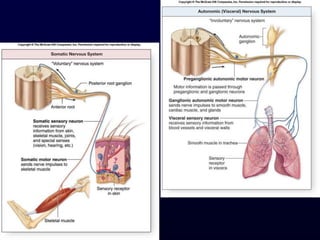
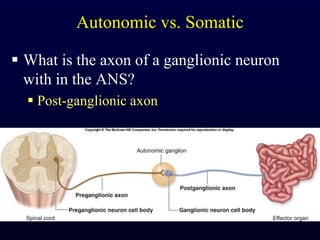
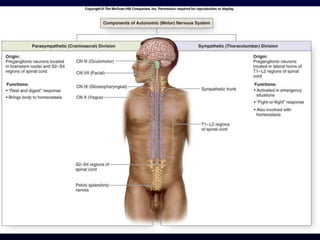
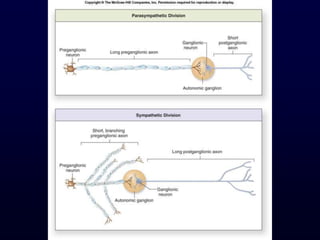
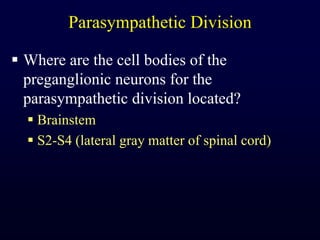
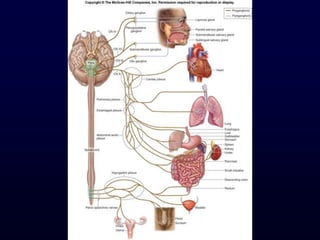
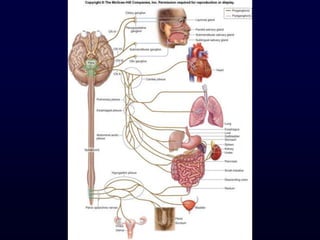
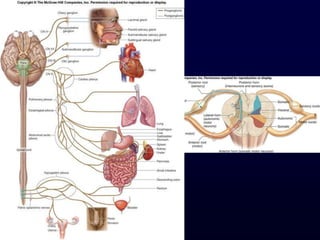
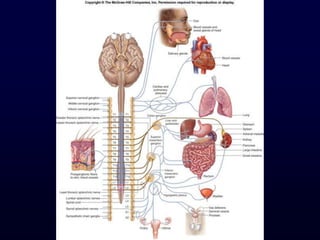
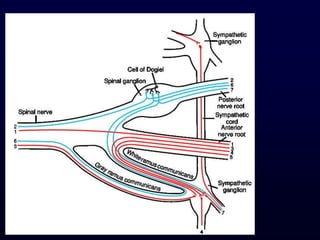
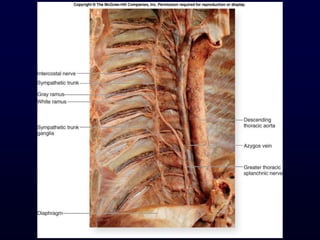
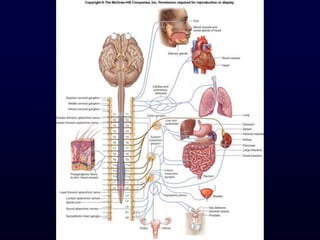
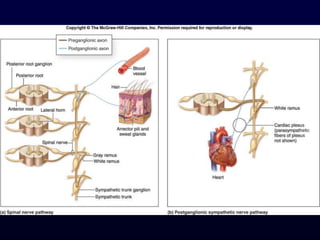
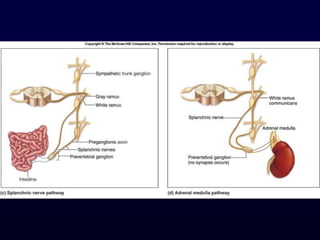
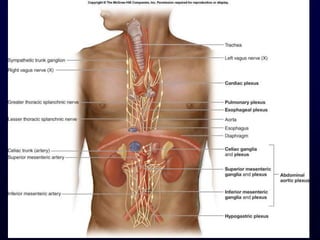
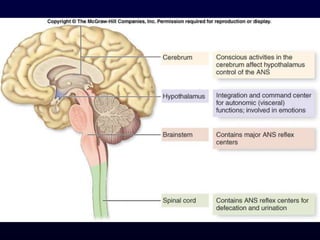
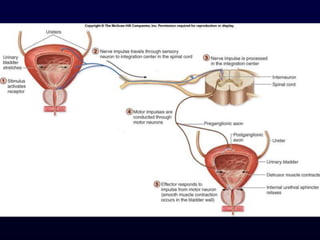
This document provides an overview of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). It discusses the two divisions of the ANS - the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The sympathetic division is involved in the fight or flight response and increases heart rate, breathing, etc. The parasympathetic division is involved in rest and digest functions like digestion. The document details the pathways, ganglia, nerves and effects of both divisions. It notes that the hypothalamus and brainstem have significant control over autonomic function.