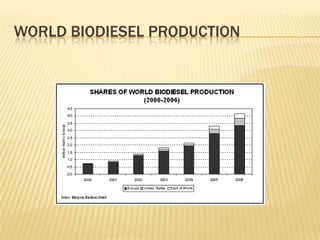
This presentation discusses biofuels as an alternative renewable energy source. It begins by outlining the global energy crisis and increasing demand for energy. The presentation then defines biofuels as fuels derived from biological resources like plant biomass. Biofuels are presented as a way to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. The main types of biofuels discussed are biodiesel, bioalcohol, vegetable oils, biogas, and syngas. Advantages and disadvantages of biodiesel production and use are also summarized.