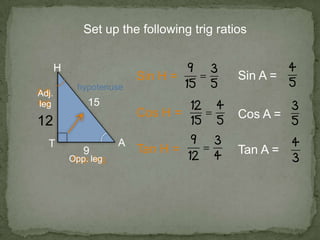
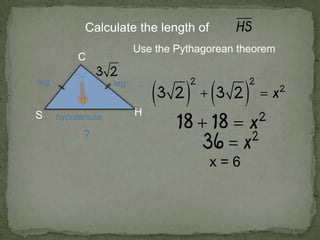
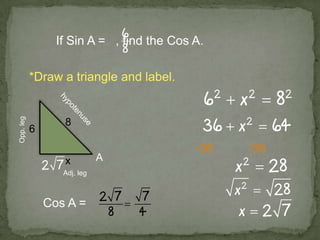
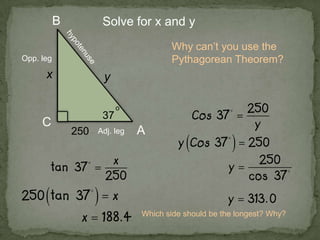
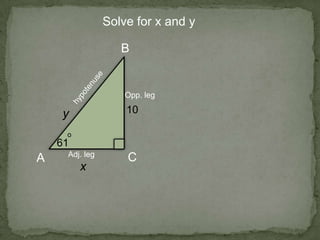
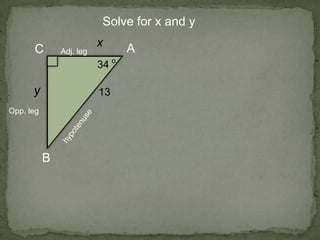
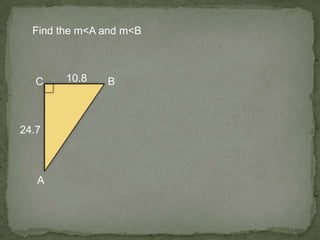
1. The document discusses trigonometric ratios and how to use them to solve for missing side lengths and angle measures in right triangles.
2. It provides examples of setting up trig ratios, using the Pythagorean theorem, and using inverse trig functions to find missing angles.
3. The key steps are to label the sides of the right triangle, set up the appropriate trig ratios based on which information is known or missing, and use trig identities or the inverse functions to calculate the missing information.