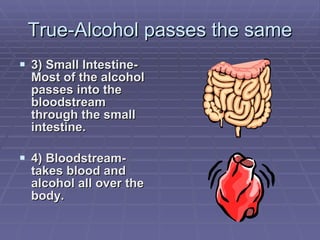
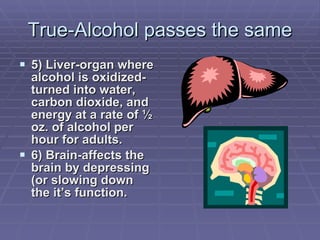
The document discusses the reasons why people both choose to drink alcohol and choose to abstain. It then provides information on how alcohol passes through the body and is processed by the liver. Several factors that can influence how alcohol affects individuals are outlined, including body weight, food consumption, amount consumed, and expectations. Common effects of alcohol are listed, such as lowered inhibitions, impaired thinking and physical skills, diseases, tolerance, changes in body temperature, and hangovers. Treatment options for alcoholism are also briefly discussed.