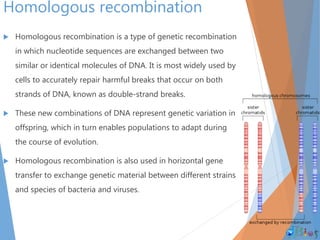
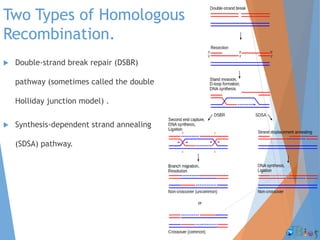
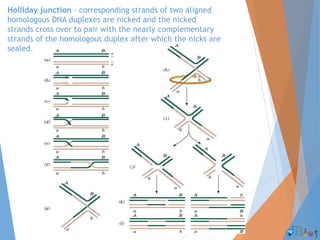
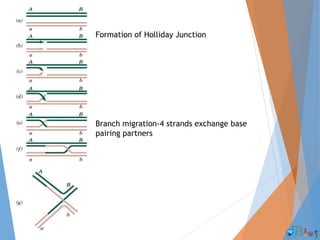
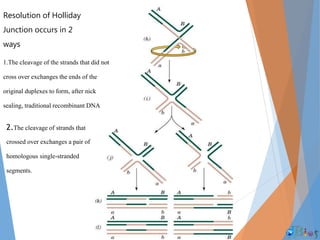
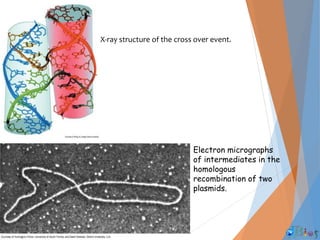
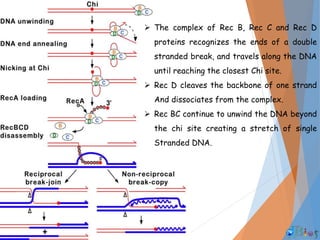
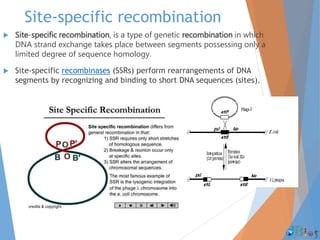
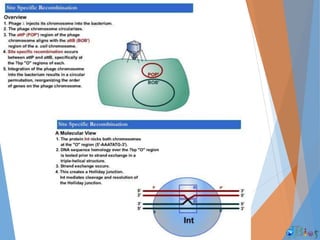
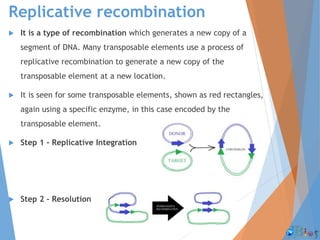
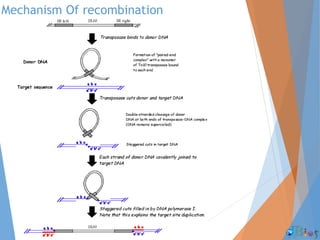
Genetic recombination involves the breaking and rejoining of DNA to form new combinations of genes. It occurs primarily during meiosis through several types of recombination, including homologous recombination where DNA exchanges occur between similar DNA molecules. This increases genetic diversity and allows for traits to be mixed. Recombination benefits populations by generating variety among offspring and allowing deleterious genes to be removed without losing the entire chromosome. It has applications in cloning, mapping genes, and making transgenic organisms.