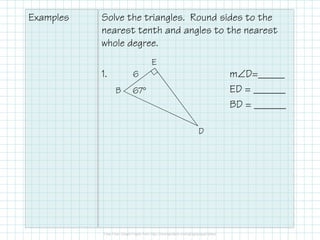
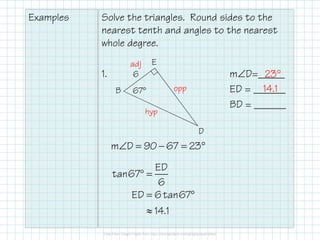
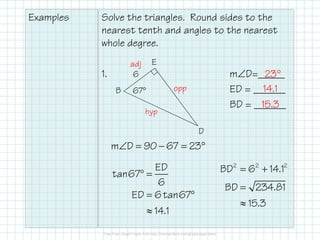
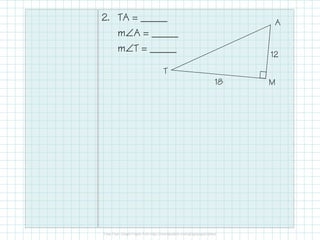
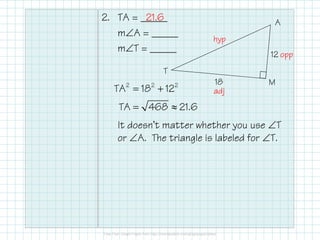
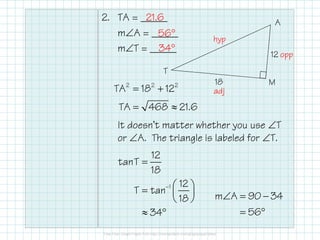
This document provides instructions for solving right triangles. It explains that to solve a right triangle, you find all the missing parts. If given an angle and side, you can use trig ratios to find the other acute angle and missing sides. If given two sides, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side and trig ratios to find an angle. It provides examples of solving right triangles when given an angle and side or two sides.