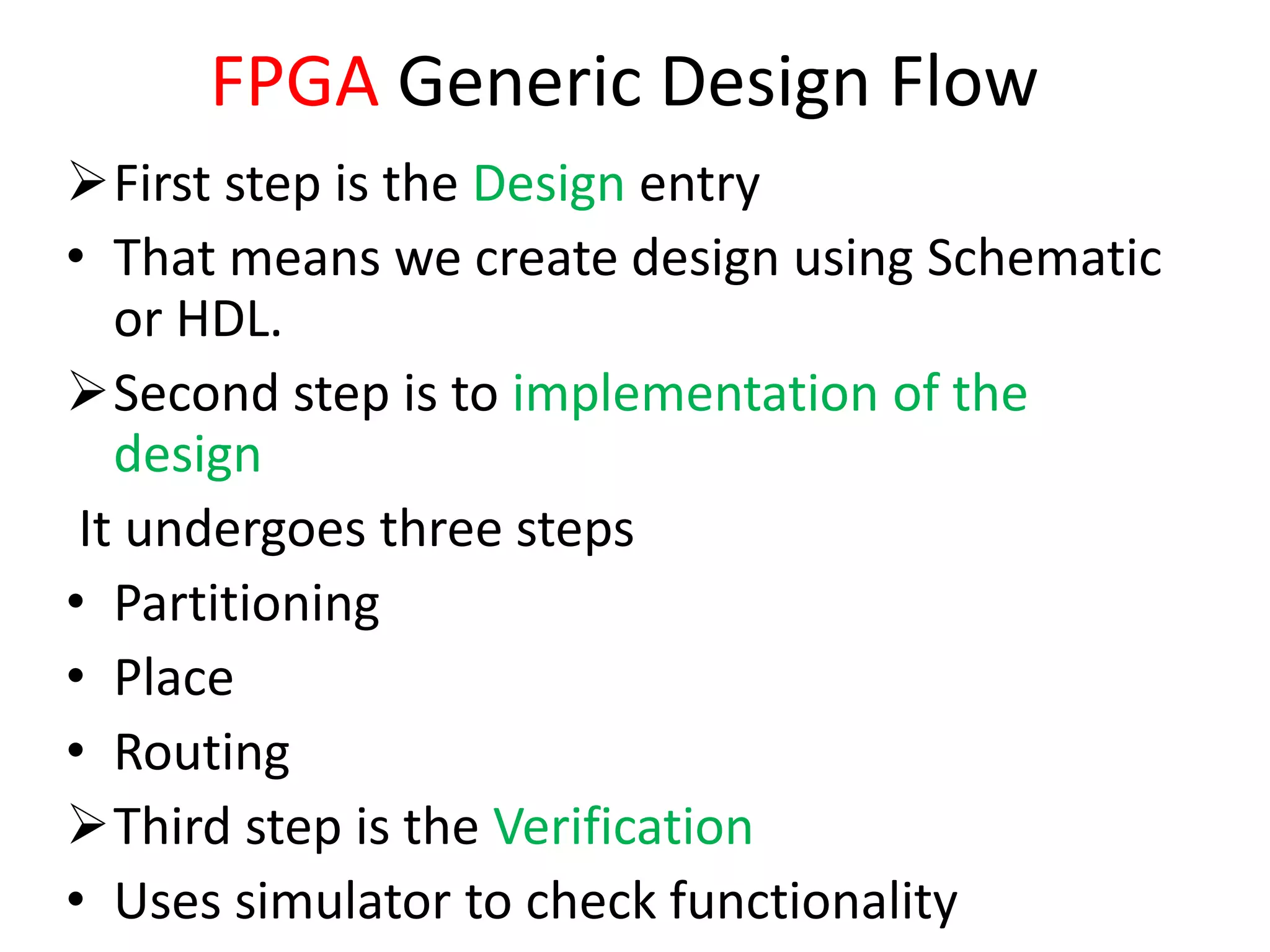
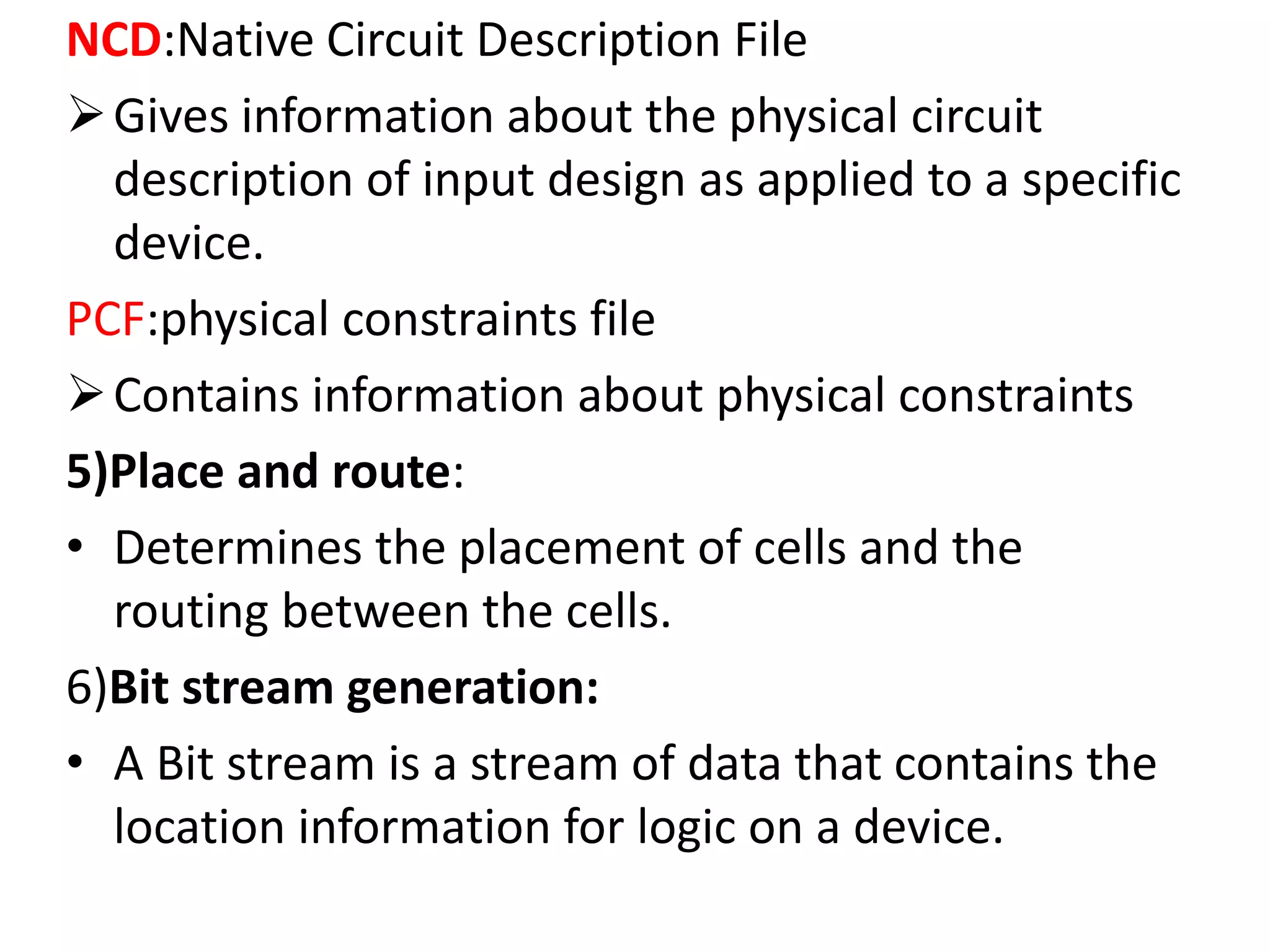
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are integrated circuits that can be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing. FPGAs contain programmable logic components called logic blocks and a hierarchical interconnect that allows the blocks to be 'wired together' as per the design. The document discusses the basic FPGA architecture including logic blocks, interconnects and I/O blocks. It also explains the different FPGA families and programming technologies like SRAM, antifuse and EPROM/EEPROM. The Xilinx FPGA development flow and tools like ISE and its components are explained.