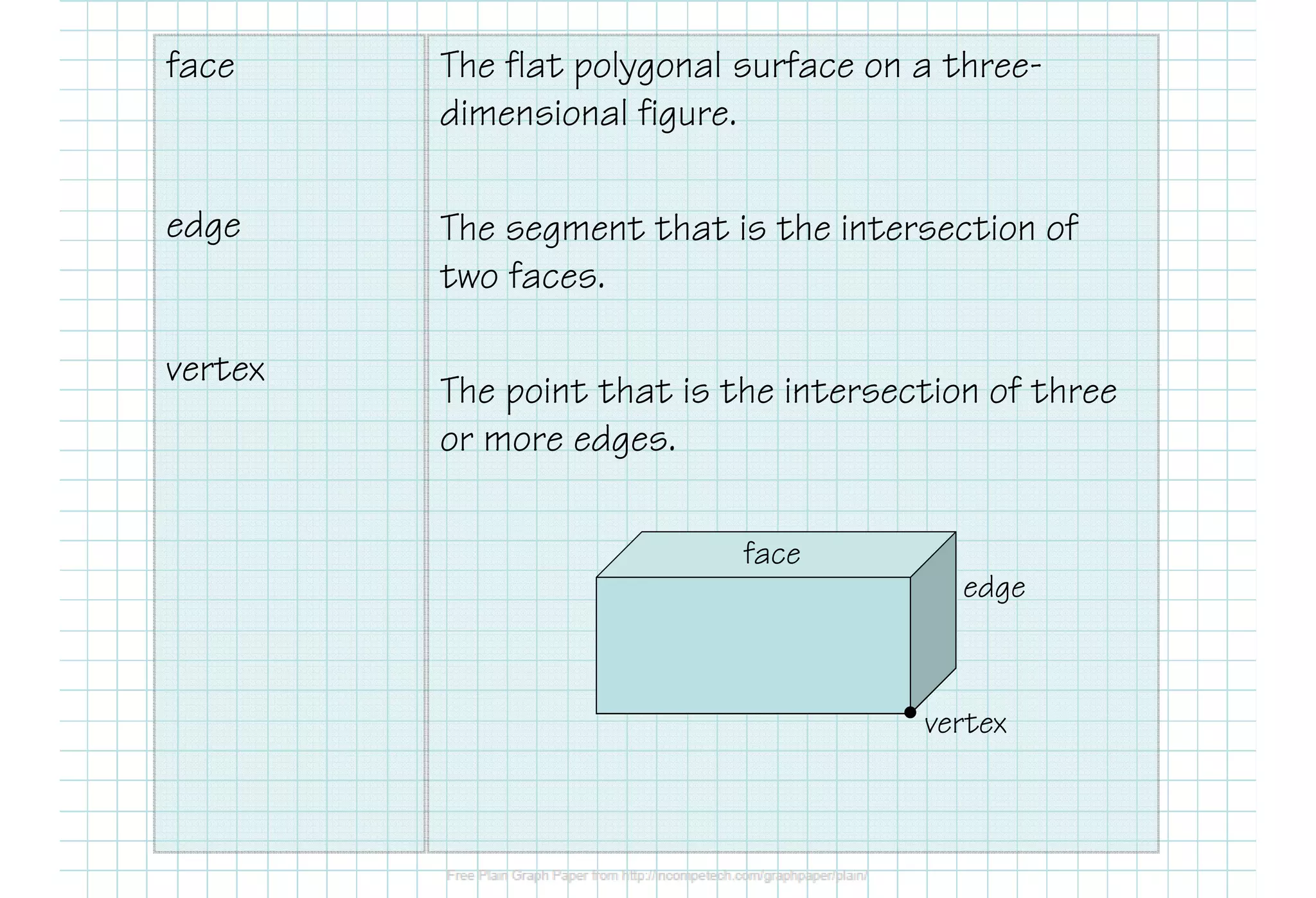
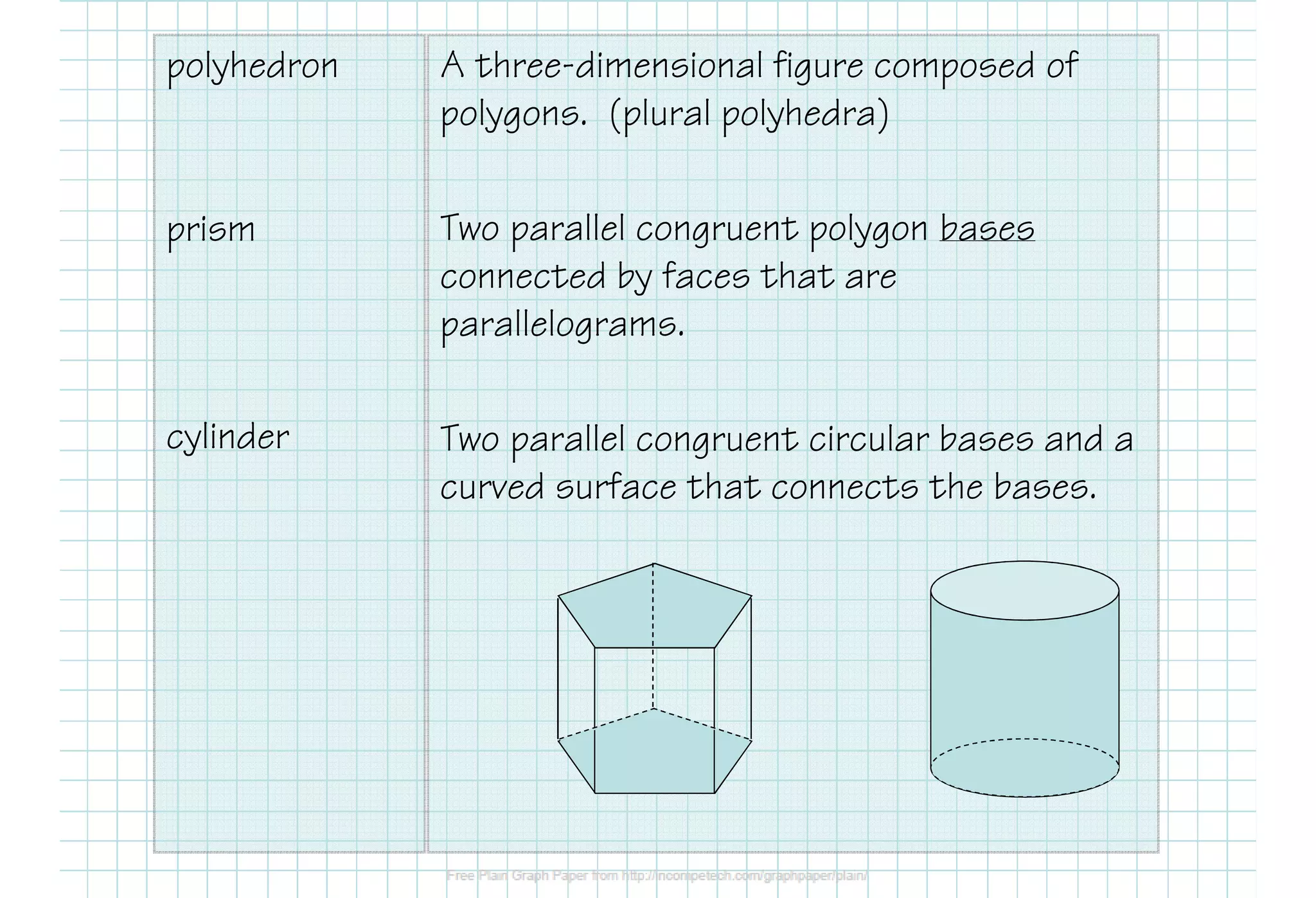
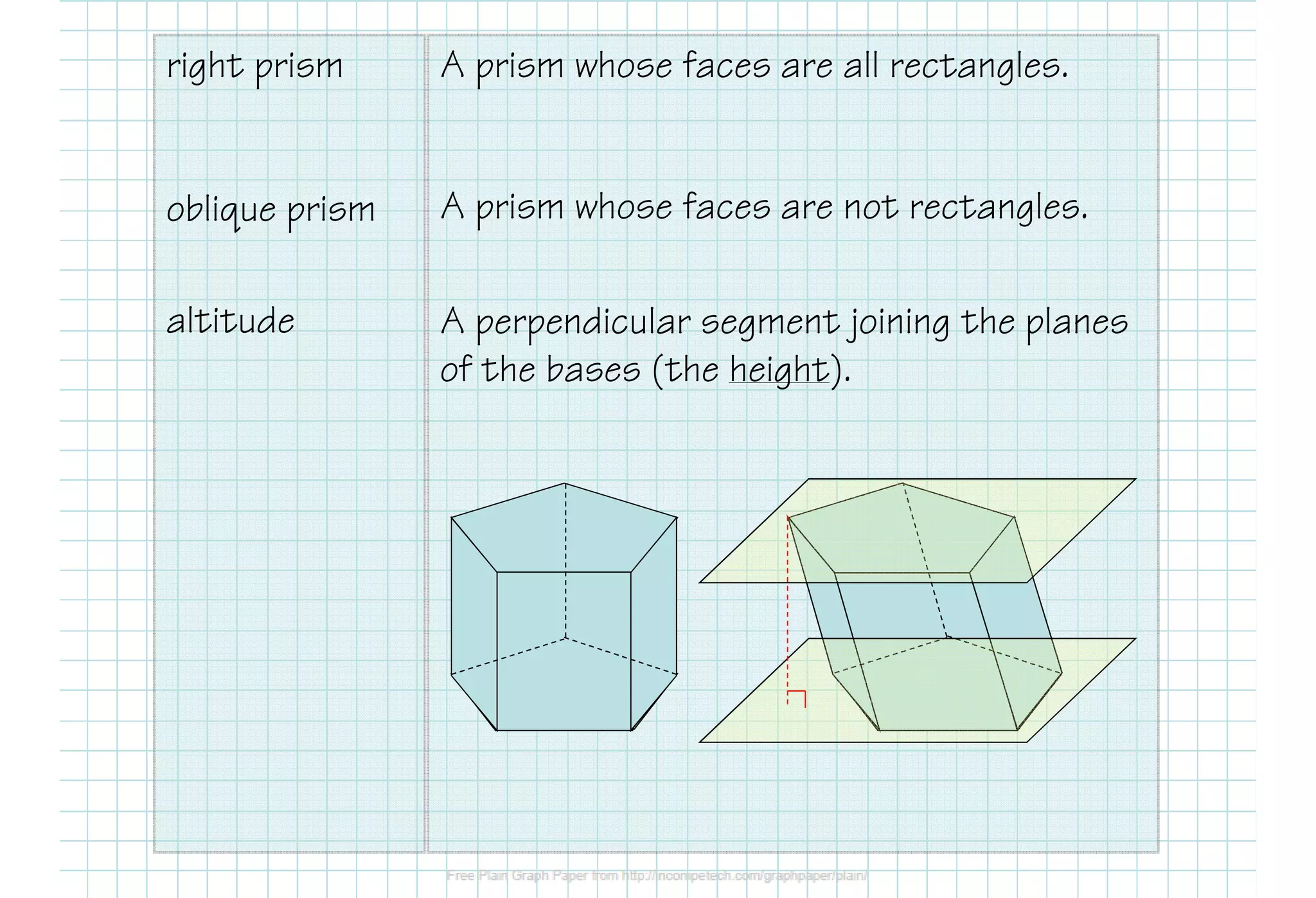
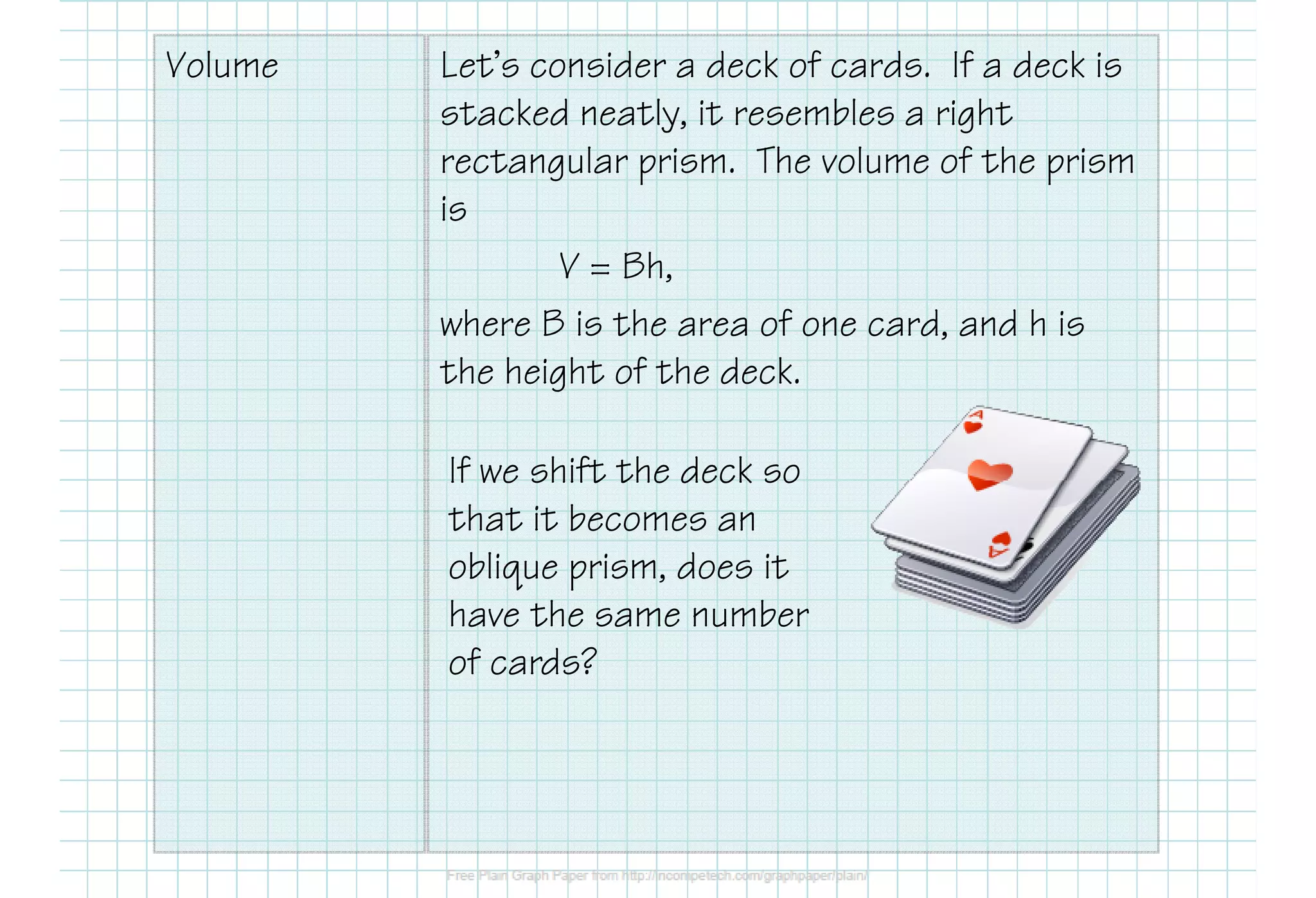
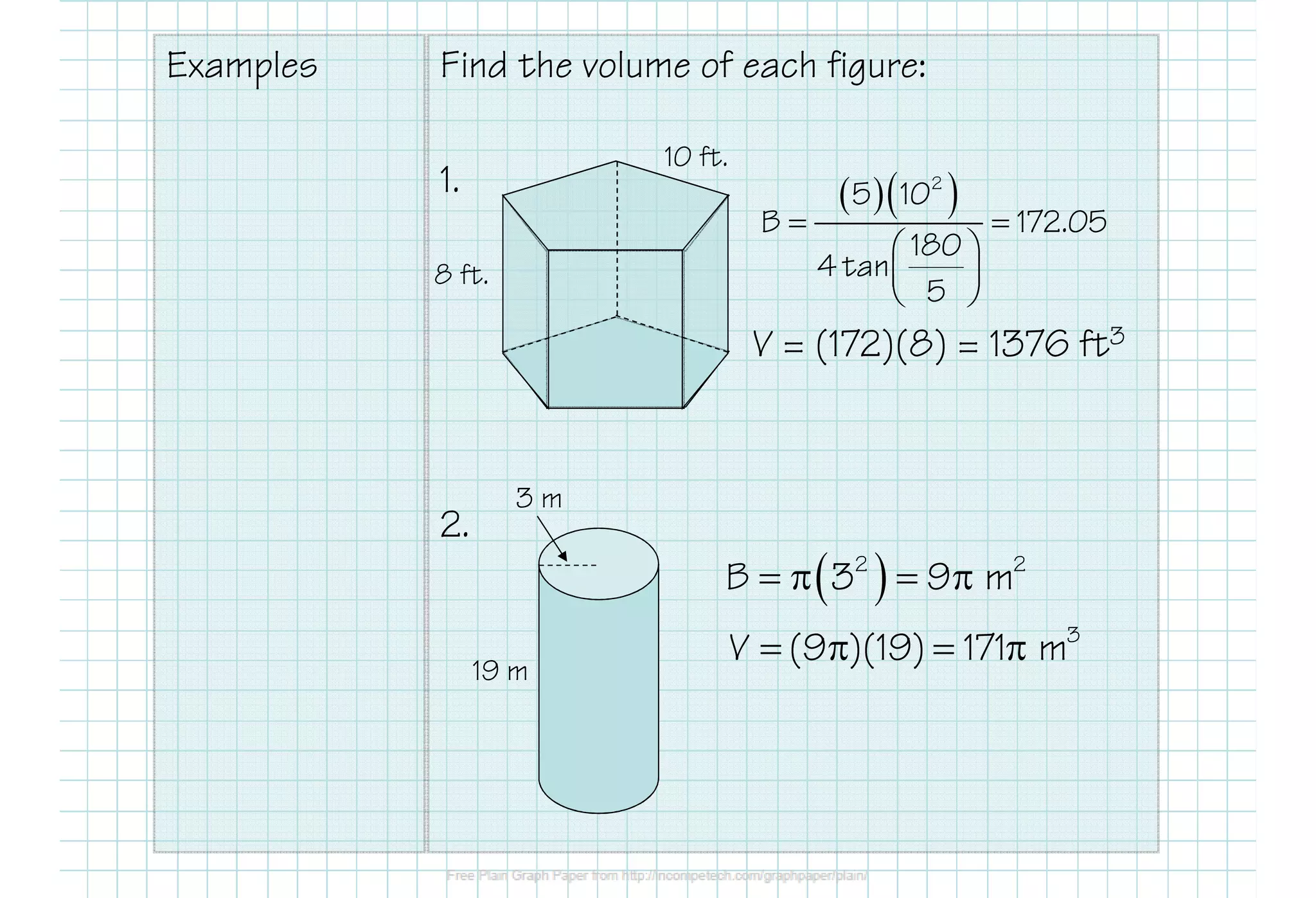
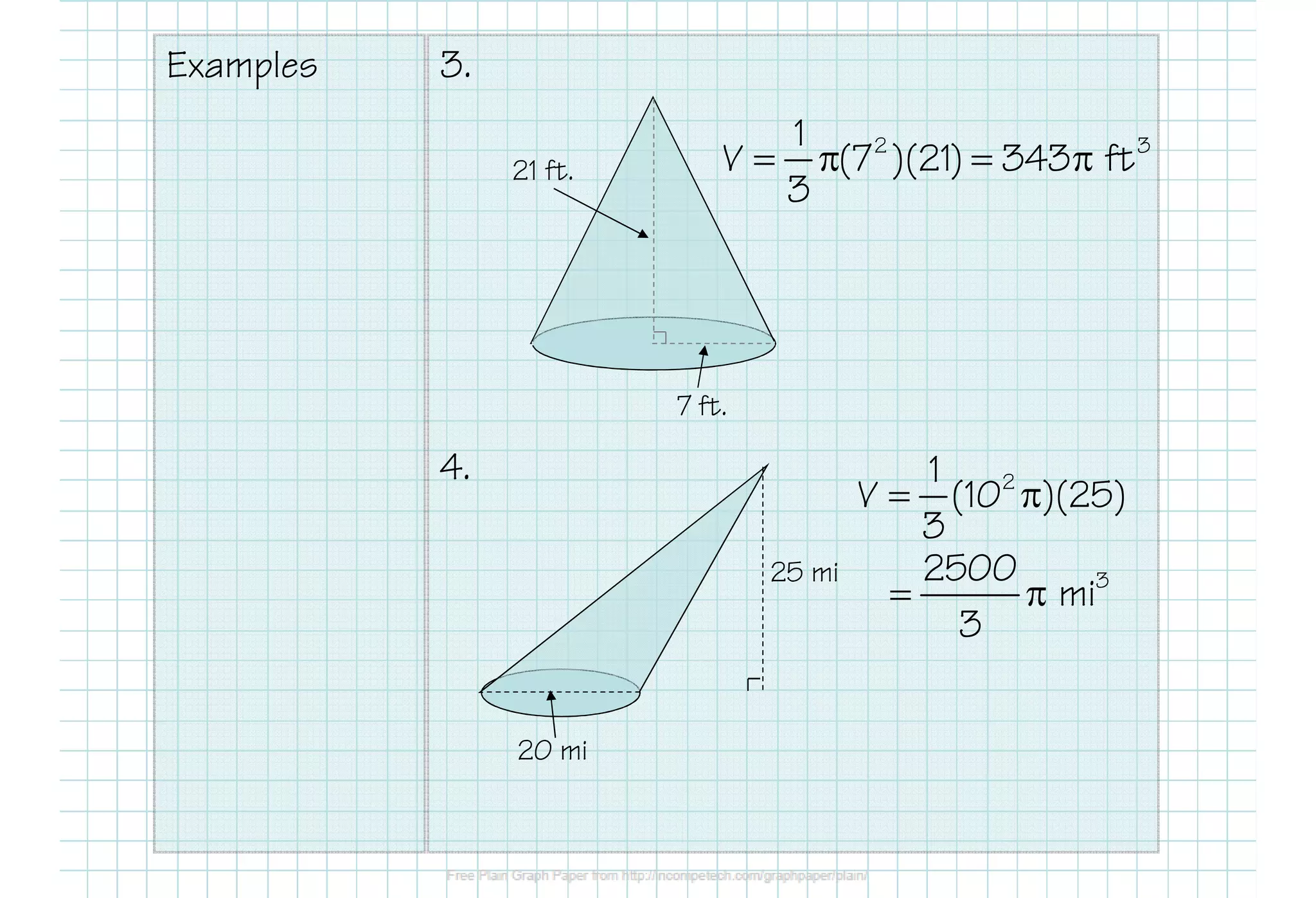
This document defines various 3D shapes and their volume formulas. It discusses how to calculate the volume of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, and cones. For prisms and cylinders, the volume is the area of the base multiplied by the height, regardless of whether the shape is right or oblique. The volume of a pyramid is one-third the area of the base multiplied by the height. For a cone, the volume is one-third pi times the area of the base times the height. Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating volumes of different 3D shapes using the appropriate formulas.