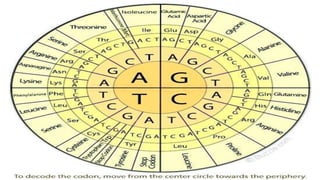
The genetic code refers to the sequence of nitrogenous bases in mRNA that encode information for protein synthesis. It consists of 64 codons made up of three nucleotide bases that dictate which of 20 amino acids will be incorporated into a growing polypeptide chain or signal its termination. Key events in discovering the genetic code included determining DNA's structure and identifying that codons encode amino acids. There are sense codons that specify amino acids, start codons that initiate translation, and stop codons that terminate protein synthesis. The genetic code is nearly universal and has several important properties including being triplet-based, non-overlapping, and degenerate.