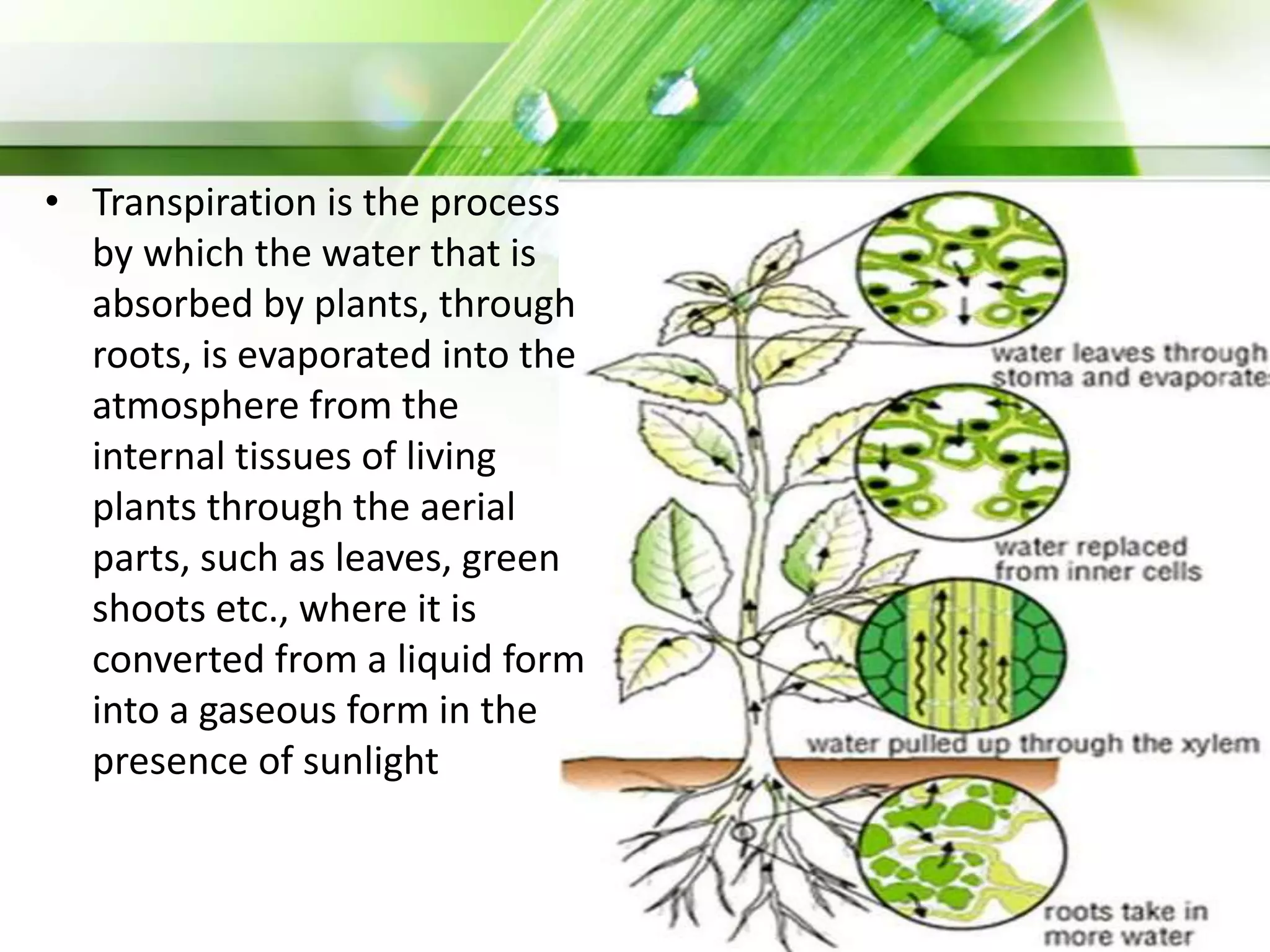
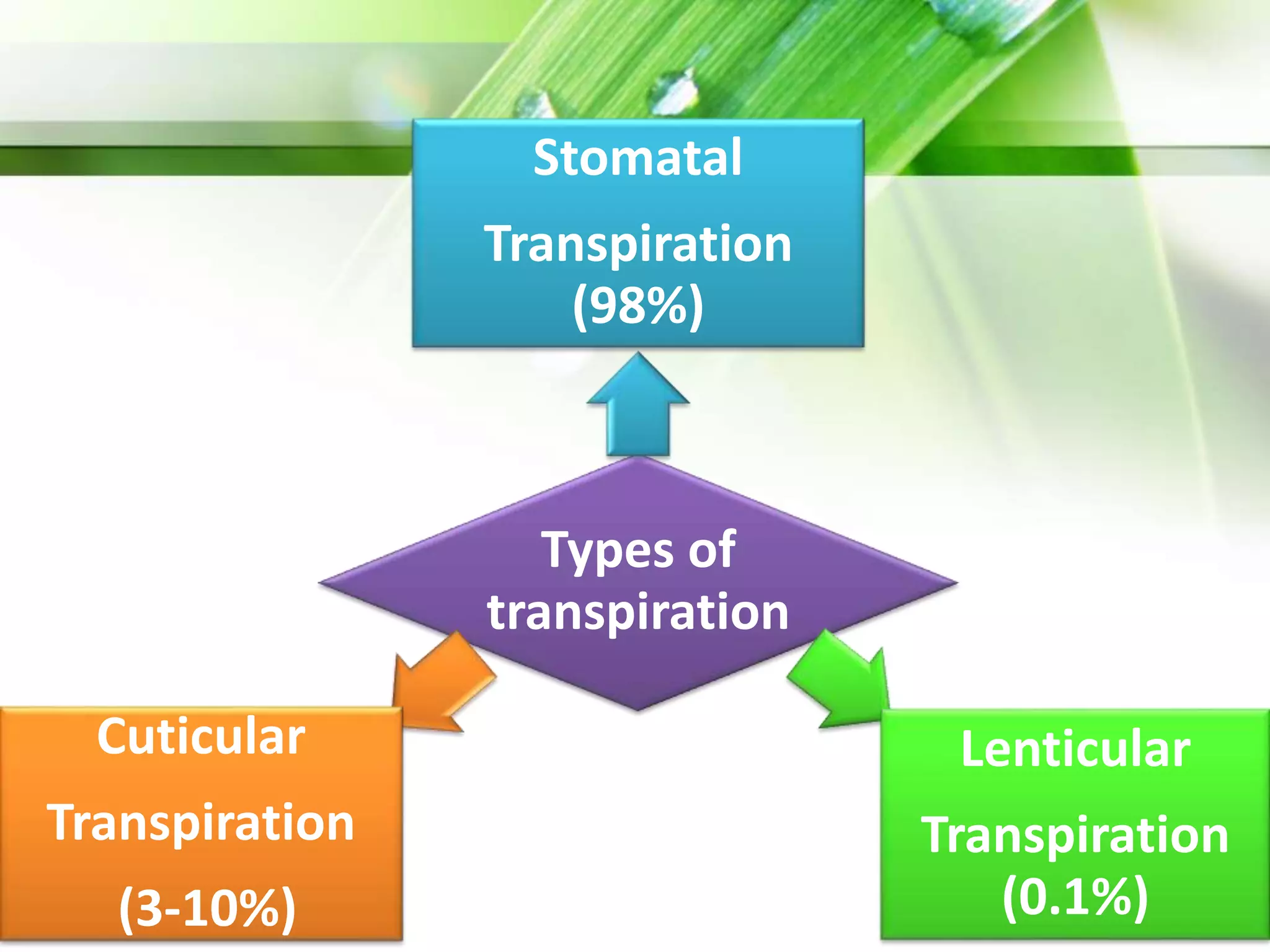
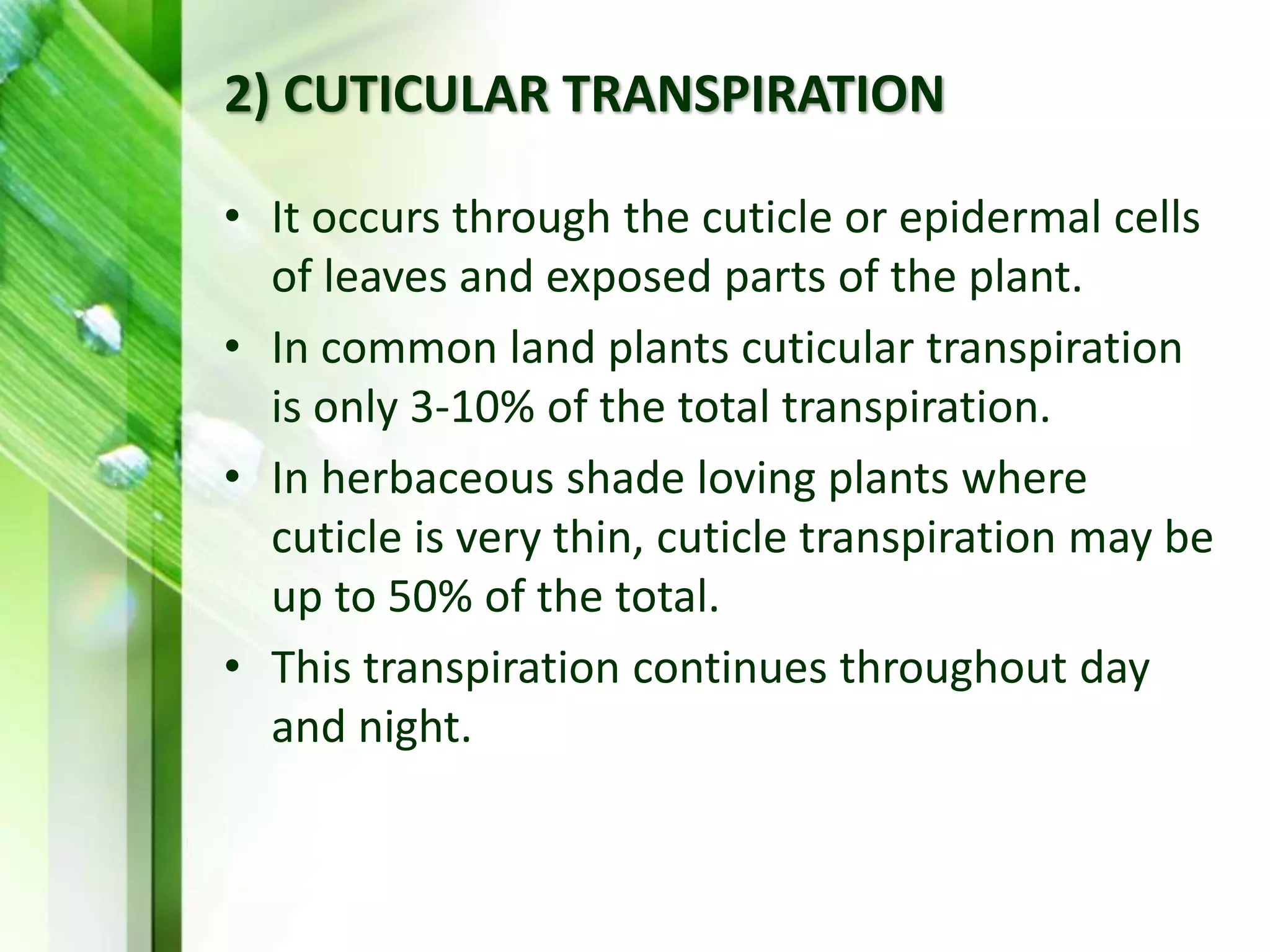
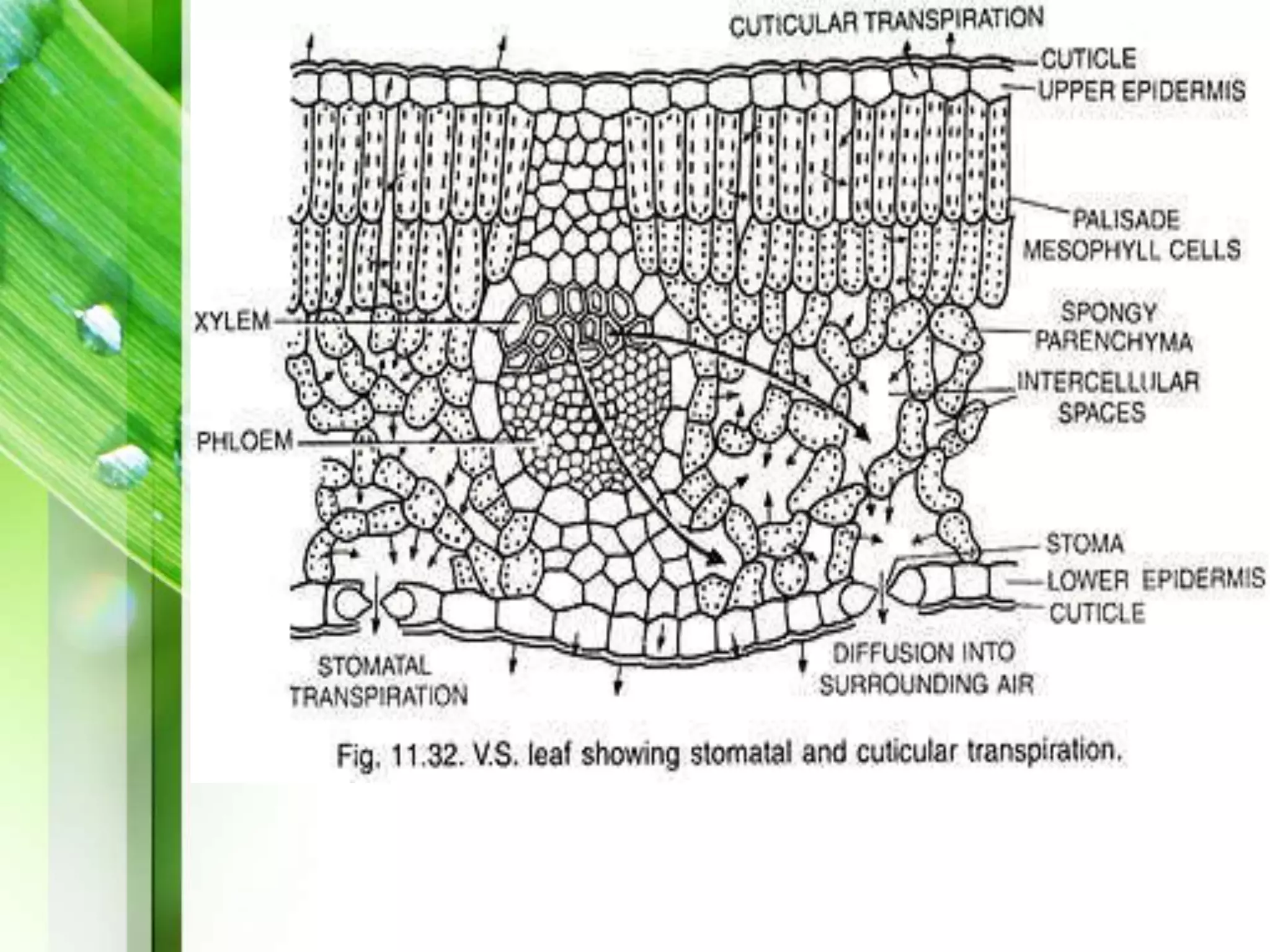
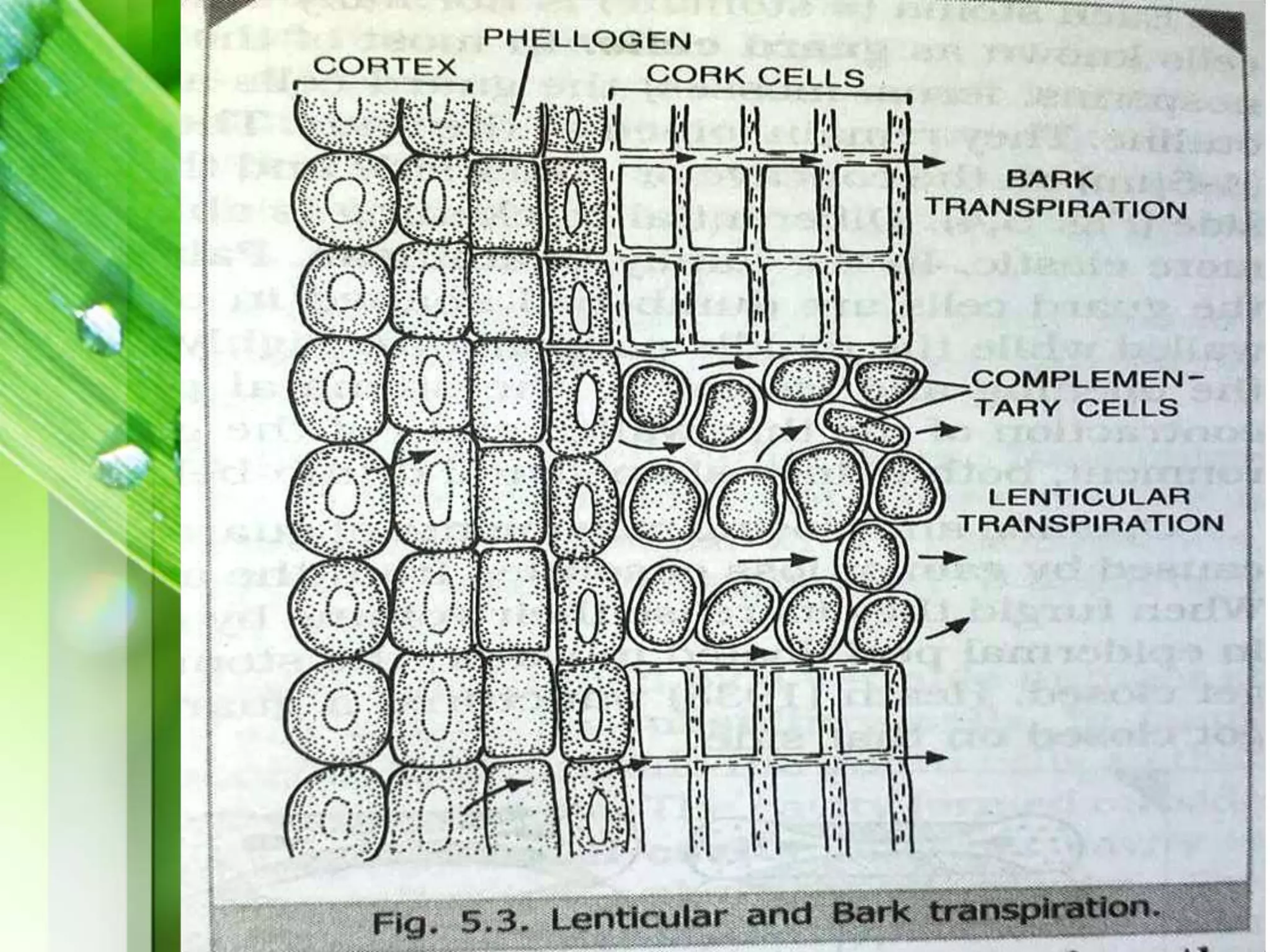
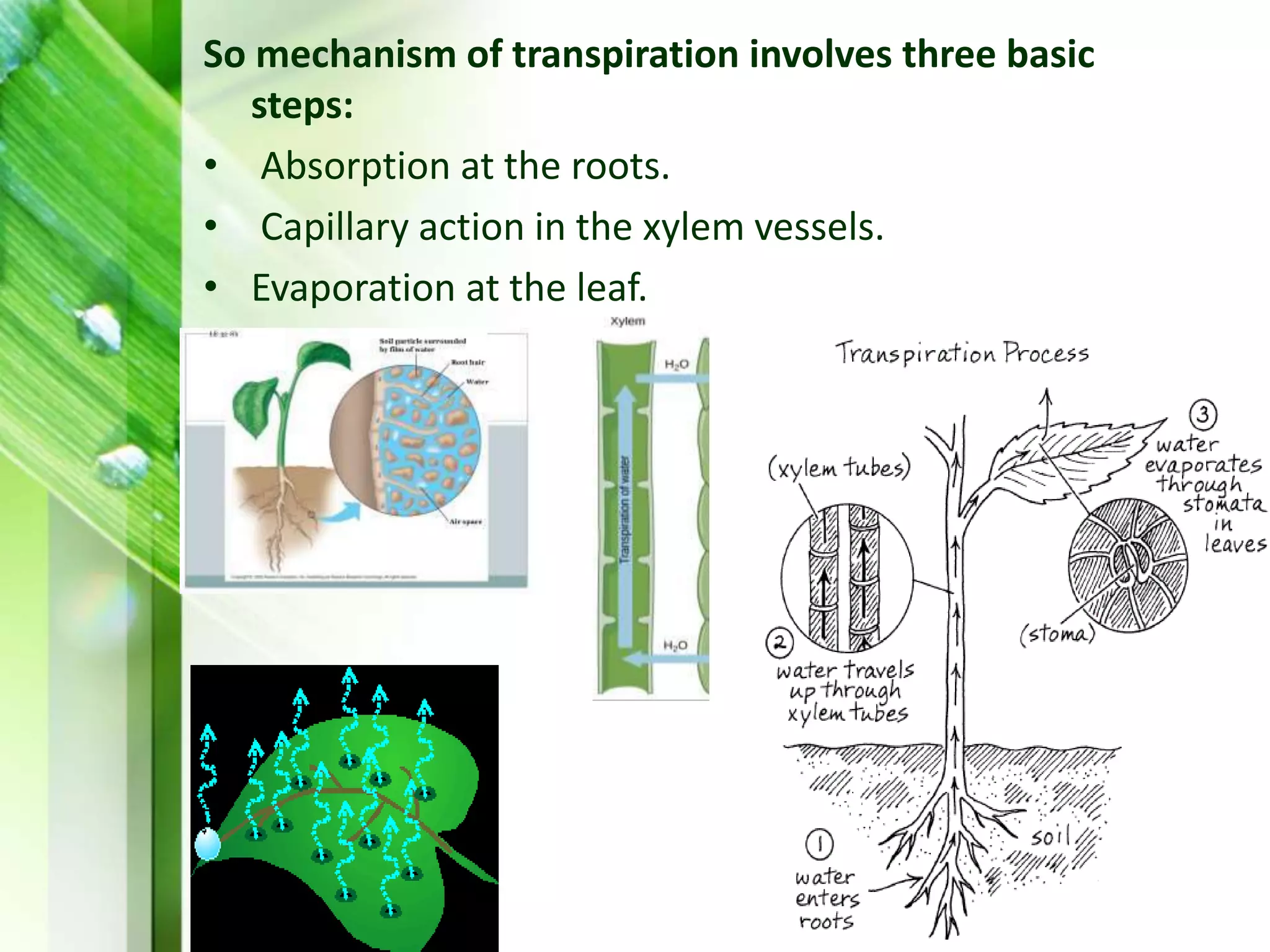
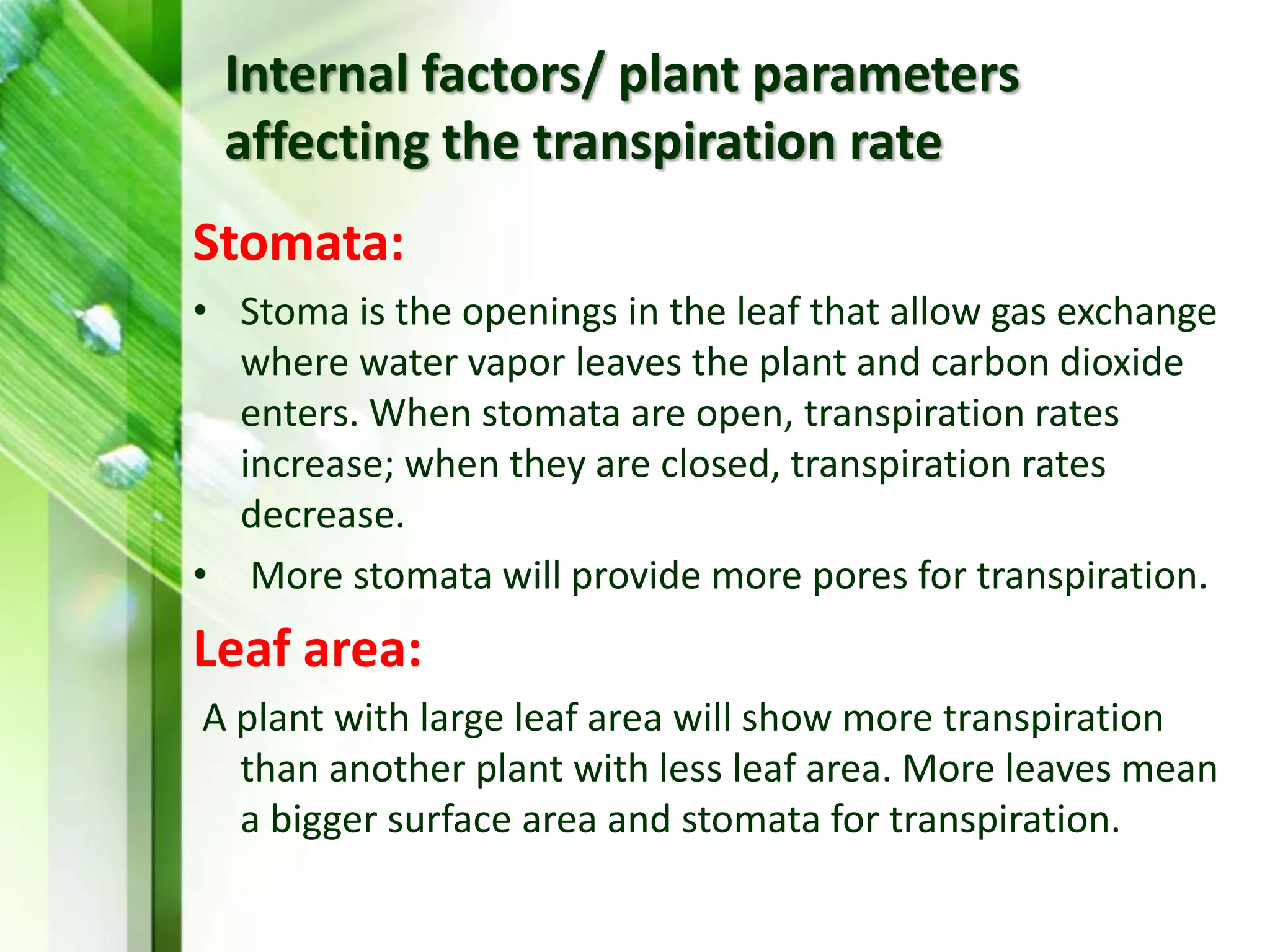
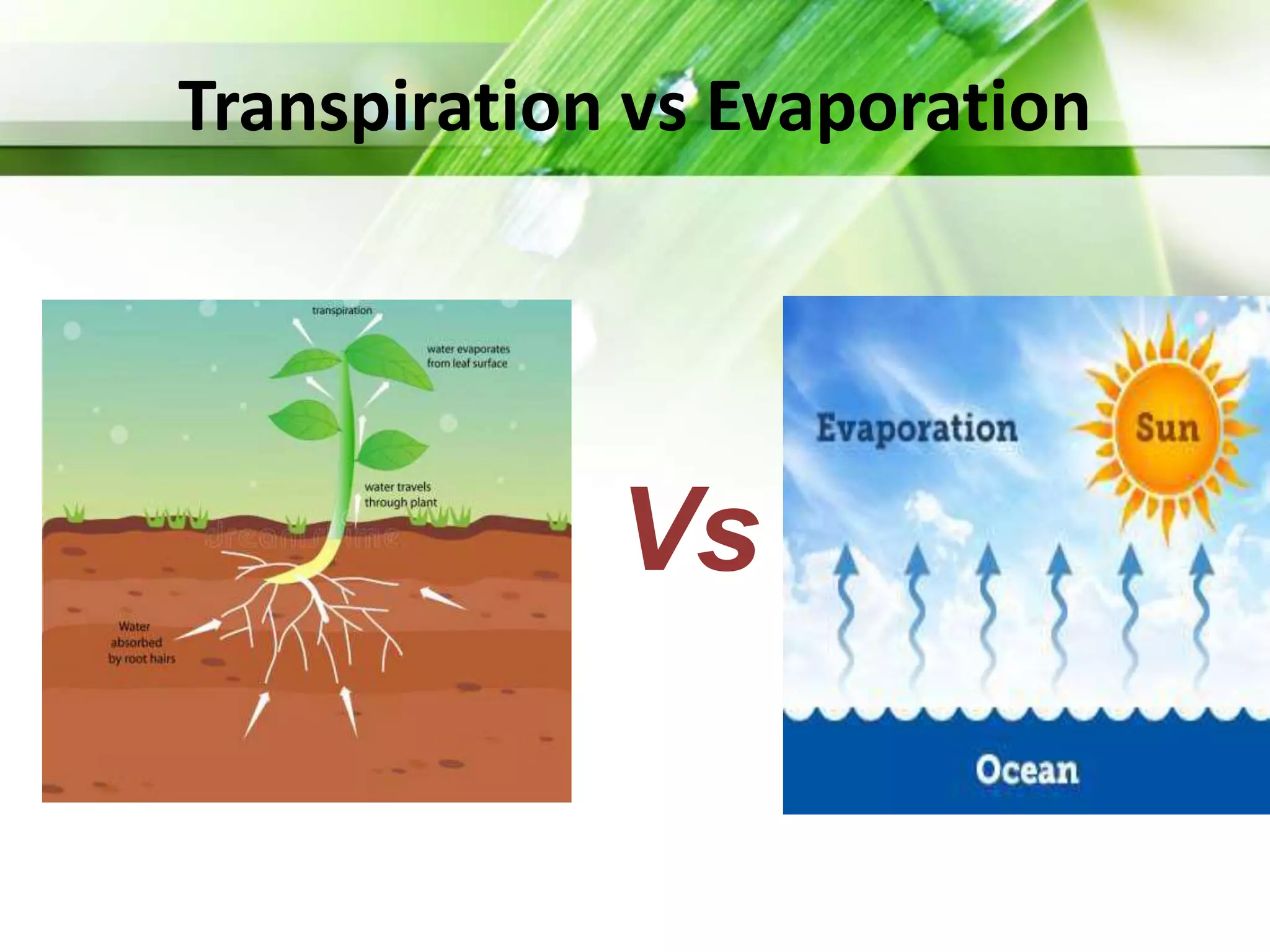
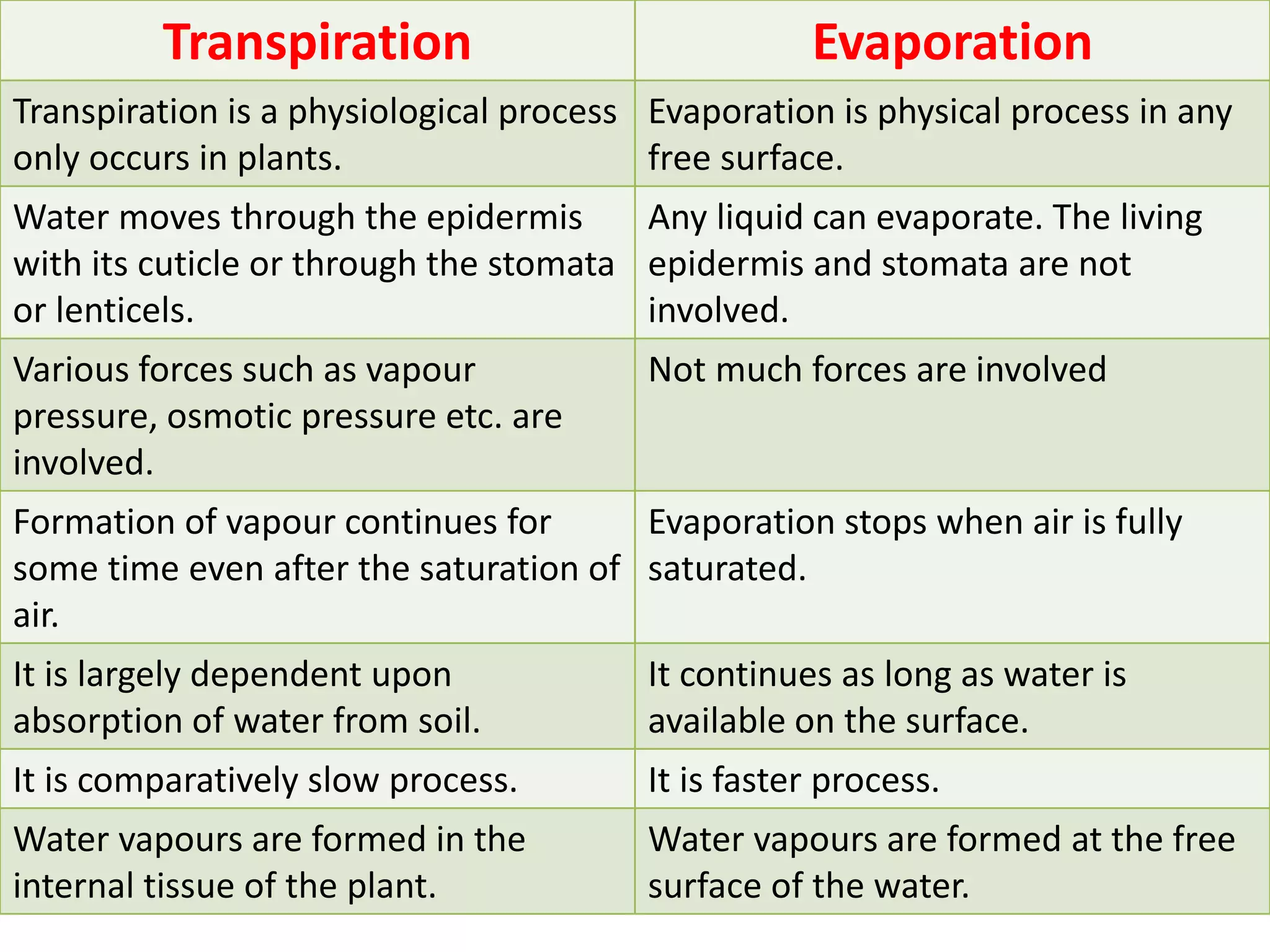
Transpiration is the process of water vapor loss from plants, constituting 98-99% of the water absorbed and significantly influencing atmospheric moisture. It occurs through three main types: stomatal (98%), cuticular (3-10%), and lenticular (0.1%), with stomatal transpiration being the most crucial for gas exchange and cooling. Factors affecting transpiration rates include internal aspects like stomatal density and leaf area, and external elements such as light intensity, humidity, temperature, and wind, highlighting its essential role in plant health and metabolic processes.