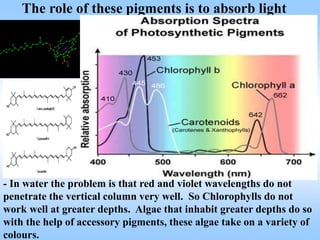
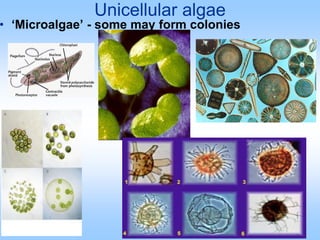
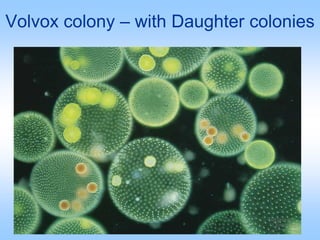
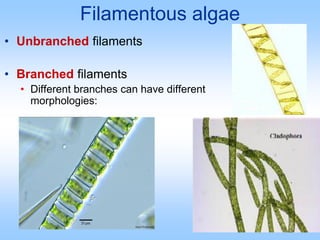
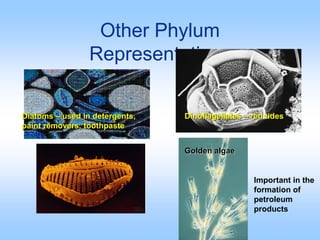
Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that are either protists or primitive aquatic plants. They vary greatly in size and structure from single-celled to multicellular forms over 70 meters long. While similar to plants in some ways like possessing chlorophyll and cell walls, algae differ in lacking true roots, stems, leaves and vascular tissue. They are classified into seven phyla based on pigments, food storage and cell wall composition, with the Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, and Rhodophyta being the major groups of green, brown, and red algae respectively. Algae play important ecological roles as primary producers and oxygen generators in many aquatic ecosystems.