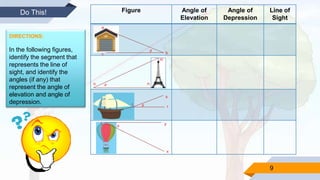
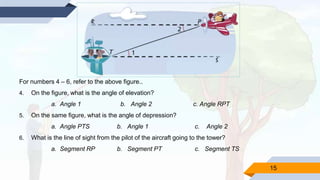
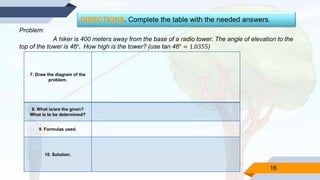
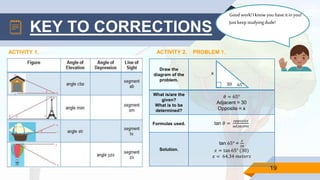
This document provides a strategic intervention material to help students learn about solving real-life problems involving right triangles using trigonometric ratios. It begins with definitions of key terms like line of sight, angle of elevation, and angle of depression. Students are given examples of problems involving these angles and their solutions. Later activities require students to illustrate problem situations, identify given information, formulas used, and solve problems determining unknown angles or distances. The material aims to supplement classroom learning and help students independently practice and understand solving right triangle problems.