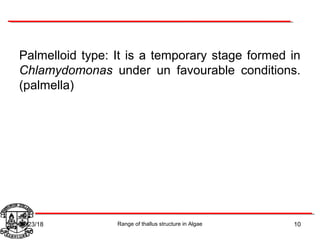
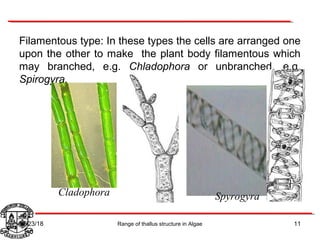
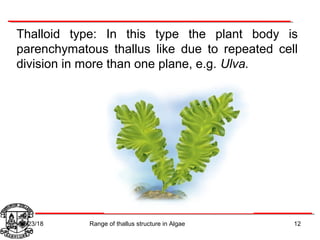
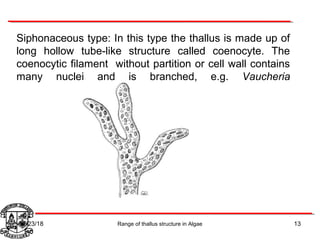
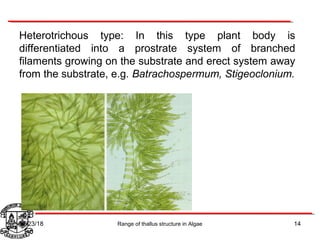
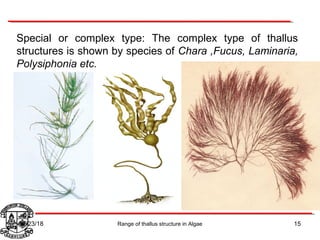
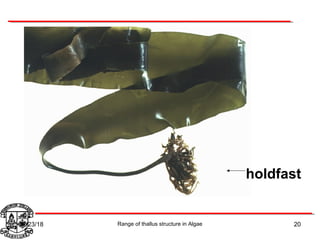
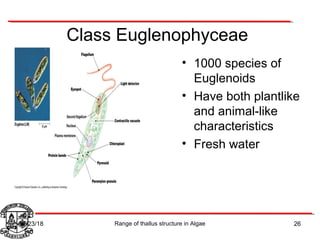
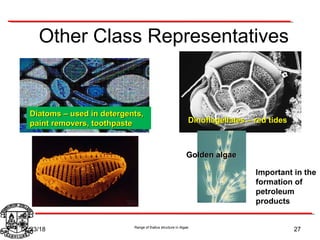
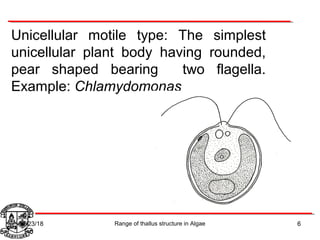
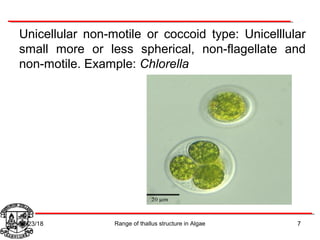
Algae exhibit a wide range of thallus structures, from single-celled organisms to large seaweeds. Their thalli can be unicellular and motile, unicellular and non-motile, colonial, filamentous, heterotrichous, siphonous, uni-axial, multi-axial, or parenchymatous. Examples include Chlamydomonas as a unicellular motile type, Chlorella as a unicellular non-motile type, Volvox as a motile coenobial type, Spirogyra as a filamentous type, and Ulva as a thalloid type. Algae reproduce both sexually through structures


![STRUCTURE
• Thallus (haploid)
• Types of algae
–Unicellular[motile and non-motile]
–Colonial[flagellated & non-
flagellated]
–Filamentous[branched &
unbranched]
3Range of thallus structure in Algae
07/23/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson-180723054343/85/Algae-thallus-structure-3-320.jpg)


![Motile coenobial type: In this type unicellular cells with their
flagella protruded out is embedded together in a gelatinous
sheath to form a more or less rounded motile colony or
coenobium. Example: Volvox [Evolution in the Volvocine
Line]
8Range of thallus structure in Algae07/23/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson-180723054343/85/Algae-thallus-structure-8-320.jpg)
![Non motile coenobial type: In this type the colony or
coenobium is composed of non-motile cells arranged in a
single layer along the long axis, e.g. Scenedesmus [Fig. a]
or cells are arranged end to end forming a pentagonal or
hexagonal meshes of net, e.g. Hydrodictyon [Fig. b] and
Pediastrum [Fig. c]
9Range of thallus structure in Algae07/23/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson-180723054343/85/Algae-thallus-structure-9-320.jpg)