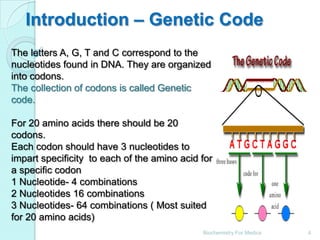
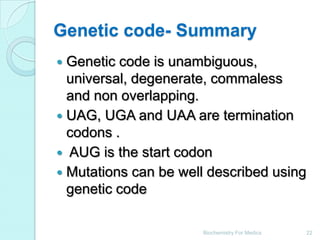
The genetic code is a dictionary that translates nucleotide sequences into amino acid sequences. It is composed of 64 codons that are read in groups of three nucleotides. The genetic code is universal, unambiguous, redundant, and non-overlapping. It specifies 20 standard amino acids through 61 codons, while 3 codons are stop signals that terminate protein synthesis. The code allows for wobbling in base pairing at the third position of codons, increasing decoding efficiency. Mutations can alter protein sequences through changes to codons.