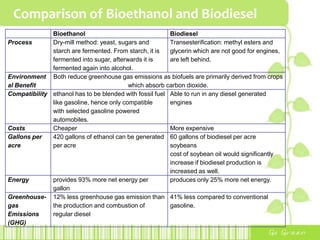
This document provides an overview of bioethanol, including its production process, feedstocks, fuel properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Bioethanol is produced through sugar fermentation of plants containing sugars and starch, such as corn, sugarcane, or wheat. It is used as a substitute for gasoline in vehicles. While bioethanol production reduces greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on oil, it also requires large amounts of land and water and has lower energy content than gasoline. Brazil is highlighted as the largest producer and user of bioethanol due to its sugarcane crops and government policies supporting ethanol production.

![CONTENTSWhat is bioethanol?Bioethanol ProductionFeedstocksFuel PropertiesApplicationAdvantagesDisadvantages and ConcernsEthanol ControversyComparison of Bioethanol and BiodieselCase study [Brazil]Future development](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-2-320.jpg)


















![Case study [Brazil]Brazil the first to produce the cheapest ethanol in the world.WHY BRAZIL?Favourable conditionsTradition of culturing sugarcaneSugarcane being the most efficient raw materials for production of ethanol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-30-320.jpg)
![Case study [Brazil]The FACTSBrazil second biggest producer of ethanol in the world (20 billion litres)Fuel used in 45 % of Brazilian vehicles is ethanolFeedstocks: sugarcane bagasse and straw (rich in cellulose and turning entire sugarcane biomass to be used with no wastage)1 tonne of bagasse produce 186 litres of ethanol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-31-320.jpg)
![Case study [Brazil]In 1930sBrazil’s ethanol industry startedGovernment directed sugarcane into ethanol productionMade addition of ethanol to gasoline compulsoryIn 1973International oil crisis doubled Brazil’s expenditure on oil importsGovernment was forced to consider alternative sources of energy to decrease its dependency and spending on fossil fuels.In 1975Increase ethanol production as a substitute for gasolineInvested in increasing agricultural productionModernising and expanding distilleriesEstablish new production plantsIntroduce subsidies to lower prices and reduce taxes for ethanol producers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-32-320.jpg)
![Case study [Brazil]Over 15 years, production of ethanol escalated from 0.6 billion litres in 1975 to 11 billion litres in 1990.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-33-320.jpg)
![Progress further with Bioethanol establishments:1975 to 1978One part of ethanol was added to four parts of gasoline.Additional processing stage to remove water from the fuel1979Production streamlined to focus on hydrous ethanolEthanol which contains 5% water that could be used in cars fuelled entirely by ethanolResearchers in Aerospace Technology in Sao Paulo, developed alloys to protect the internal parts of gasoline-powered engines and fuel tanks from corrosion by ethanol. 1986 to 1989, 90% of all new vehicles sold in the domestic market were ethanol-fuelled.Case study [Brazil]PROBLEMS faced:Waste!!VINASSE – a corrosive liquid byproduct of ethanol distillationBeing dumped in rivers causing environmental damageBagasse – leftover sugarcane fibre](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-34-320.jpg)
![Case study [Brazil]SOLUTIONS:Vinasse was found to be a good fertiliser.Transportation system was developedCombination of trucks, pipes and ducts to carry Vinasse from the distilleries to the fieldsBagasse was collectedProduce energy, building on existing methods of burning the bagasse to power steam turbines for electricity generationDeveloped cauldrons under greater pressureMore energy could be produced allowing ethanol plants to become more autonomous in terms of energyCONTRIBUTIONS IS TO KEEP ETHANOL PRODUCTION COSTS LOW](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-35-320.jpg)
![Case study [Brazil]Social impactsCreated jobs for locals (mainly in rural areas)Brazilian sugarcane industry has a particularly poor record in respecting worker’s rightsExpansion in sugar cane cultivation may increase food prices. This would leave the poor with a harder survival.Although the ethanol industry has greatly increased the wealth of the sugar and alcohol sector’s industries, the poor have to be the one handling the negative impacts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioethanol2-110211063006-phpapp01/85/Bioethanol-36-320.jpg)