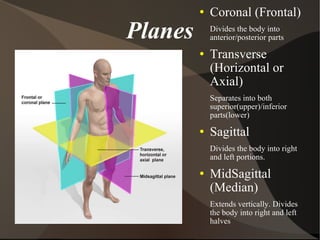
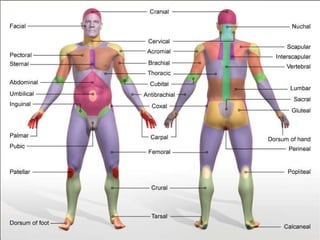
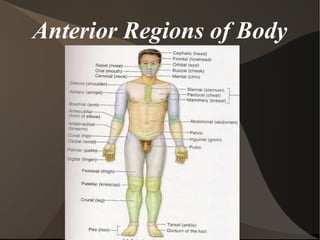
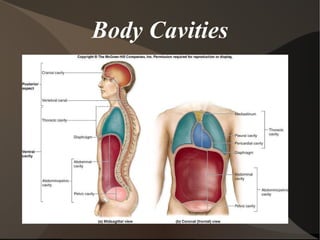
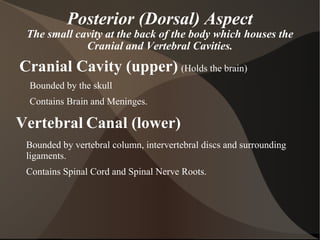
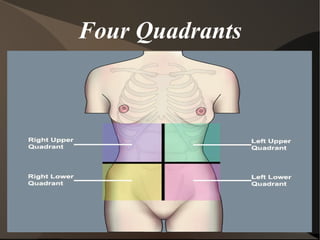
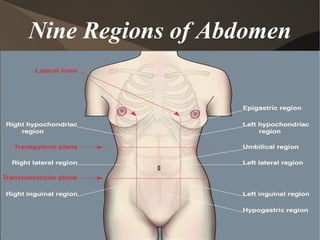
The document summarizes body organization and terminology by defining three anatomical planes used to divide the body and various regions of the body. It then discusses the axial and appendicular regions and the major body cavities including the cranial, vertebral, thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities. Finally, it outlines the serous membranes that line body cavities, including the parietal and visceral layers of the pericardium, pleura, and peritoneum that form serous cavities around organs.