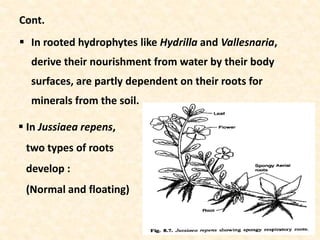
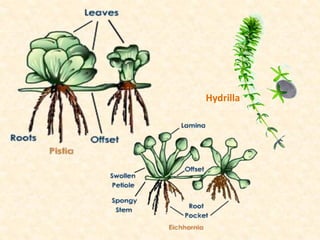
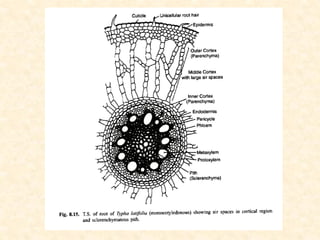
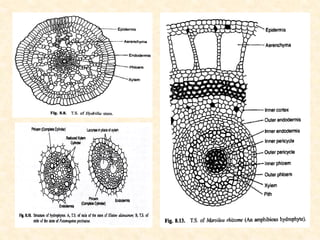
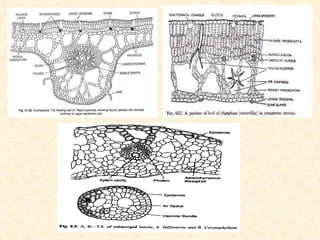
The document discusses hydrophytes, or water plants, which are categorized based on their growth adaptations in aquatic environments. It outlines various types of hydrophytes—free-floating, rooted with floating leaves, submerged, and emergent—along with their morphological, anatomical, and physiological adaptations for survival in water. Additionally, it highlights the factors that influence their growth, such as water temperature, osmotic concentration, and toxicity.