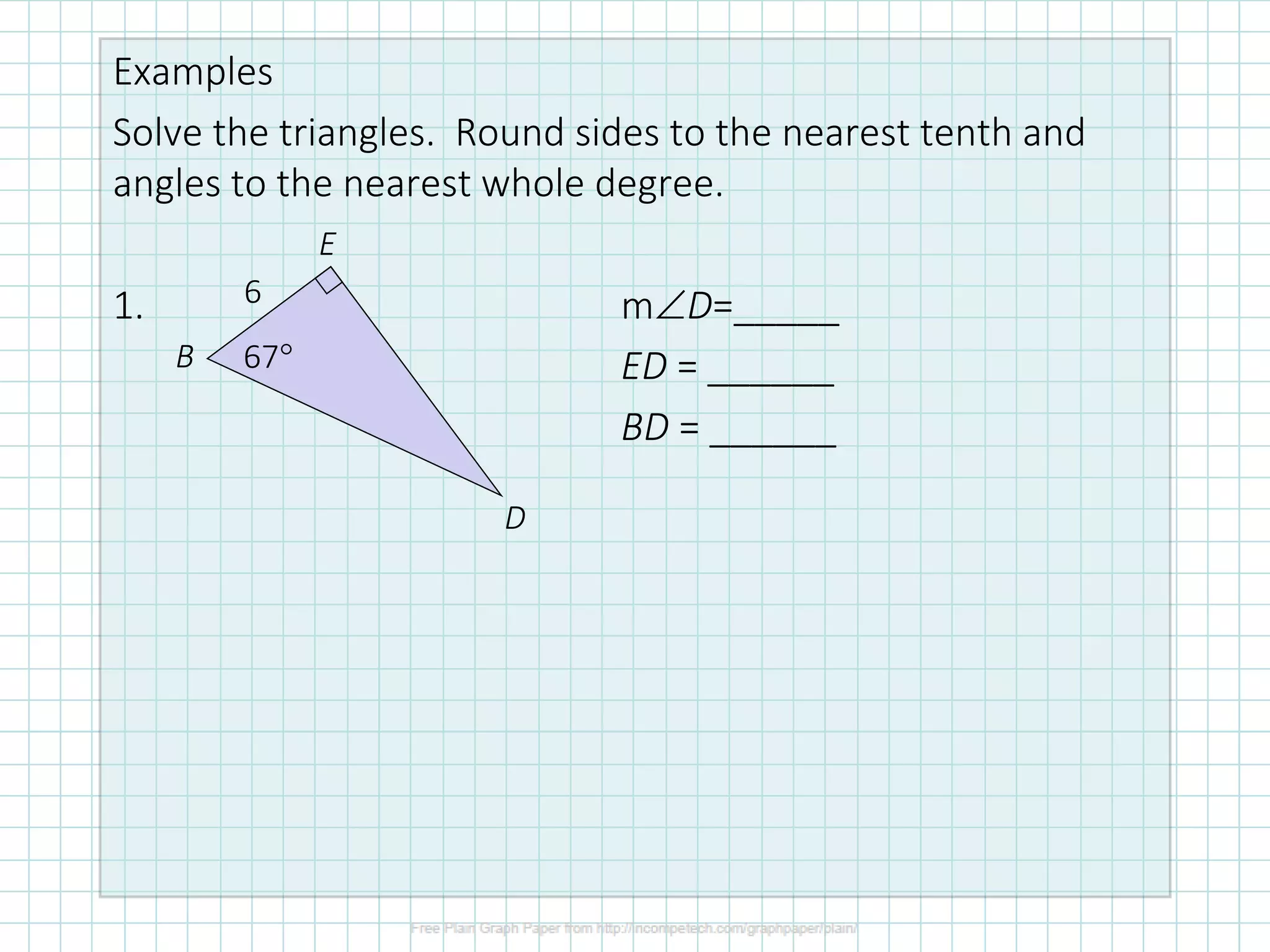
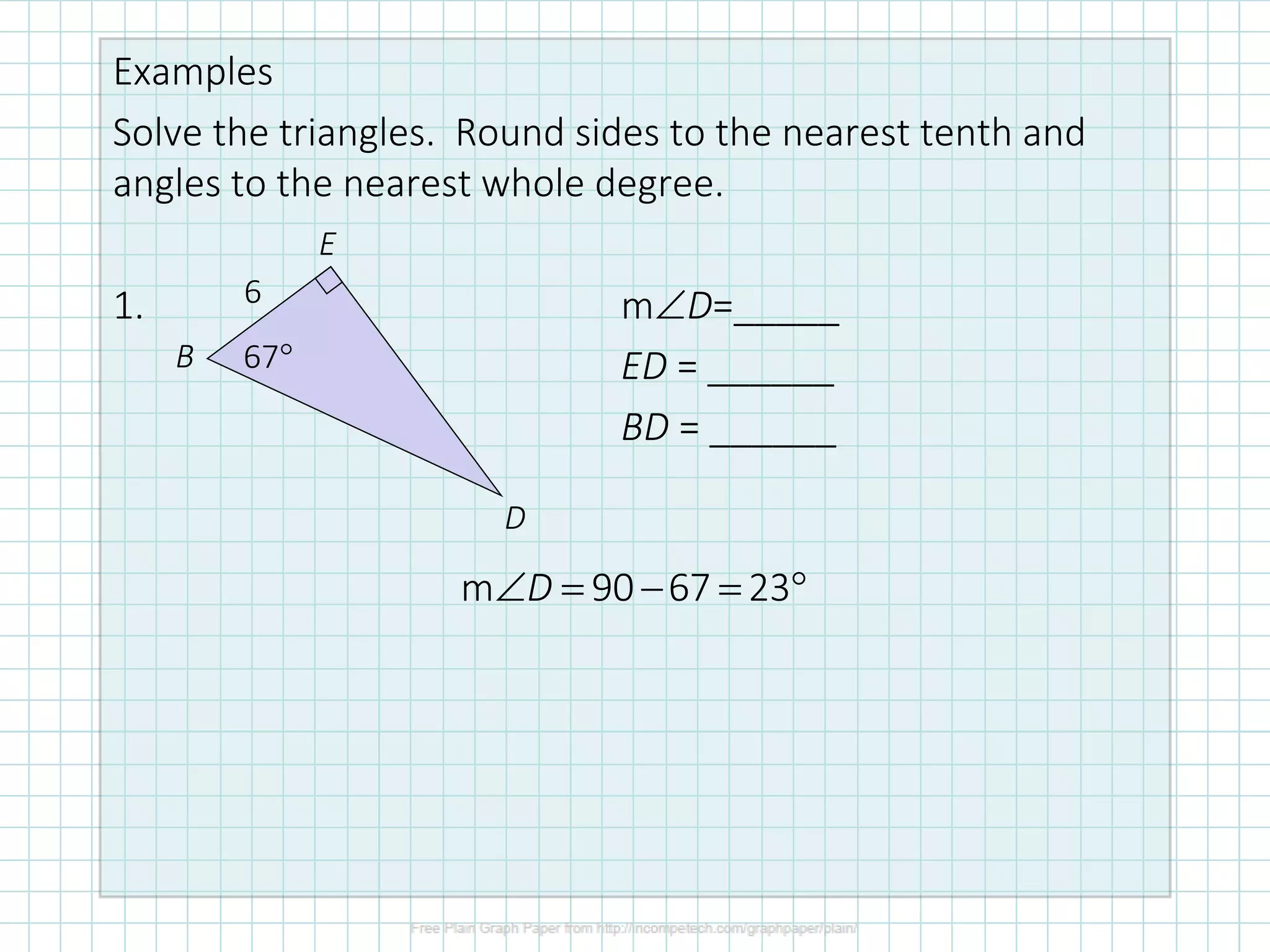
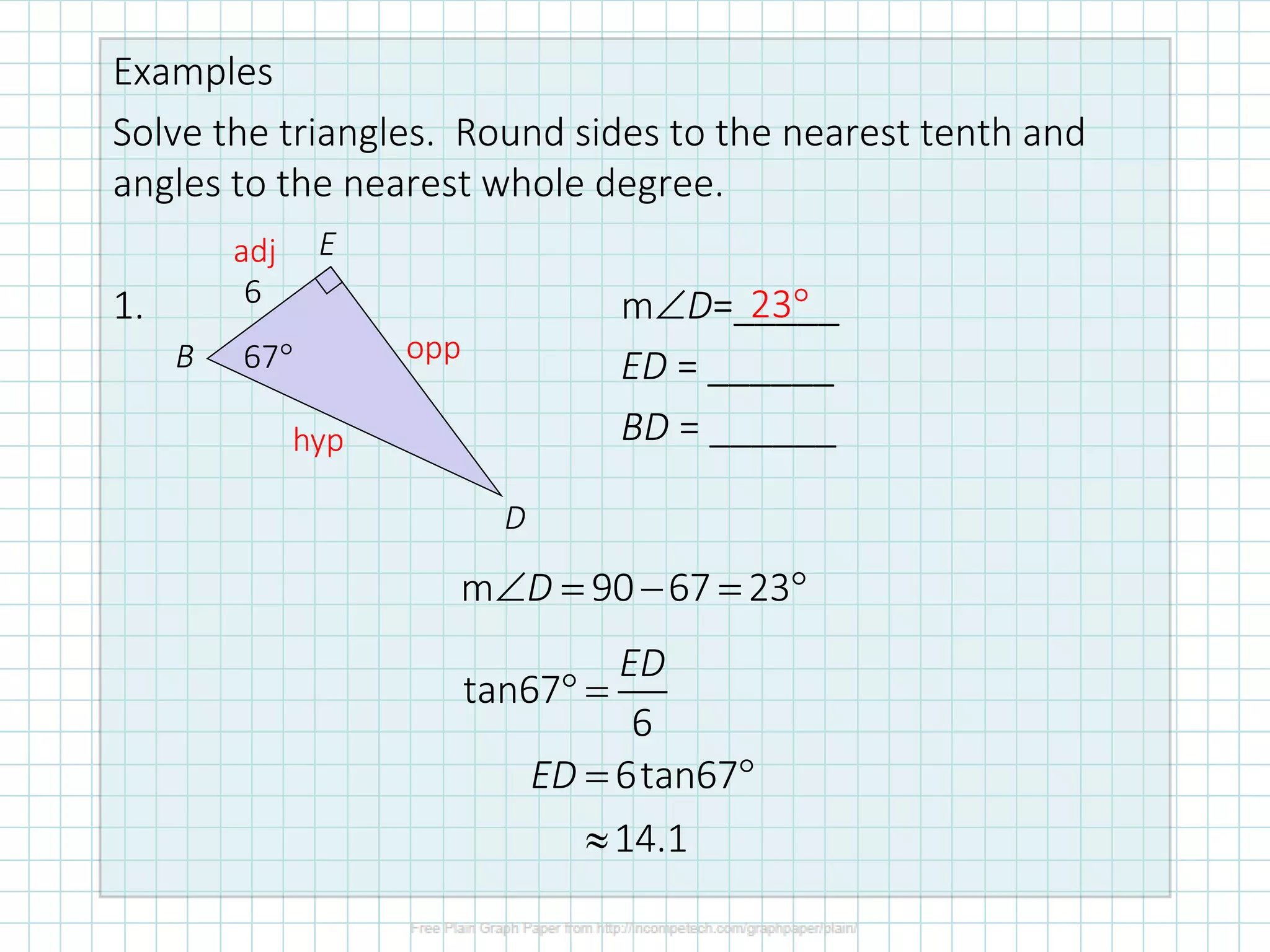
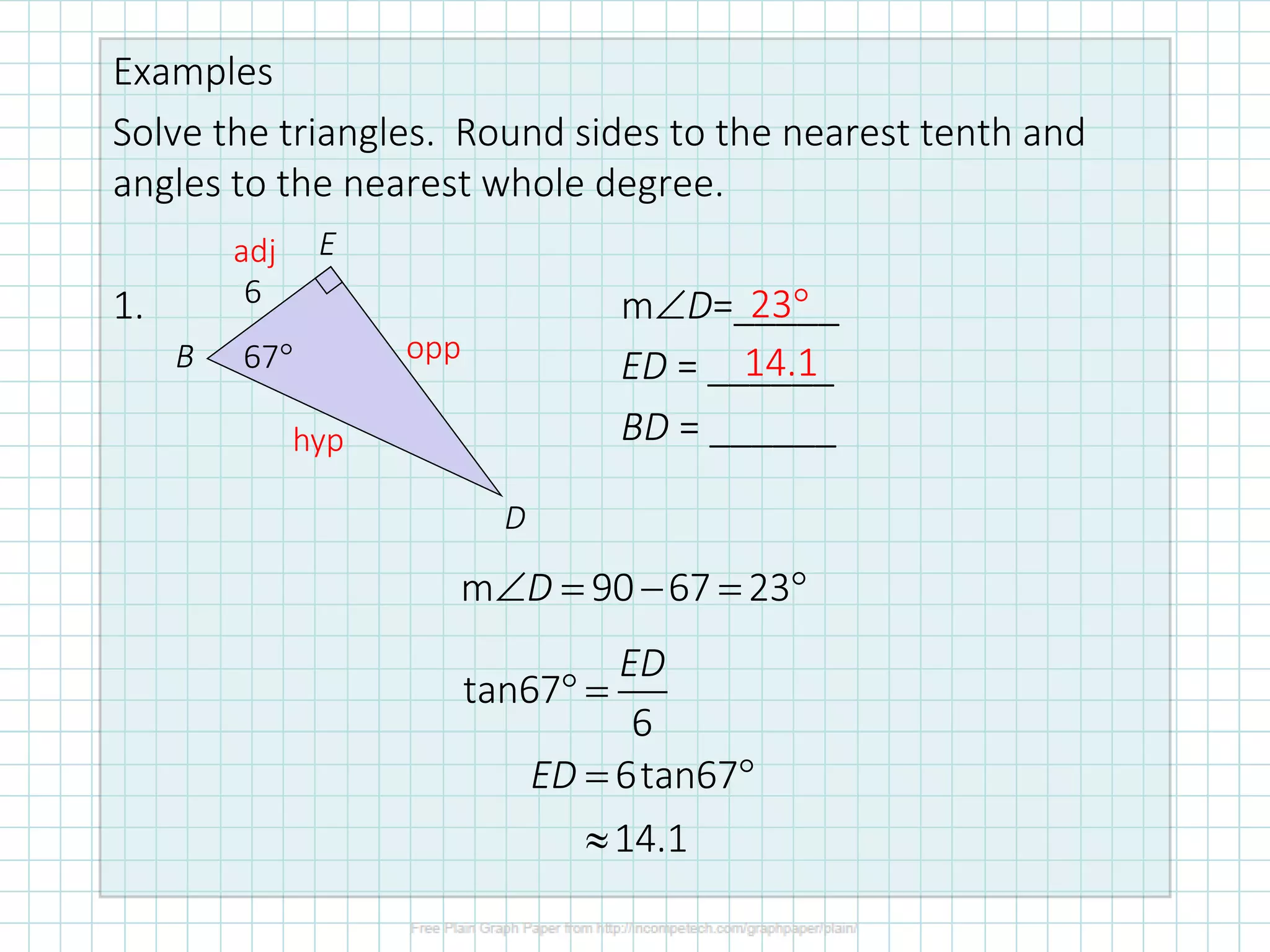
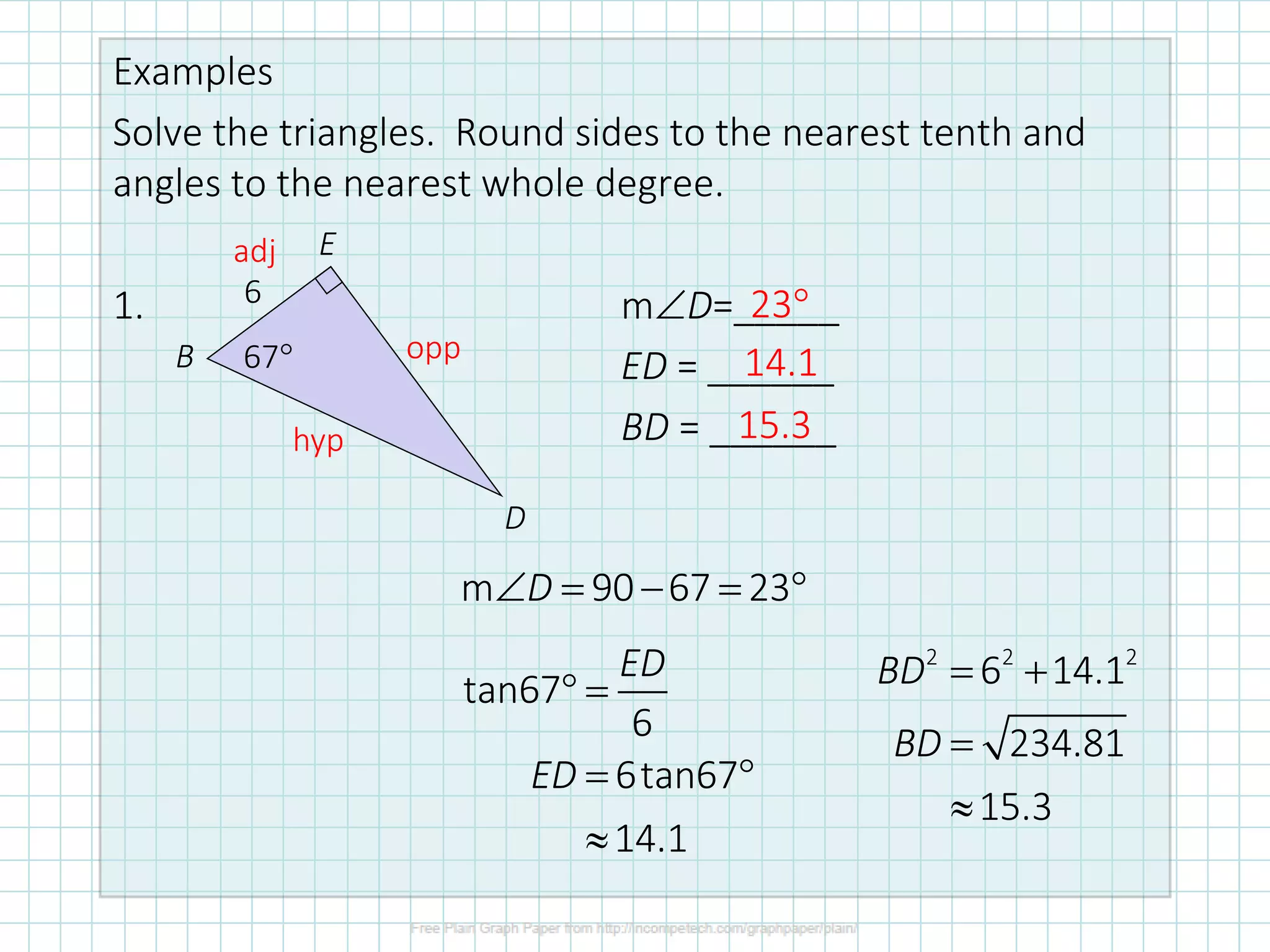
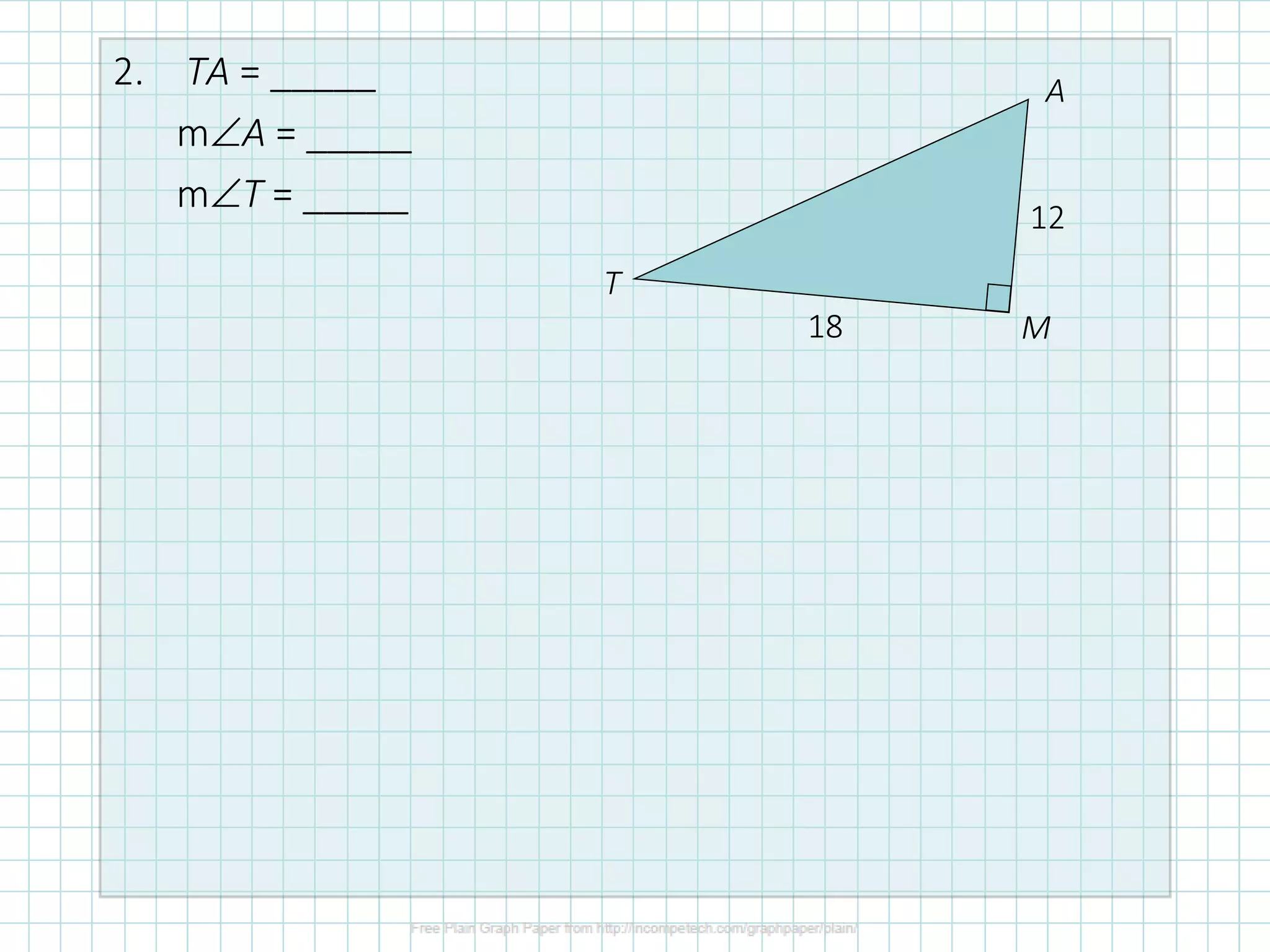
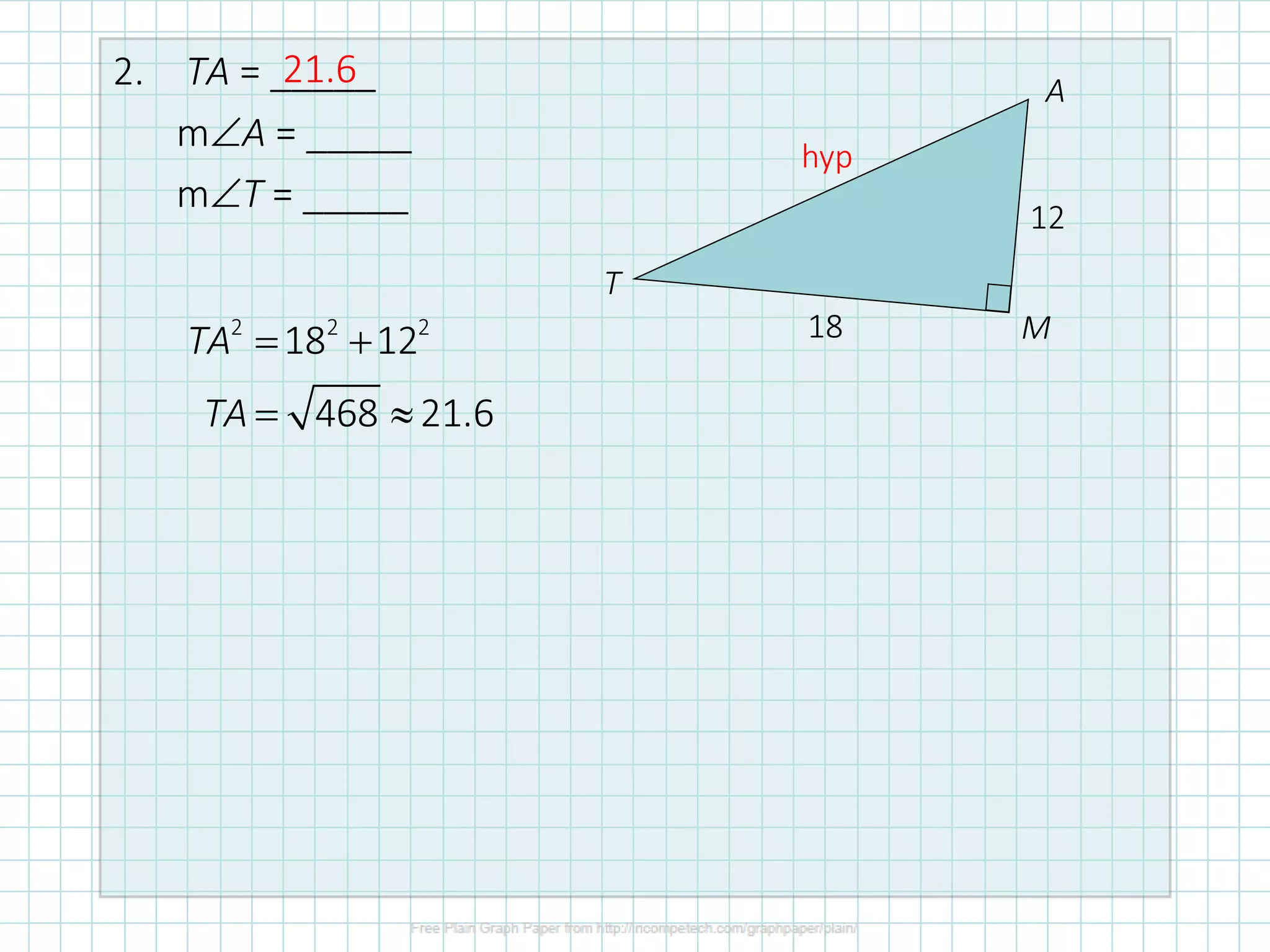
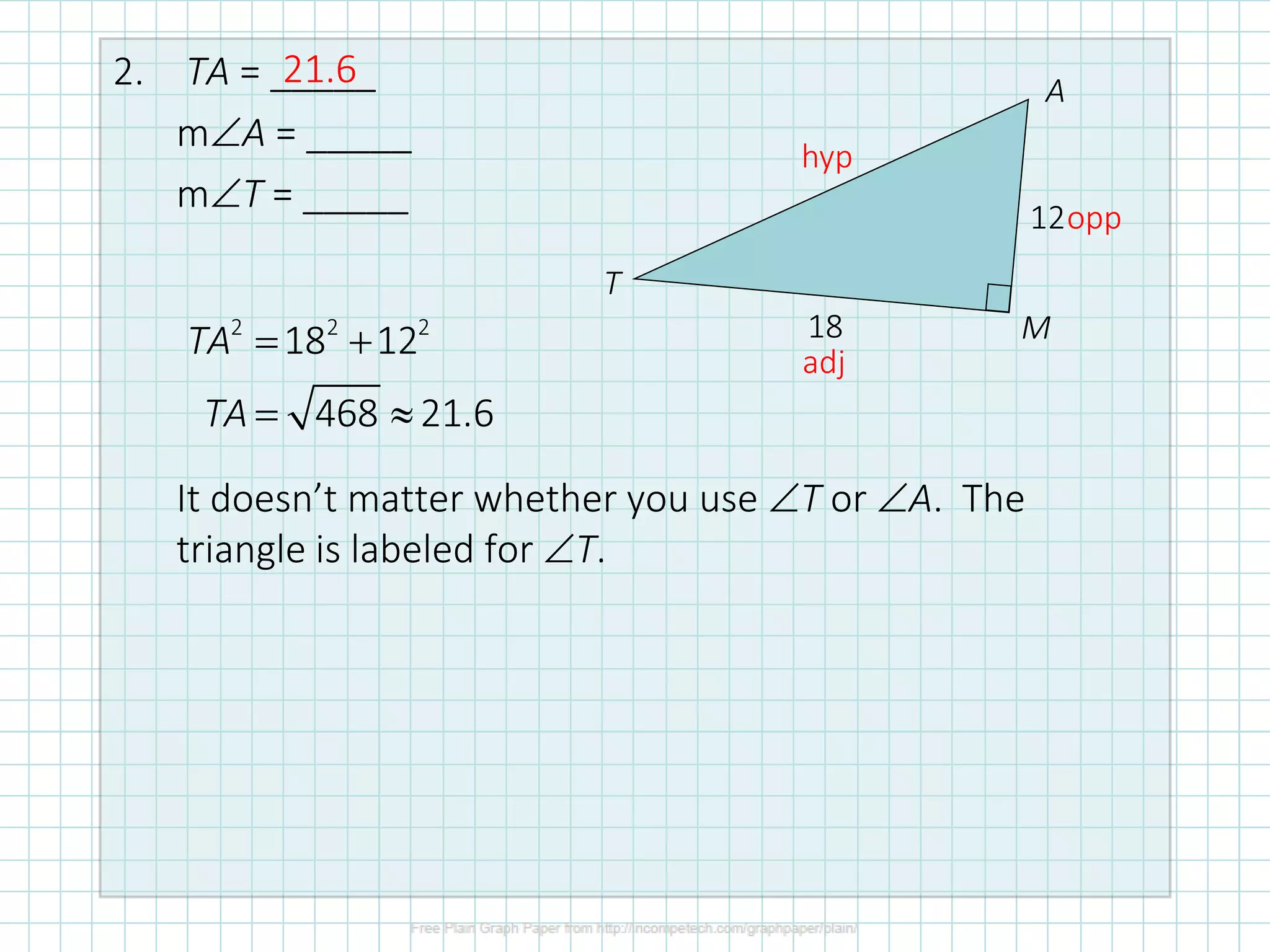
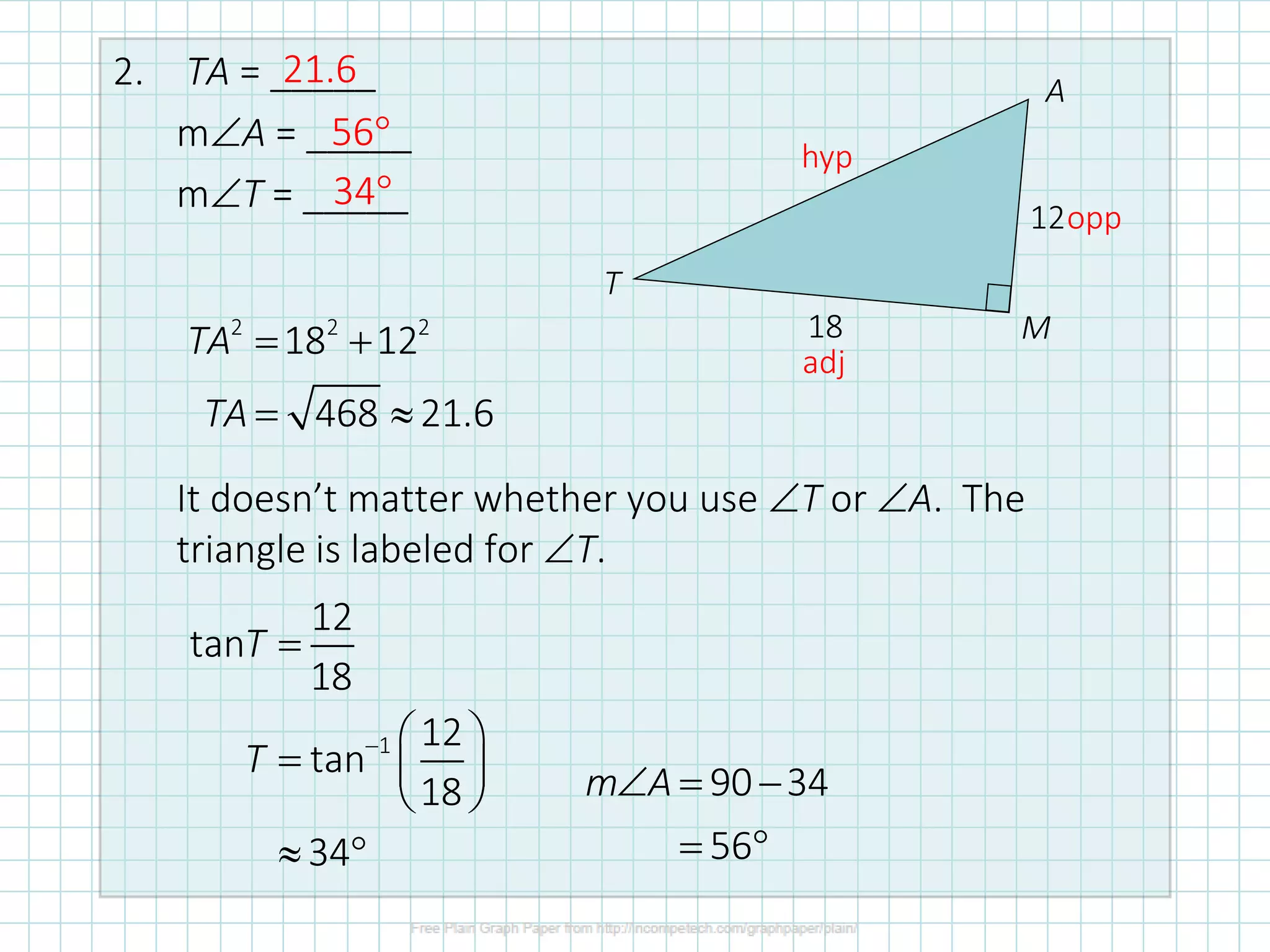
This document discusses how to solve right triangles by finding missing parts. It explains that if an angle and side are given, trigonometric ratios or the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the other parts. If two sides are given, the Pythagorean theorem or trig ratios can determine the remaining side and angle. Examples demonstrate using trigonometric functions like tangent to calculate missing side lengths or angles in right triangles.