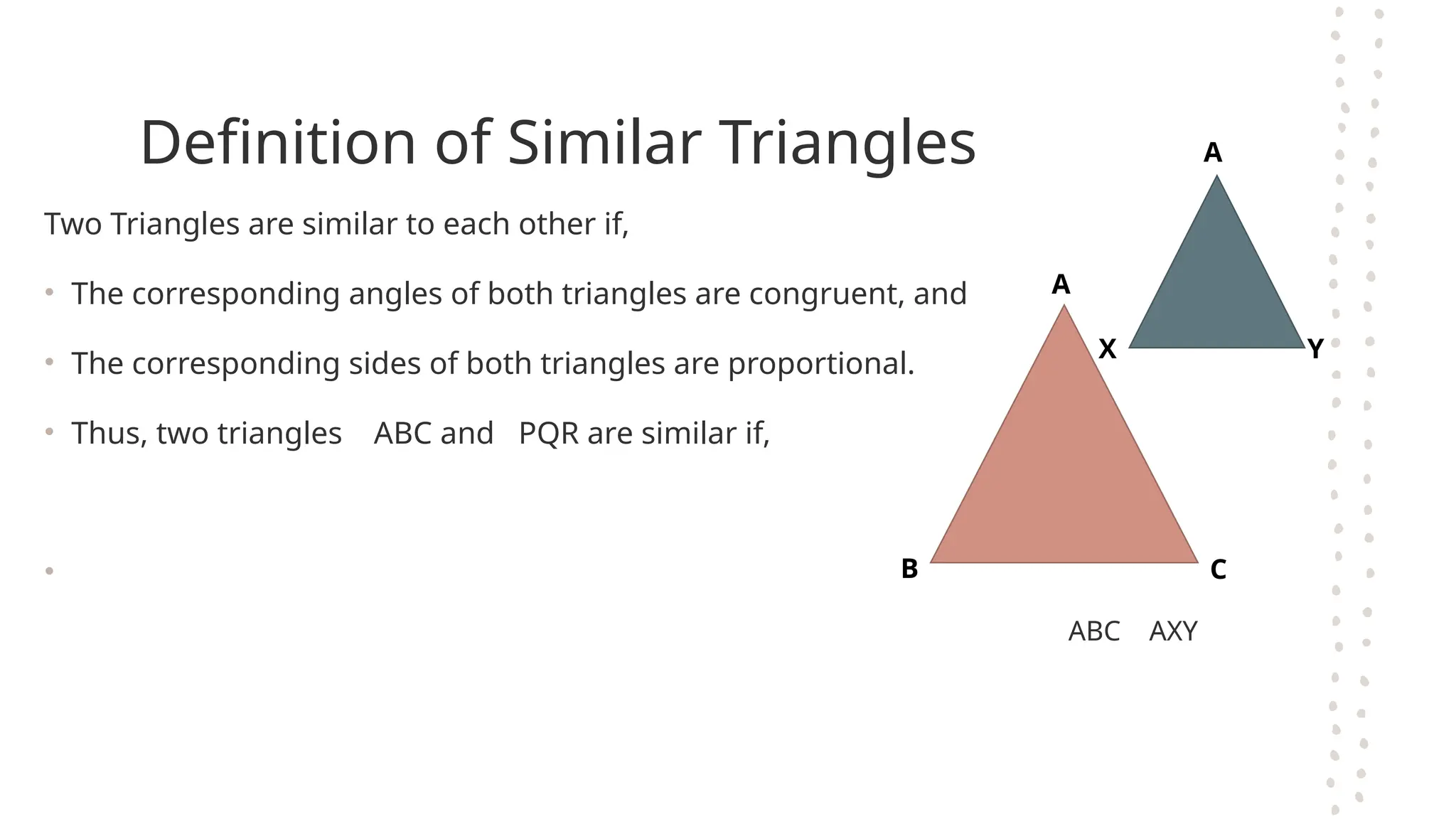
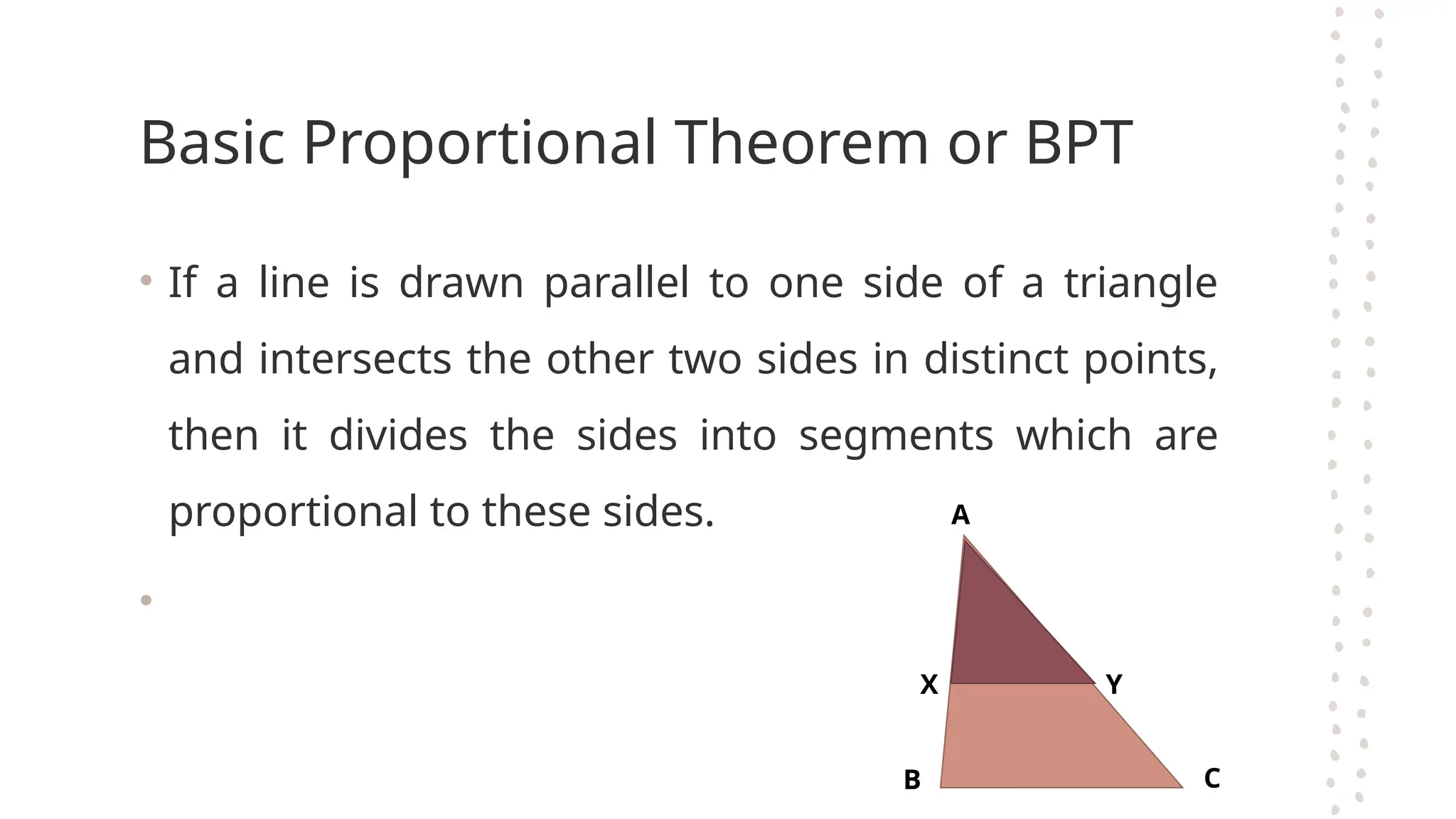
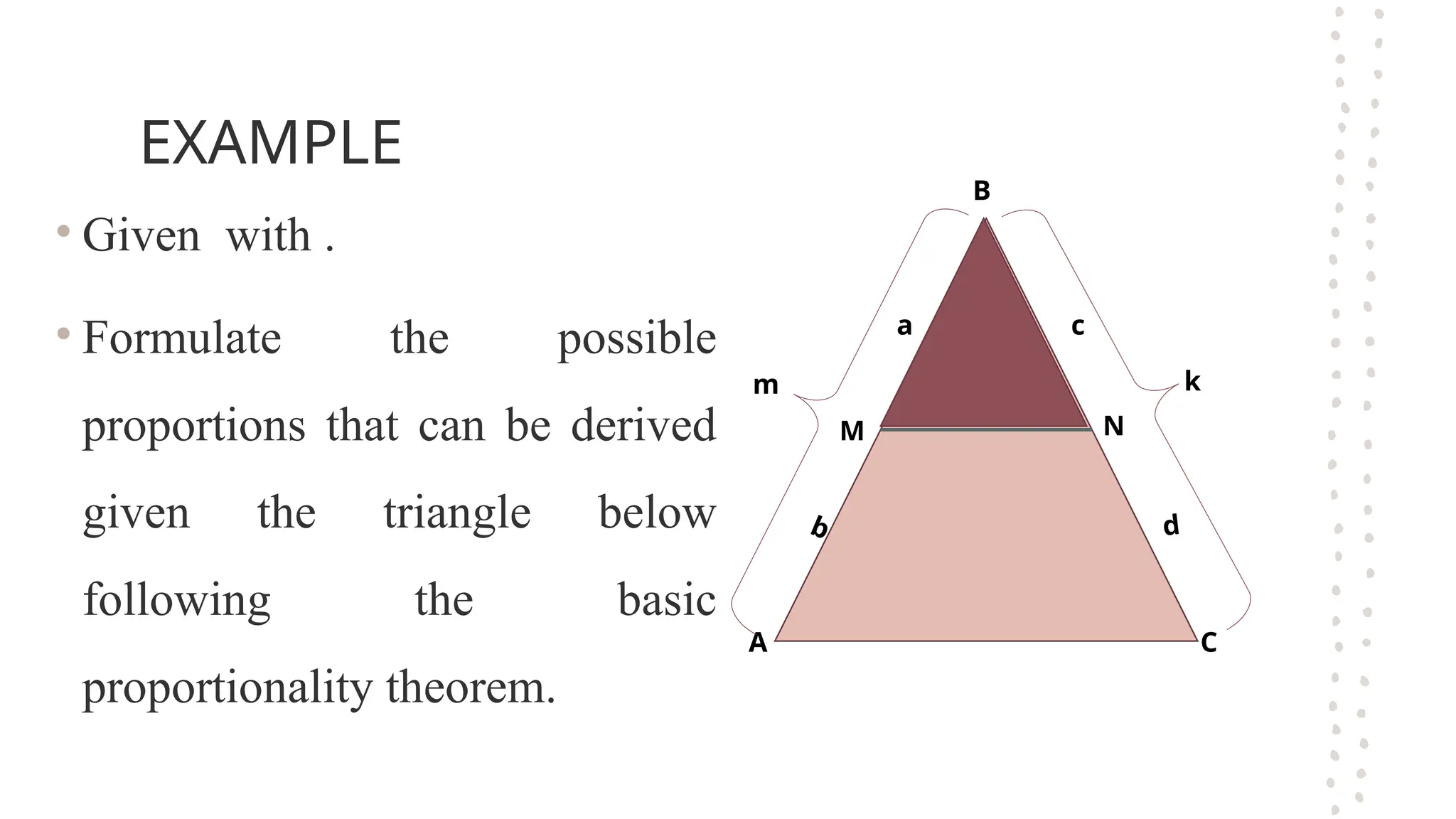
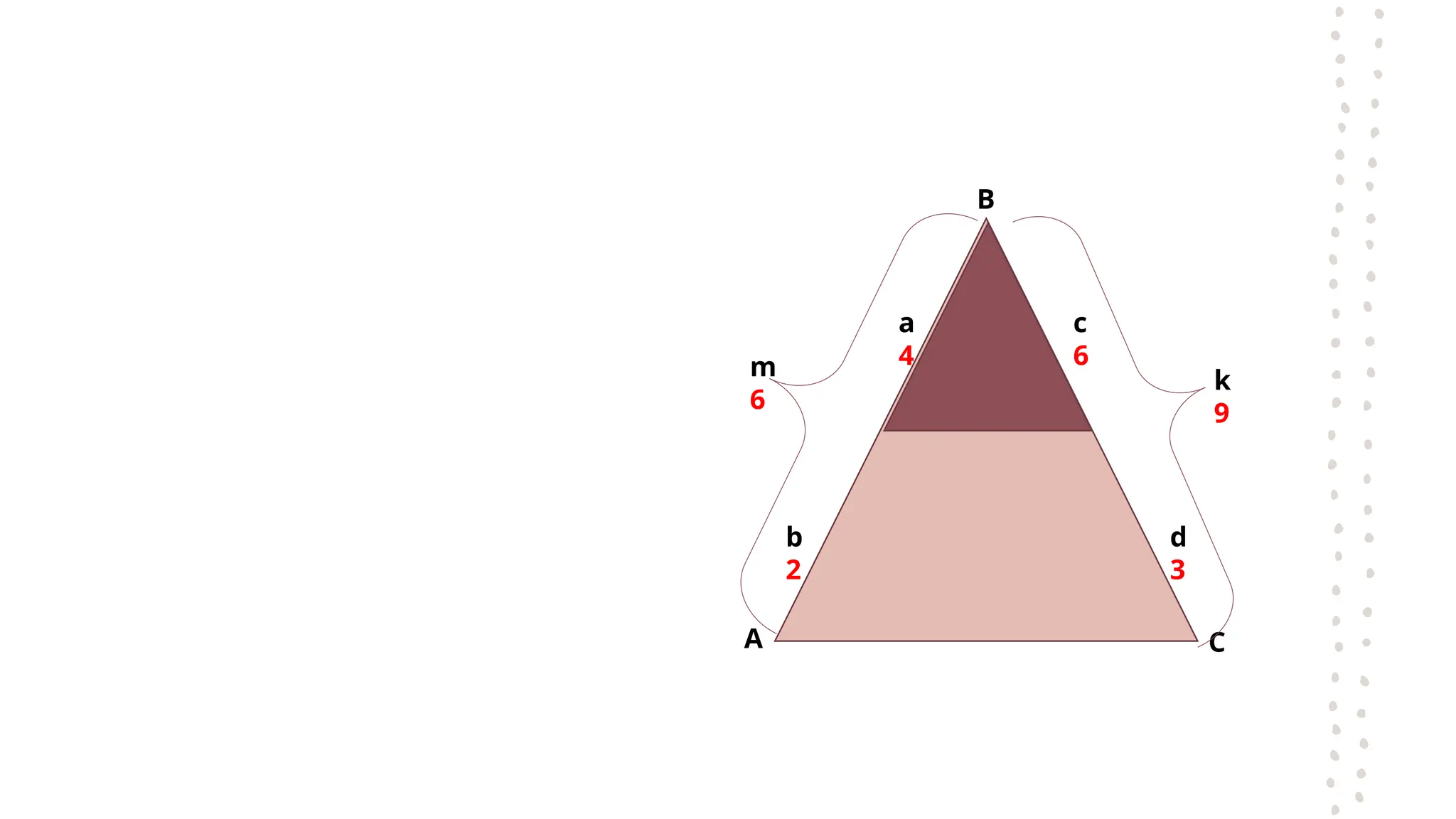
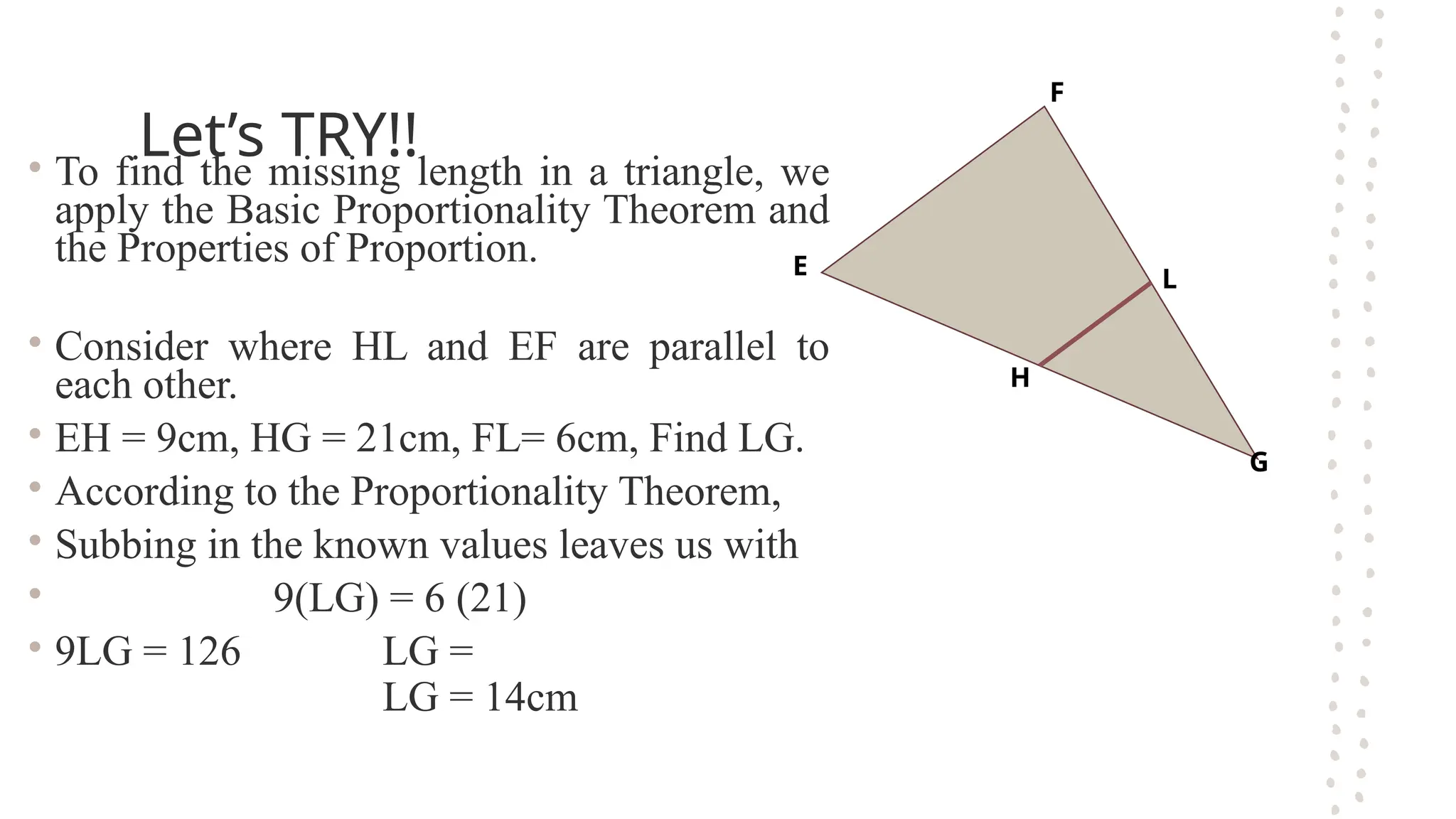
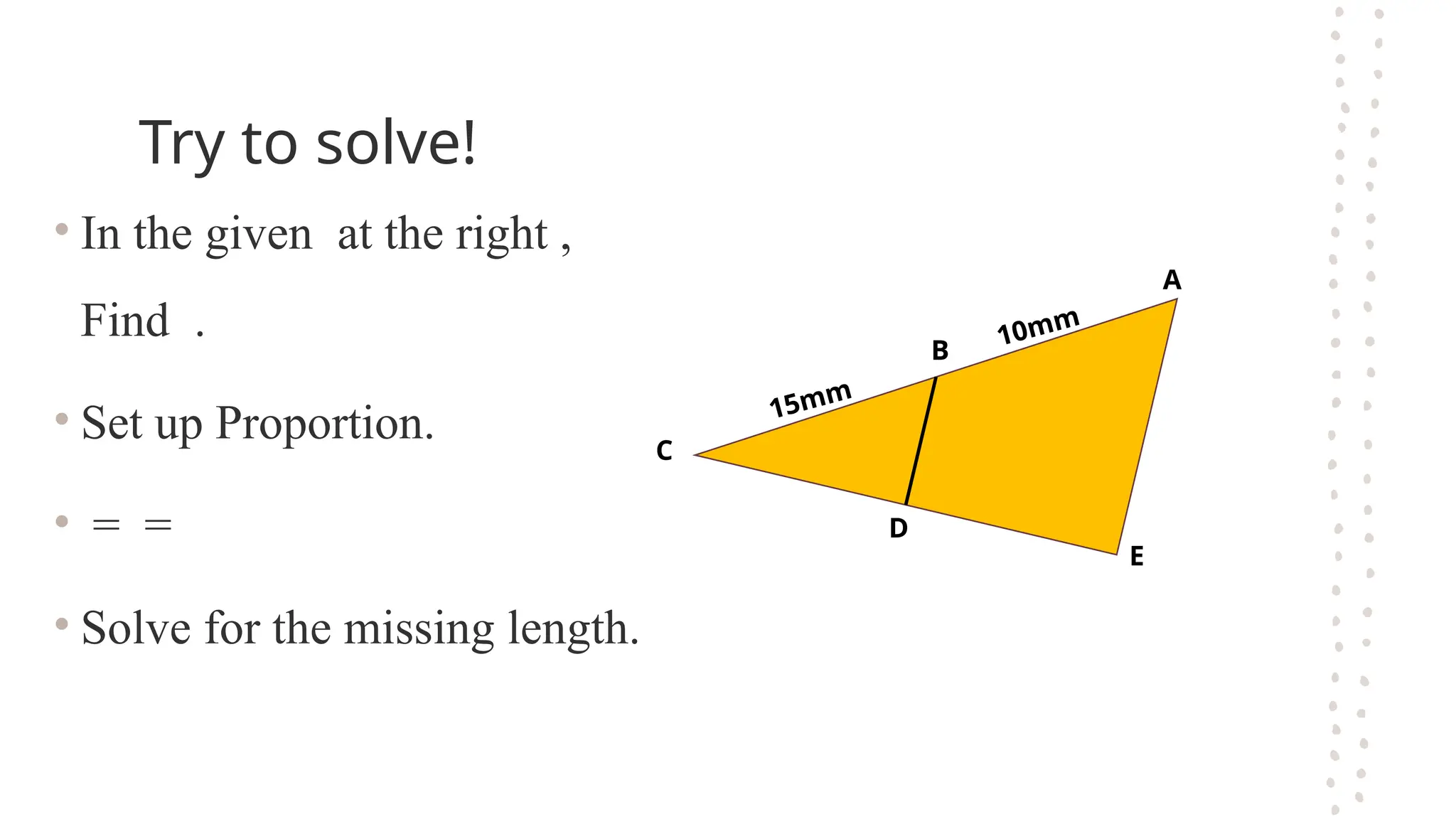
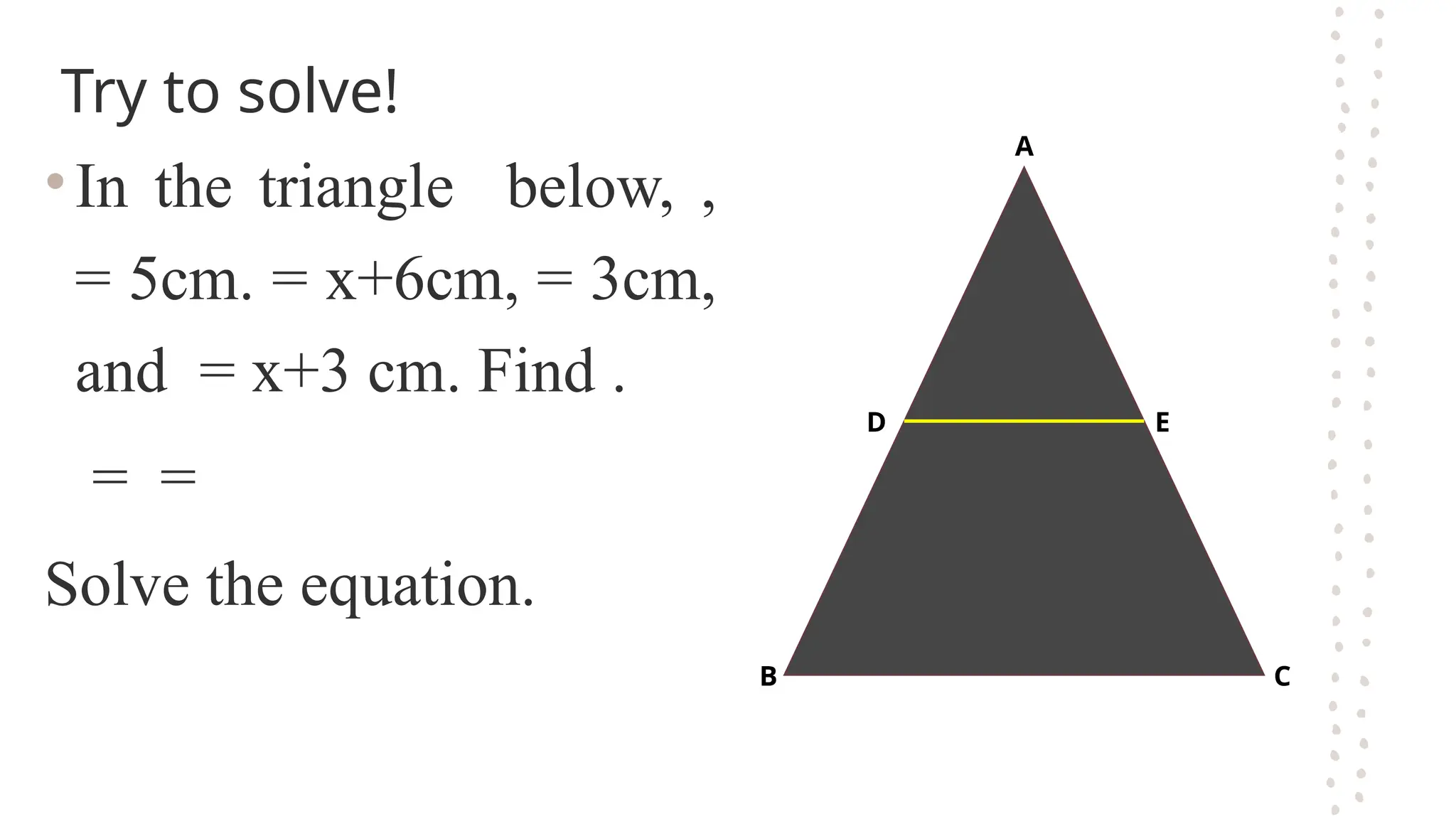
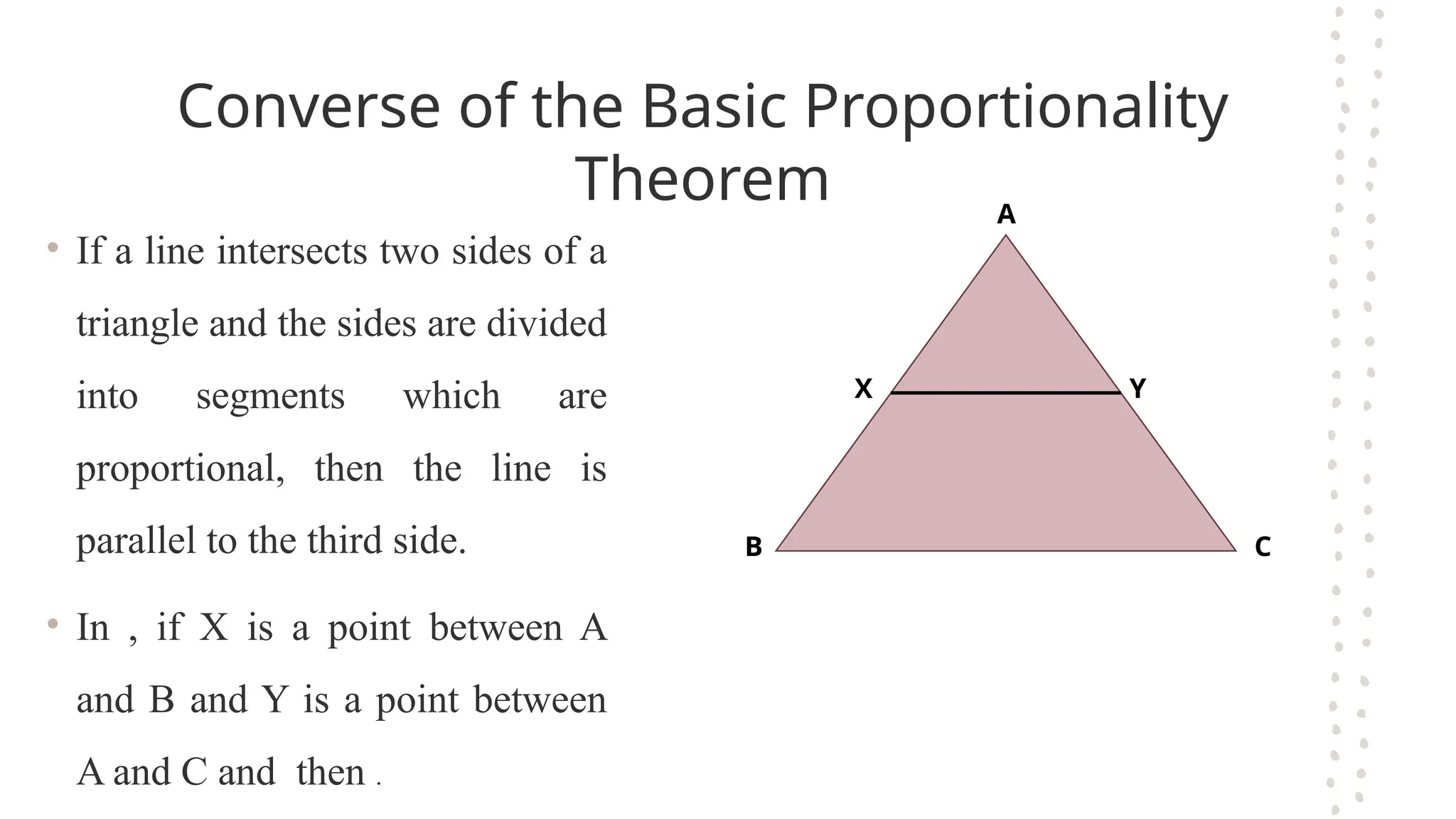
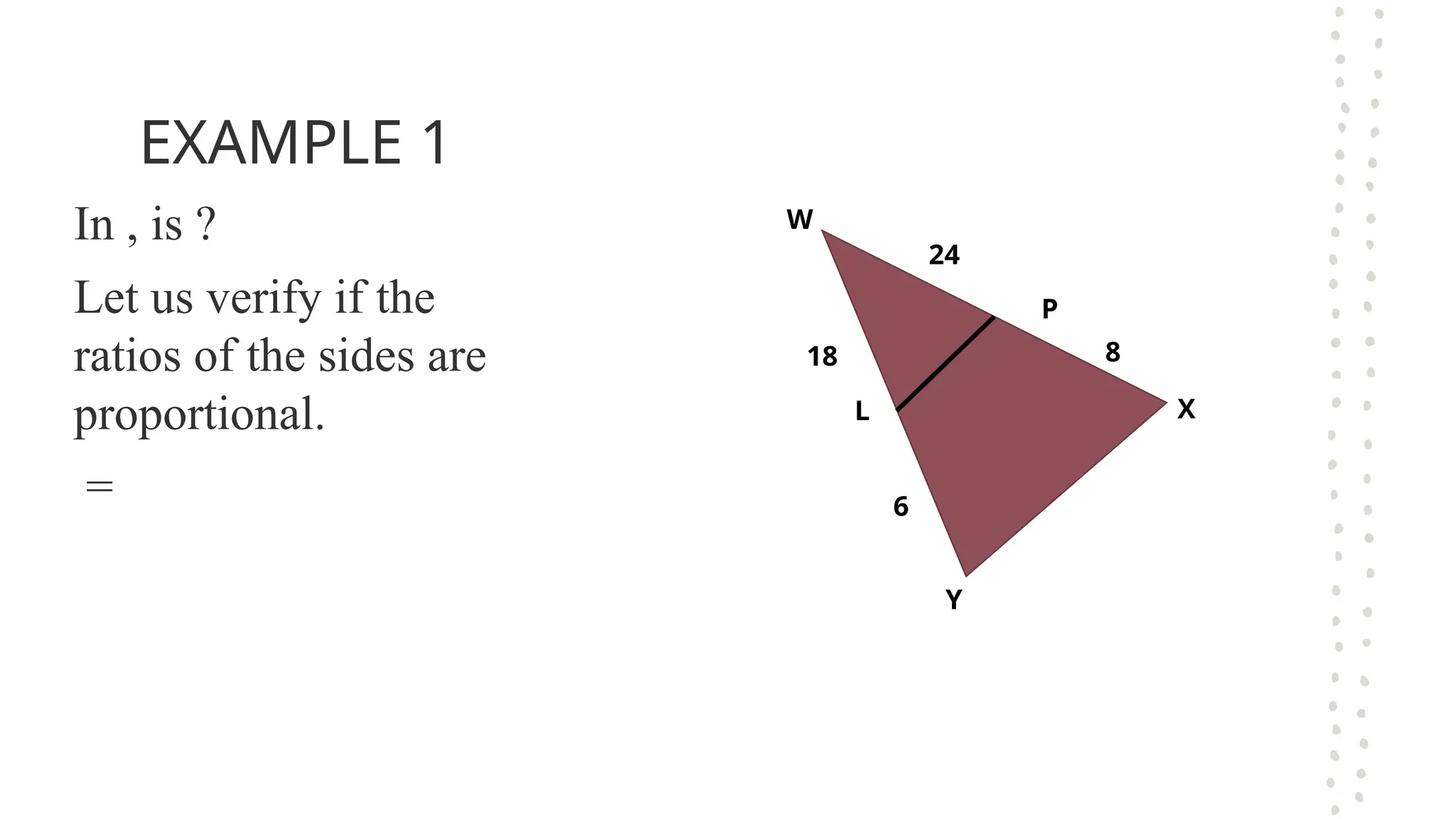
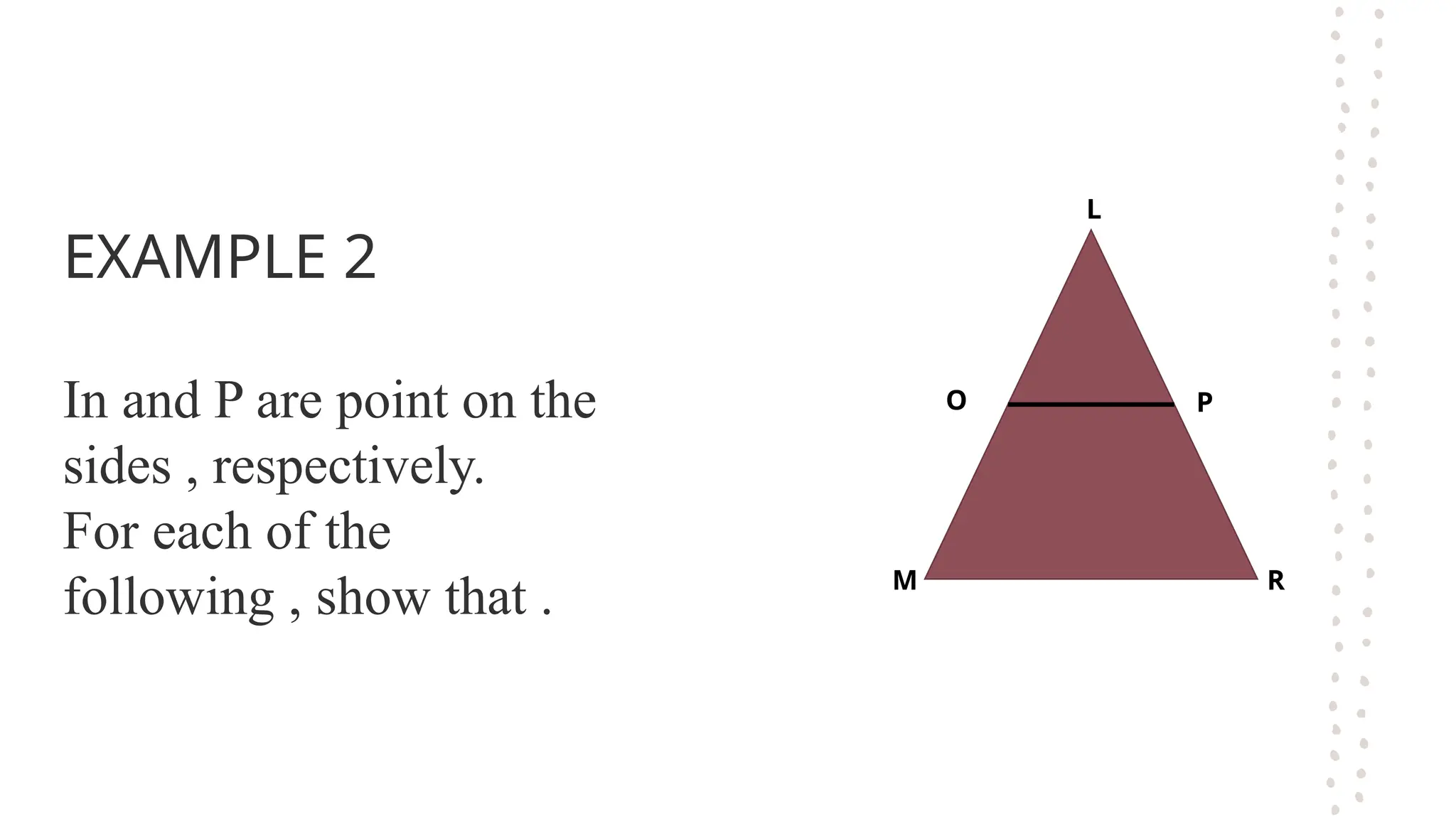
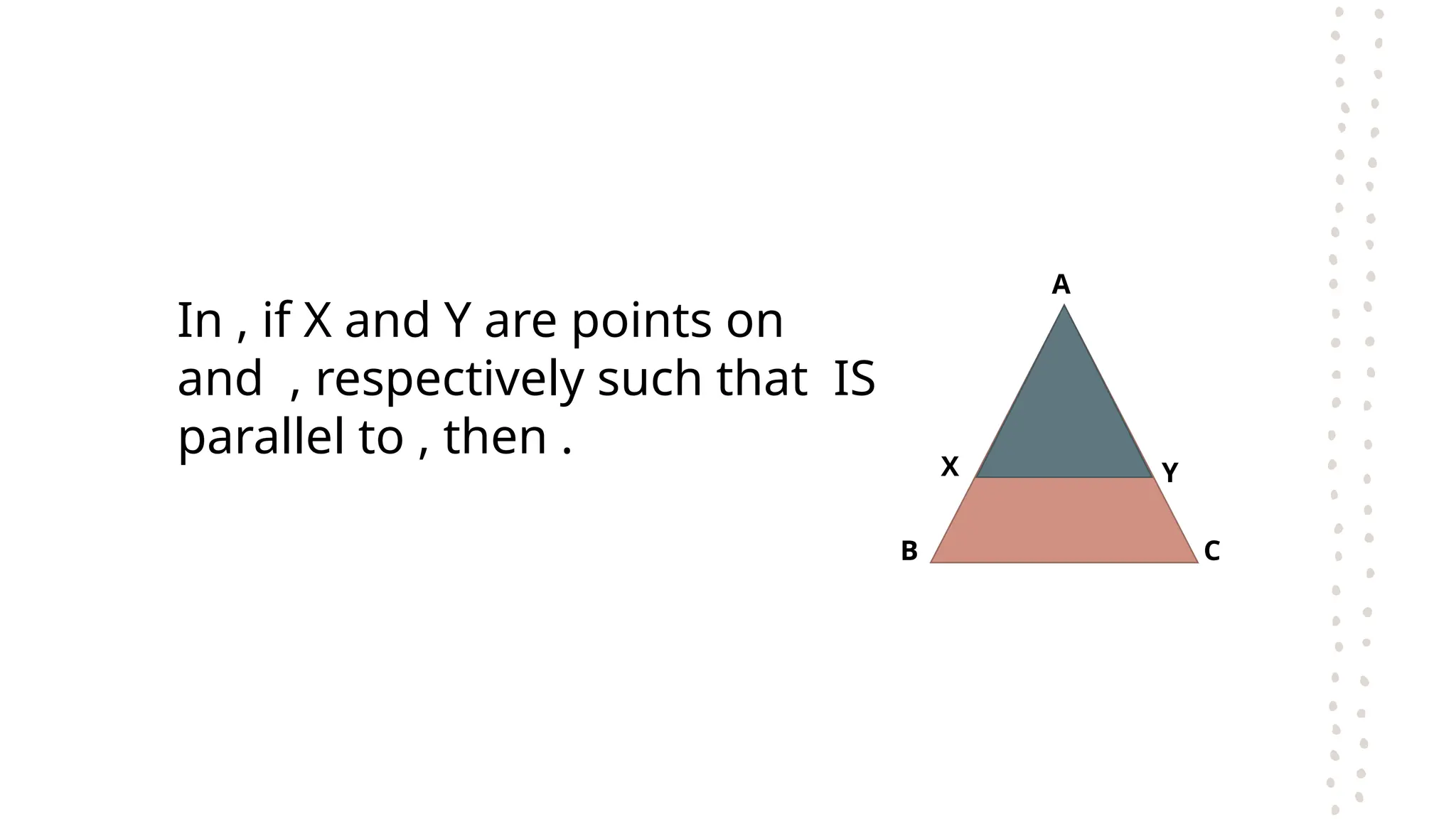The document discusses the fundamental theorems of proportionality, particularly in relation to similar triangles and the basic proportionality theorem (BPT). It explains how to apply these theorems to solve for unknown lengths in triangles by establishing proportions based on corresponding sides and angles. Additionally, it covers the converse of BPT, stating that if a line divides two sides of a triangle proportionally, it is parallel to the third side.