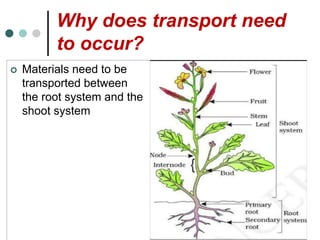
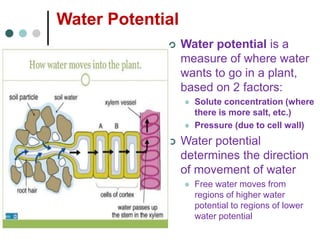
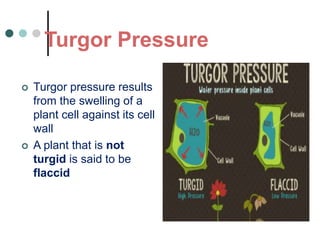
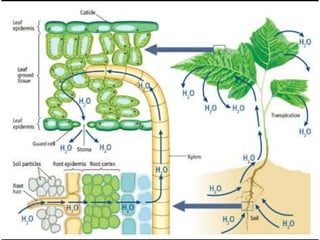
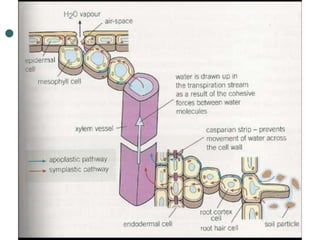
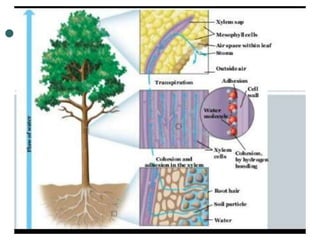
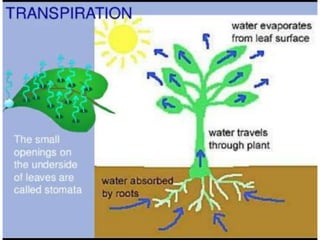
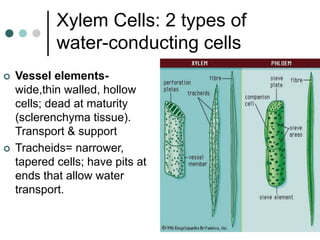
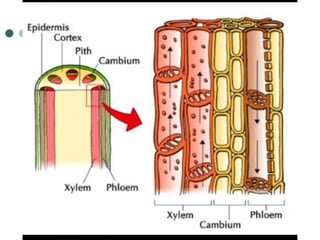
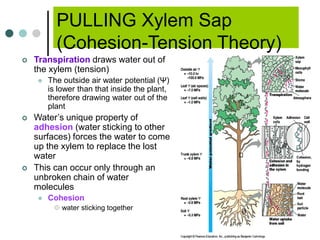
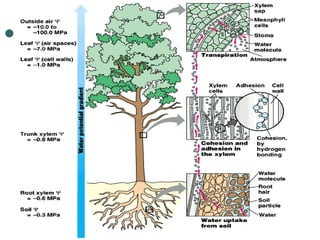
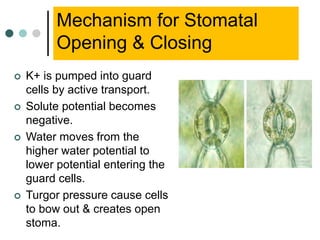
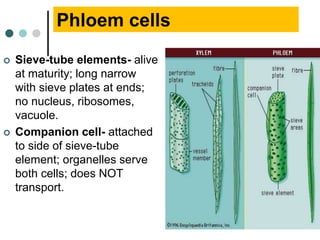
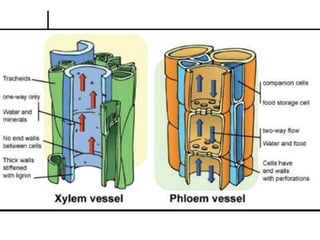
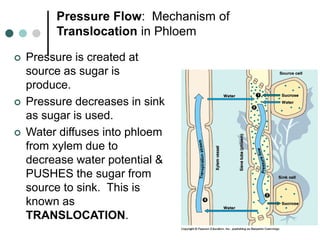
Transport in plants occurs through two main tissues: xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals up from the roots through the stem and leaves using a combination of root pressure and transpiration pull. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from leaves, which creates a negative water potential that pulls water up through the xylem vessels and tracheids. Phloem transports sugars made during photosynthesis from leaves to areas of growth or storage through pressure flow, where sugars move from high pressure source tissues to low pressure sink tissues.