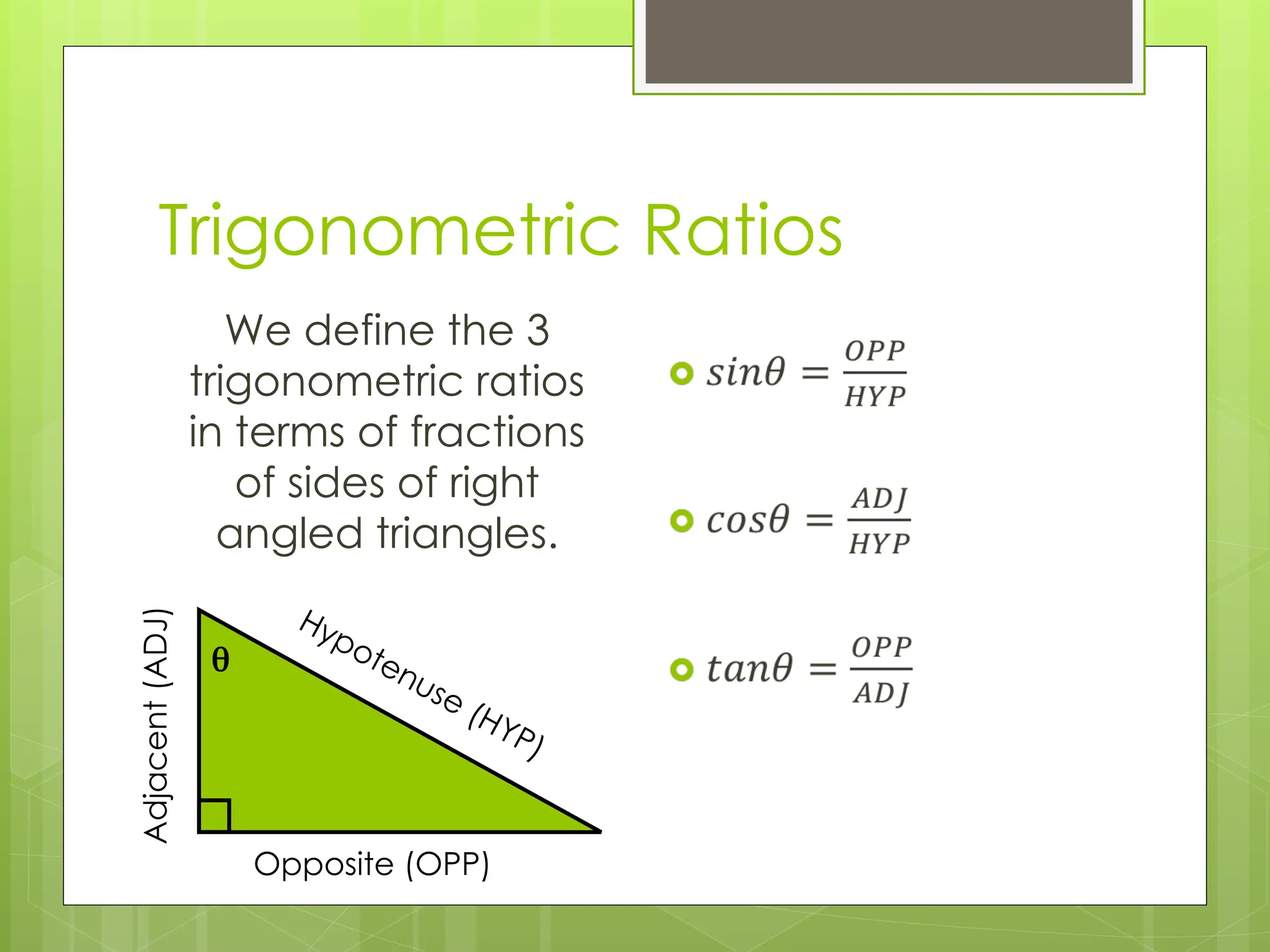
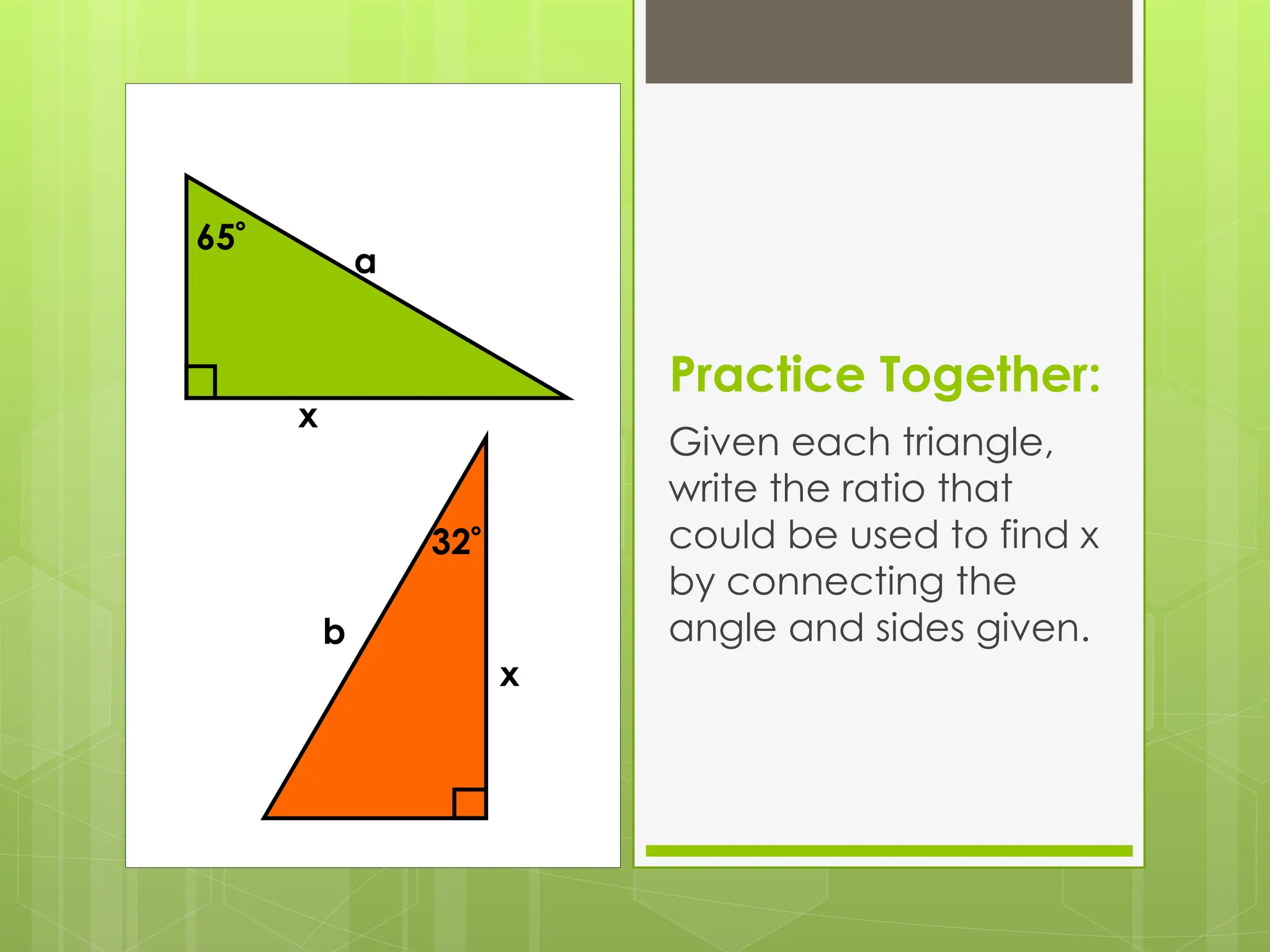
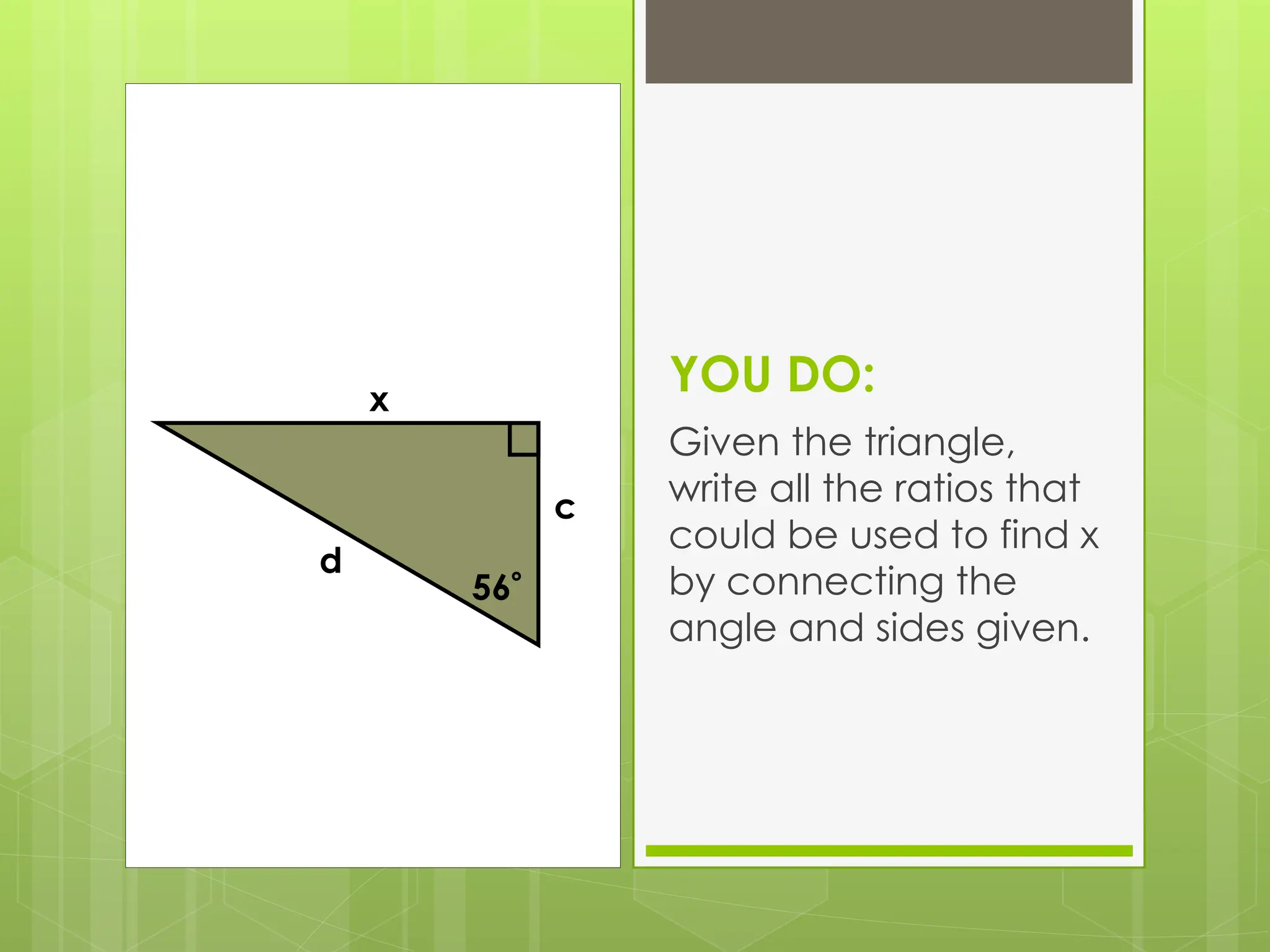
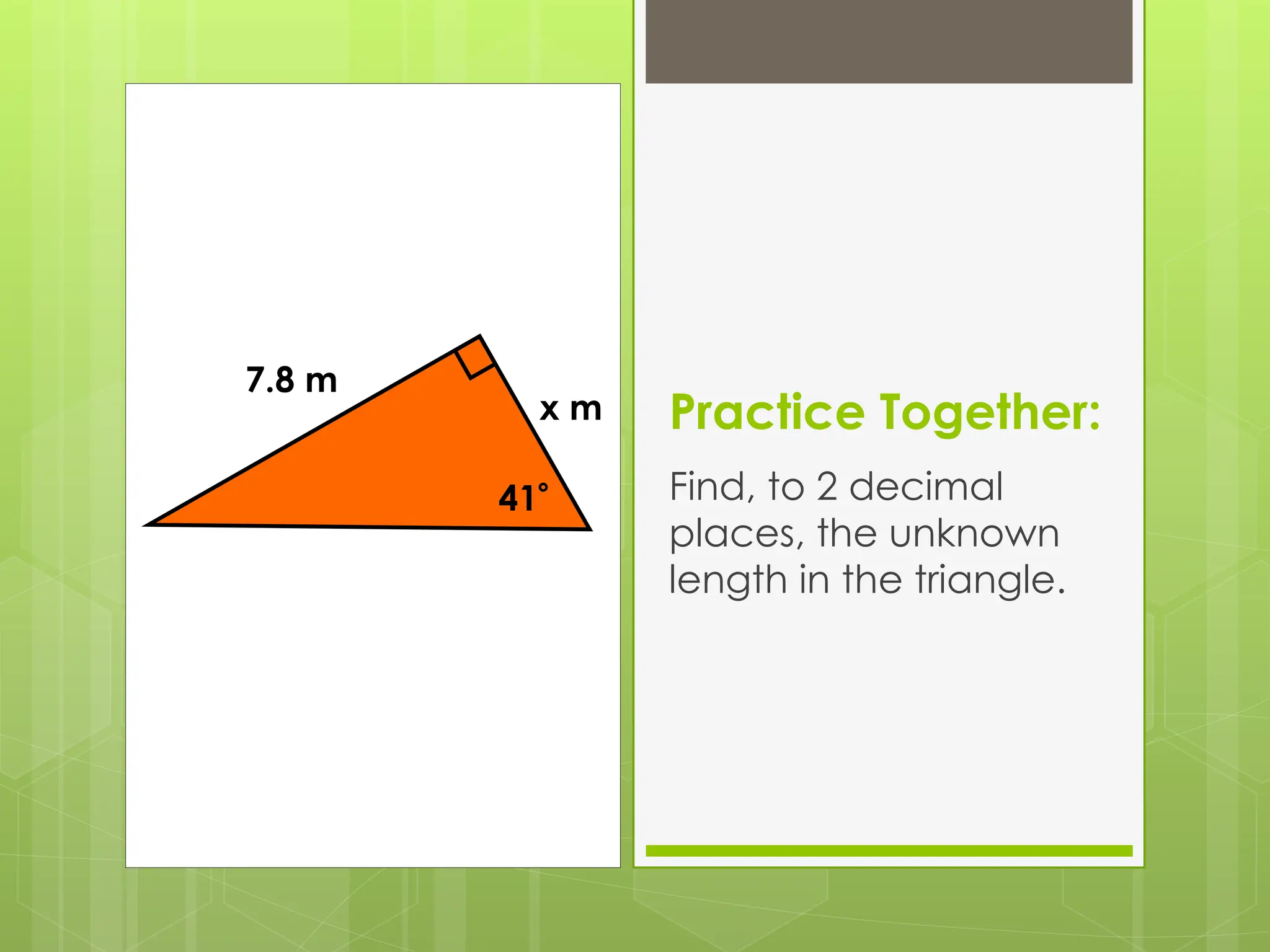
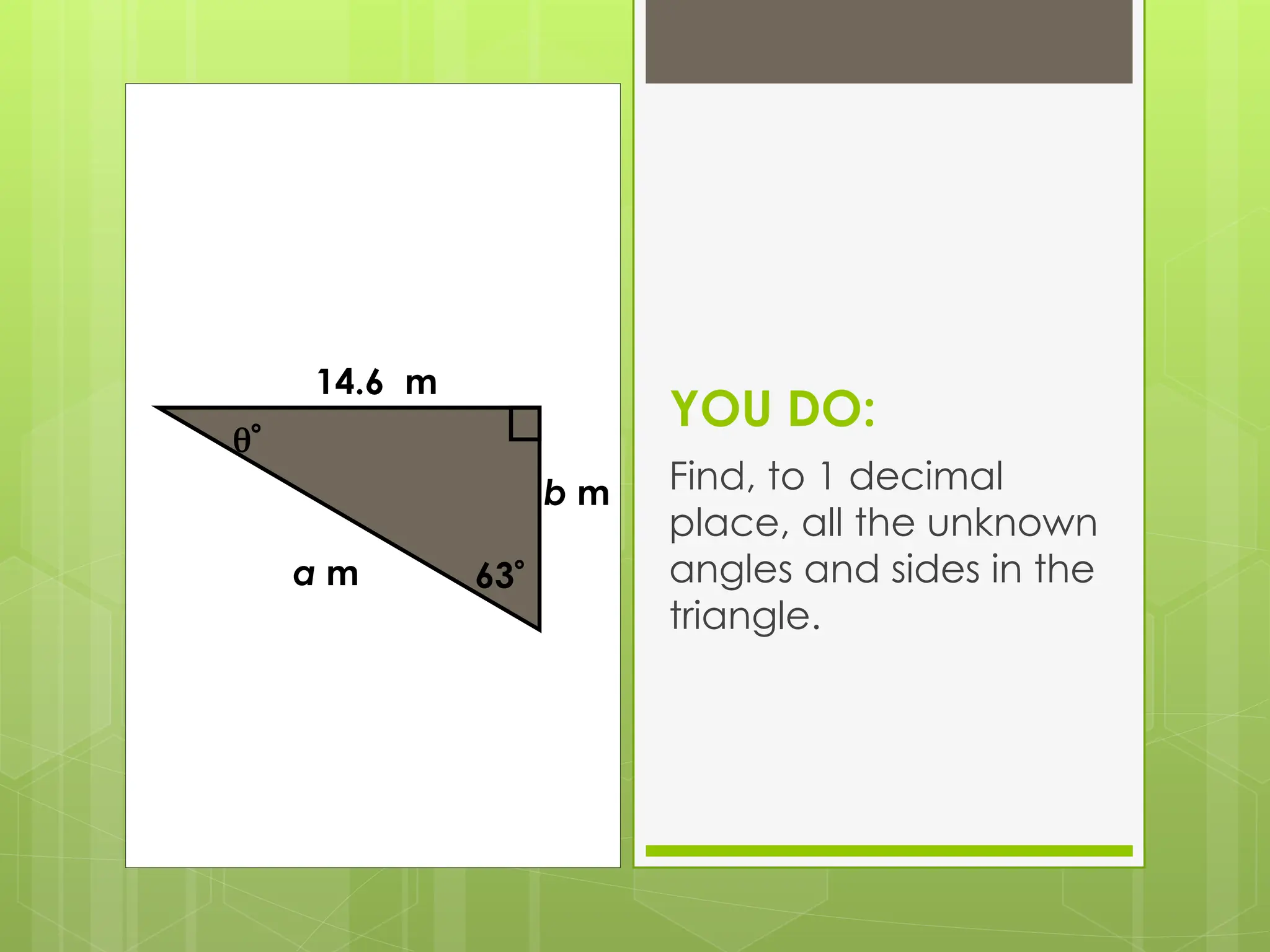
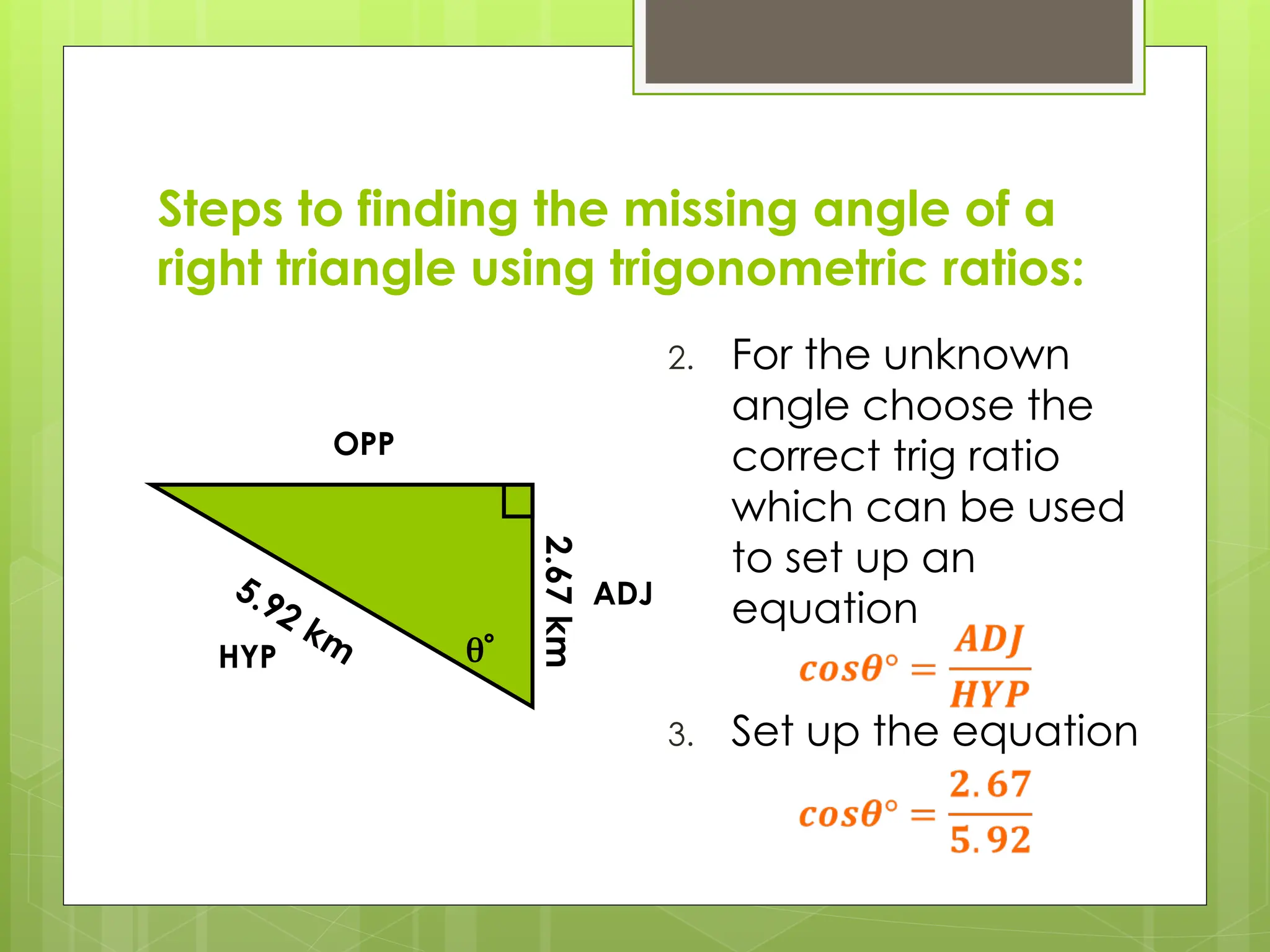
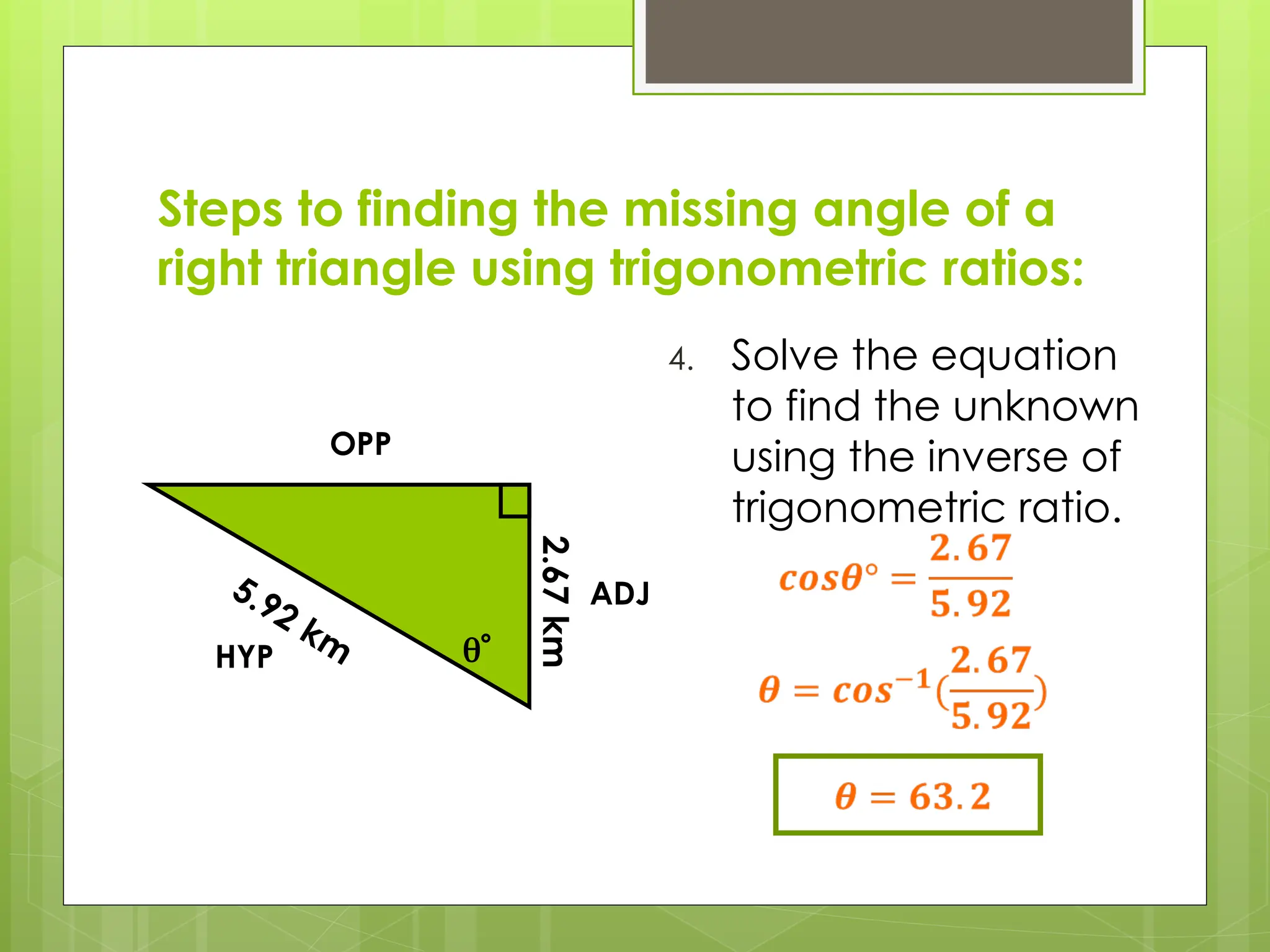
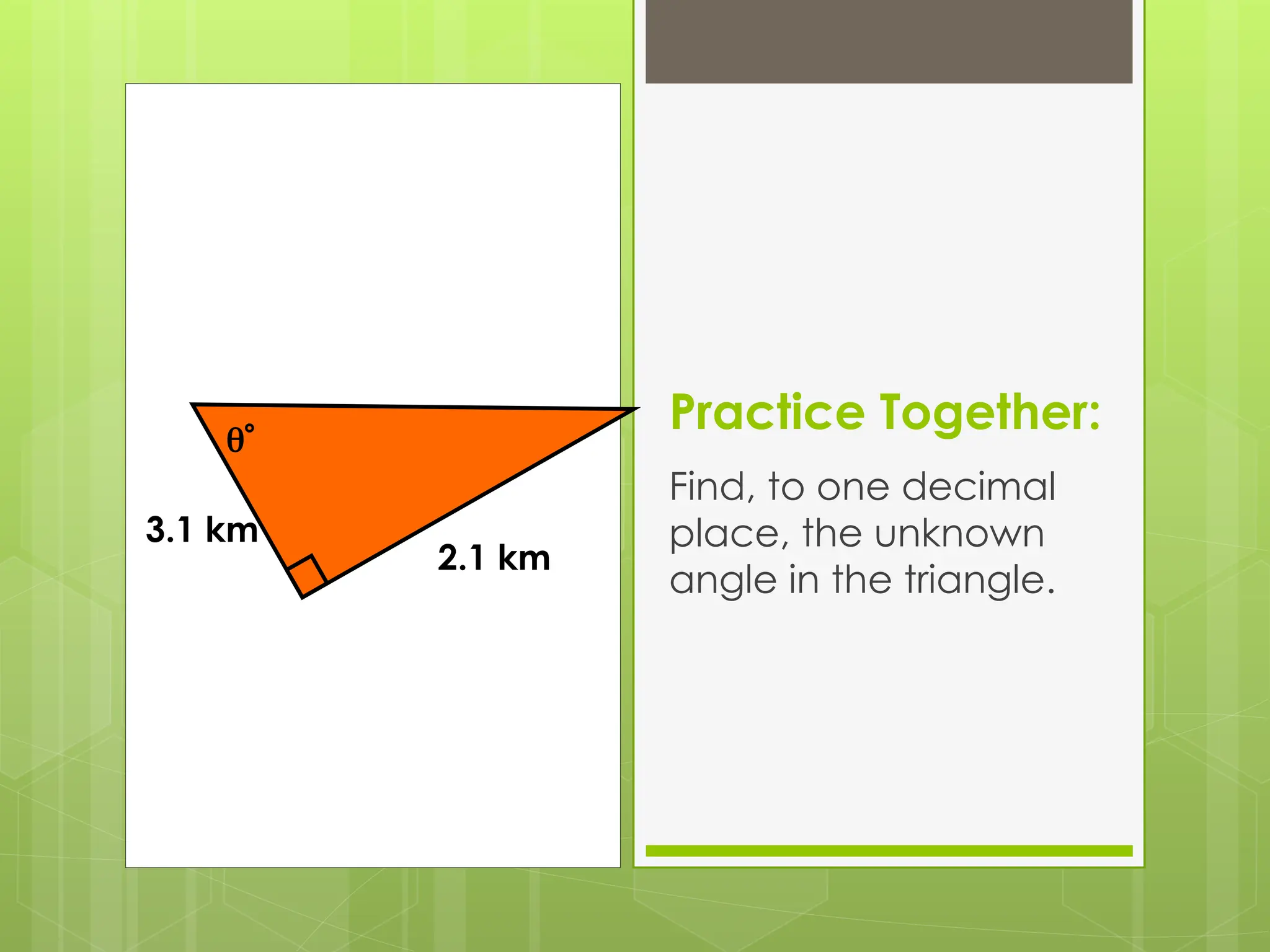
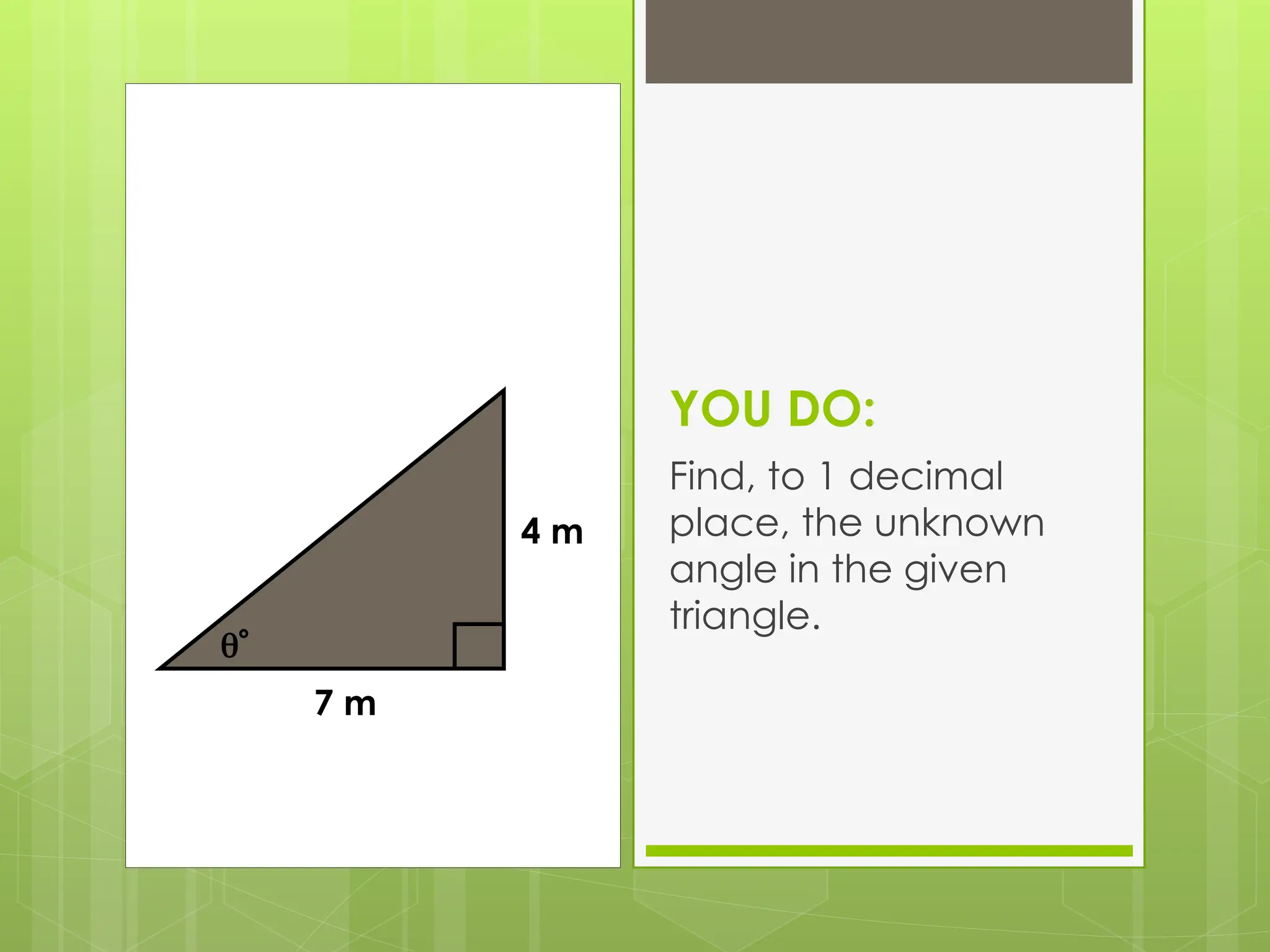
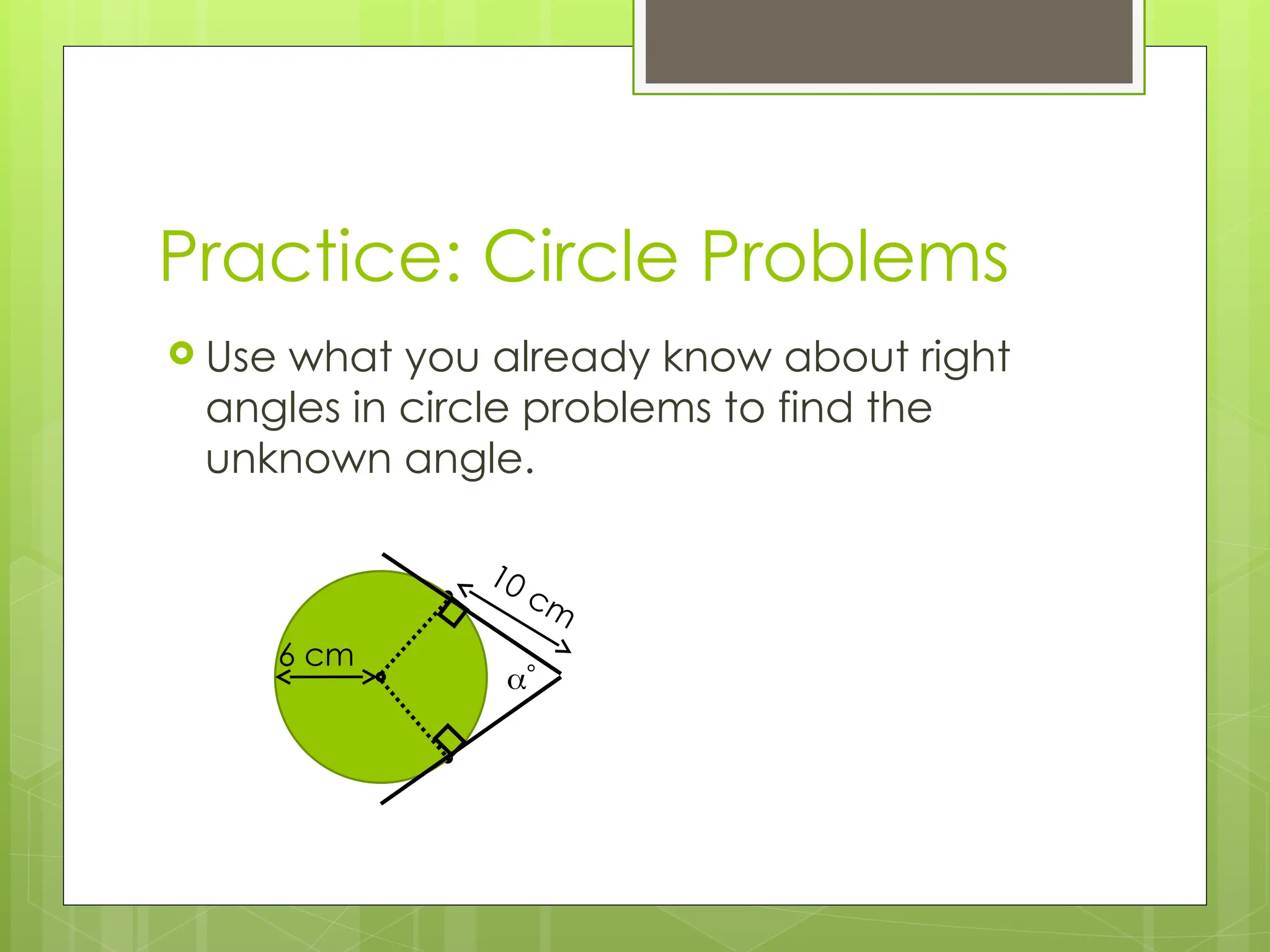
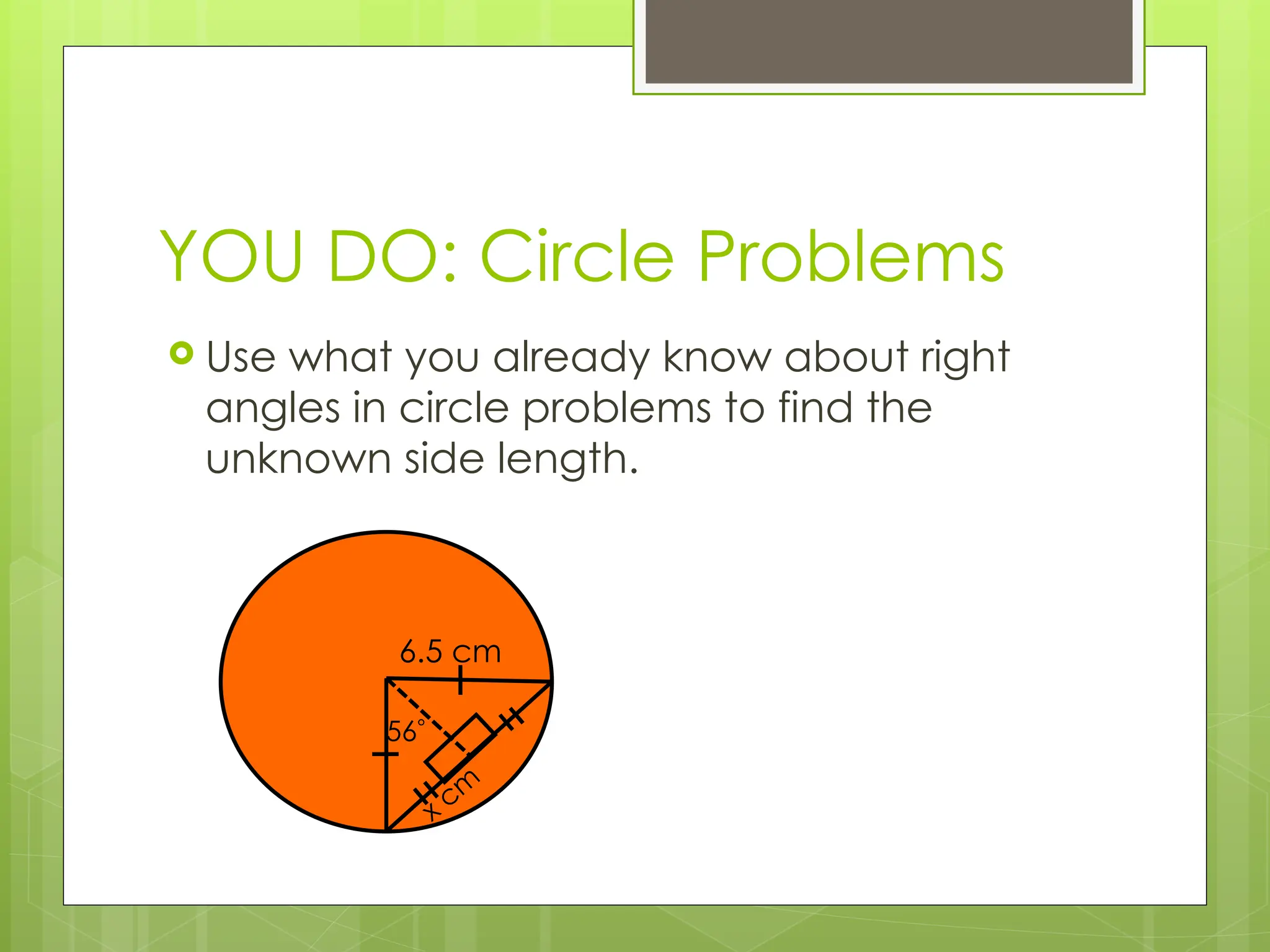
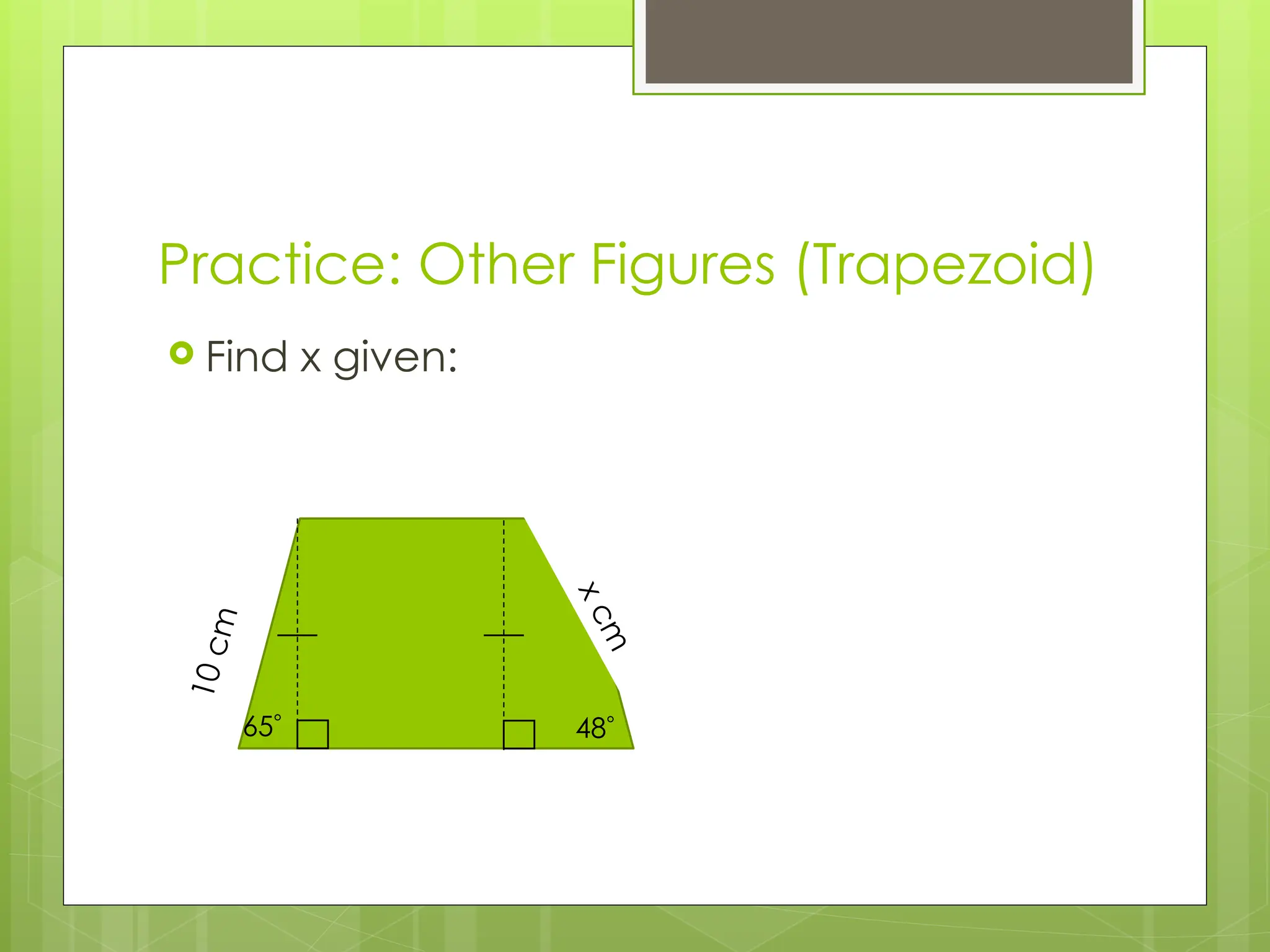
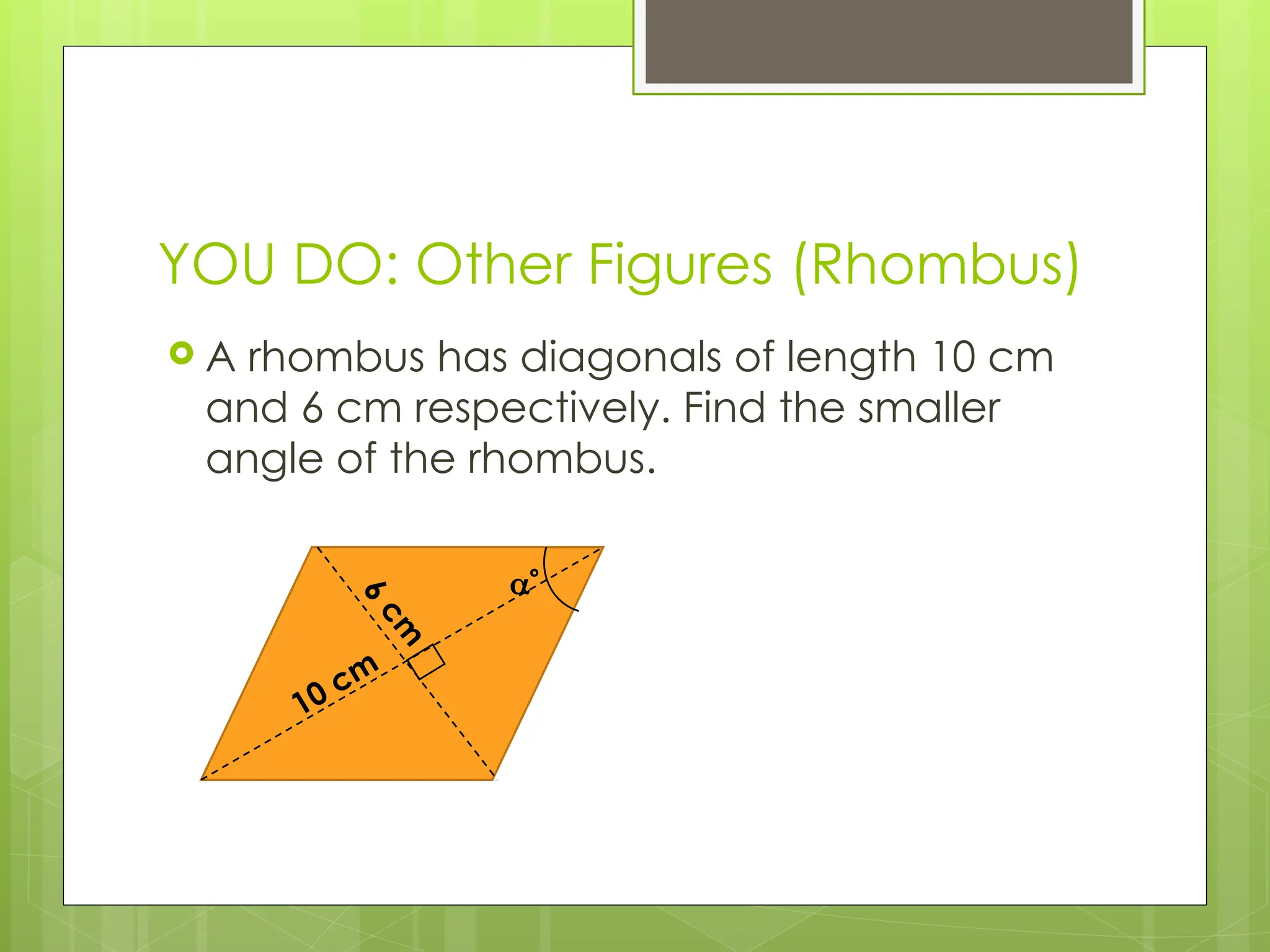
The document explains right-angled trigonometry, focusing on labeling triangles and defining key terms like hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent. It details how to use trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, and tangent) to find missing sides and angles in right triangles, and includes practice problems for reinforcement. Additionally, it touches on isosceles triangles and circle problems, employing previously learned concepts to solve for unknowns.