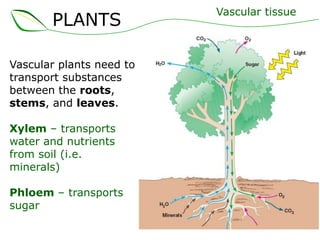
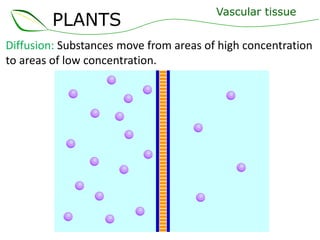
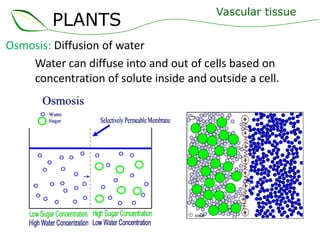
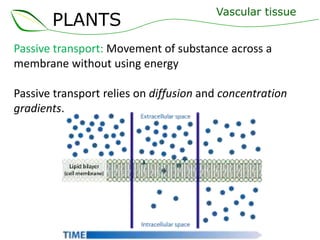
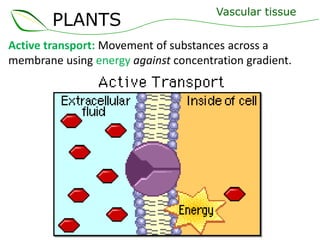
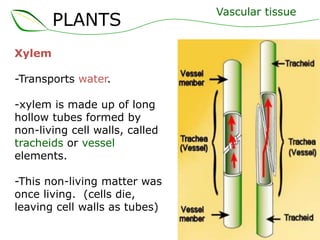
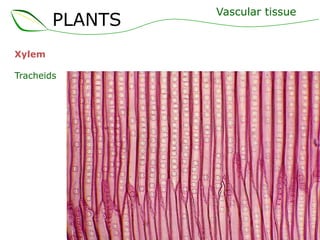
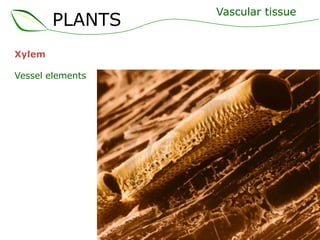
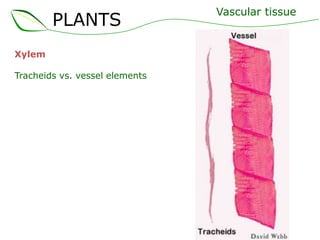
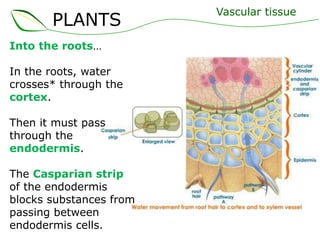
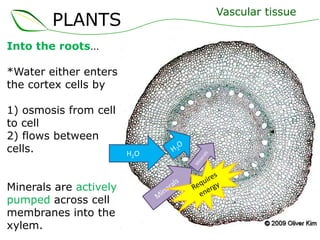
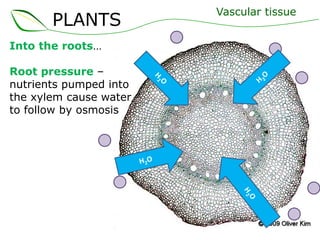
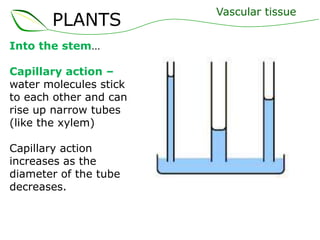
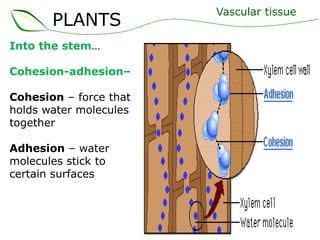
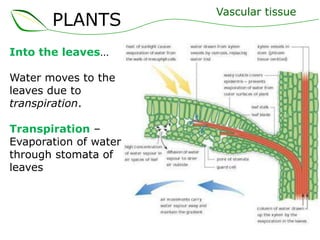
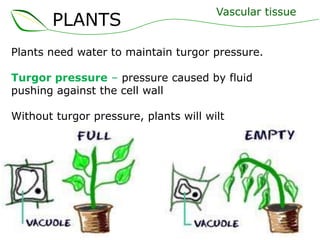
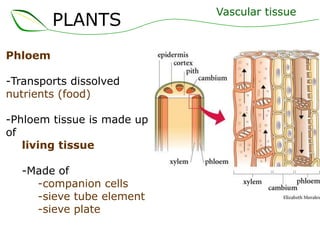
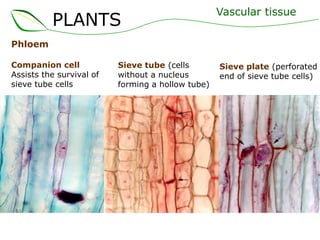
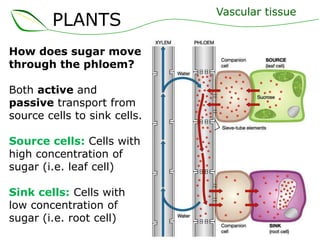
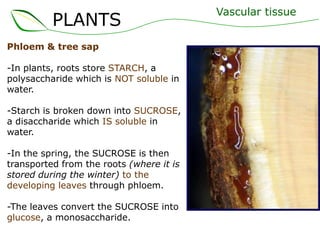
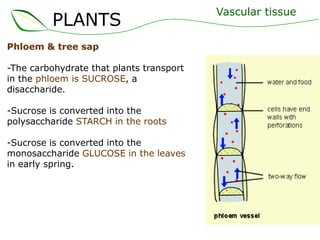
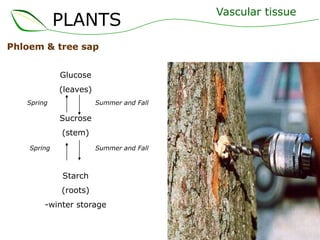
Vascular plants have vascular tissue composed of xylem and phloem that transport water, nutrients and sugars between roots, stems, and leaves. Xylem transports water and minerals up from the roots through hollow tubes called tracheids and vessel elements. Phloem transports sugars made in leaves to all plant parts through sieve tube elements and companion cells. Substances move through vascular tissue via diffusion, osmosis, and active or passive transport across cell membranes according to concentration gradients.