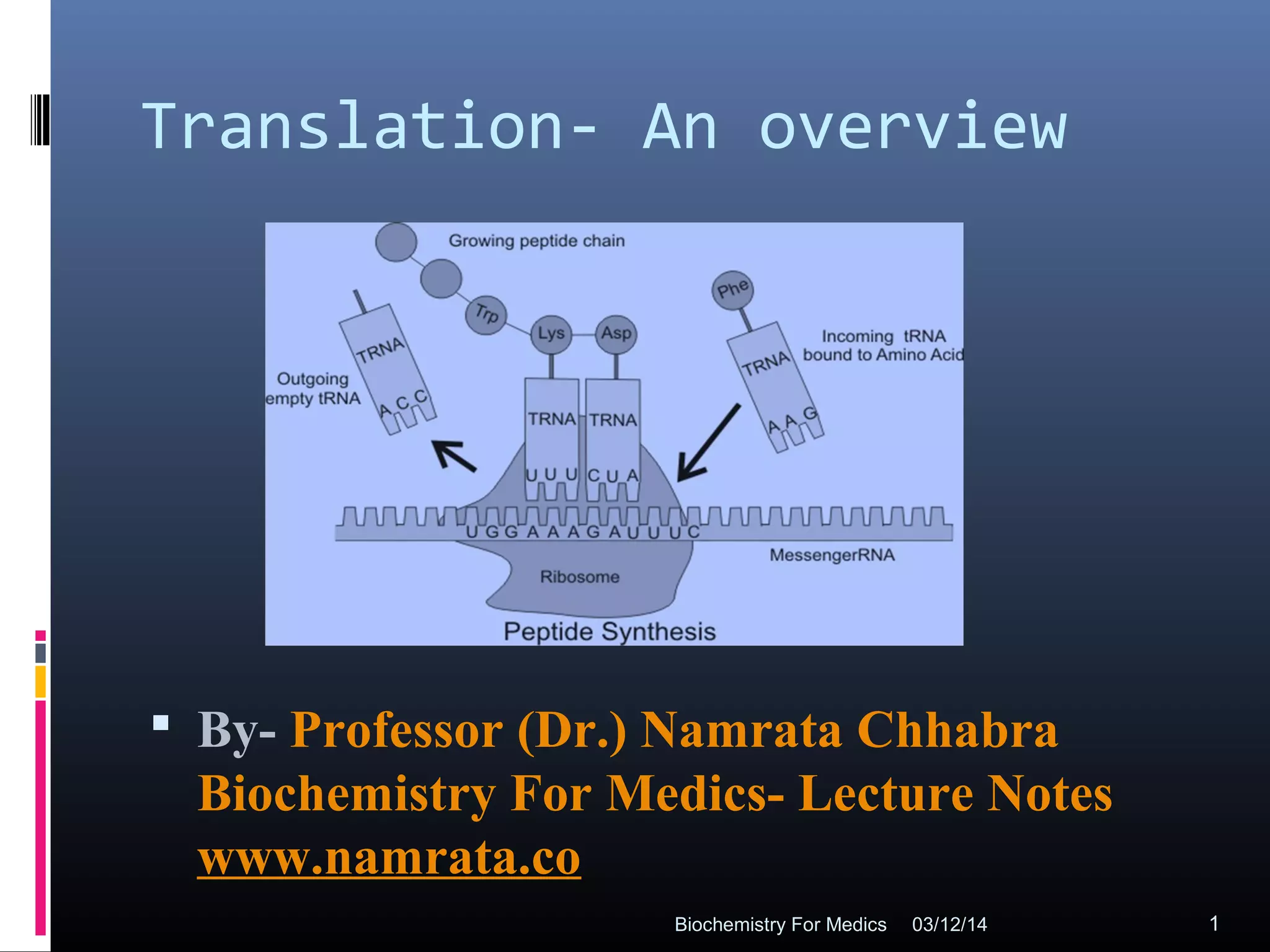
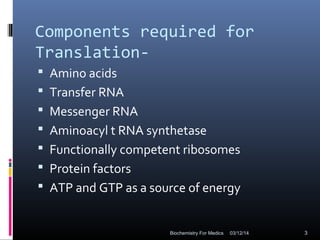
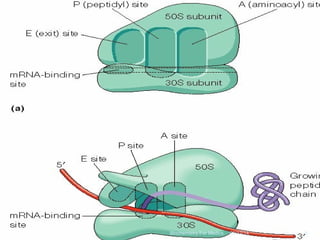
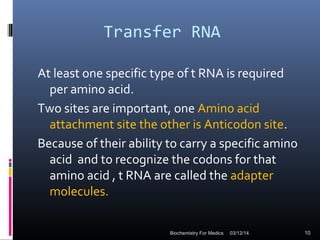
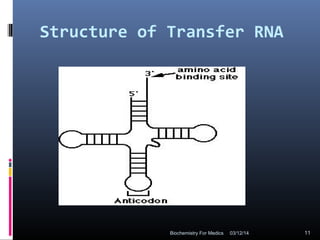
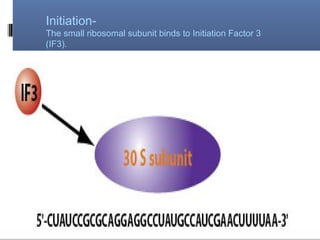
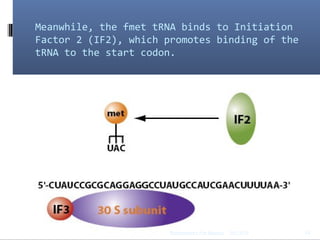
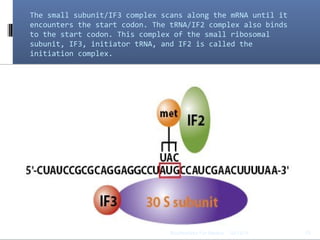
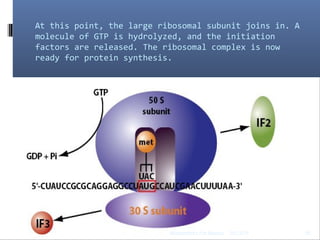
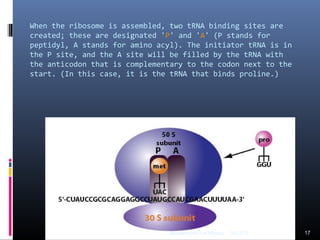
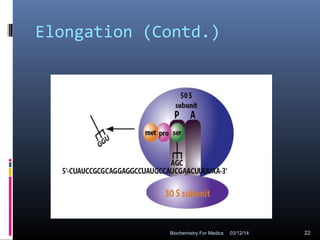
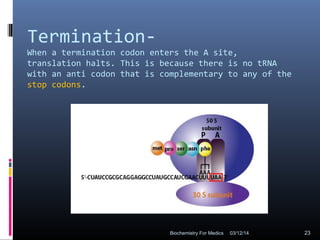
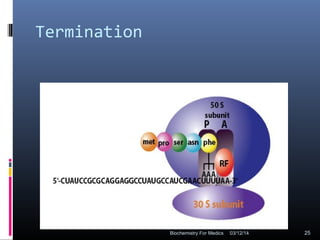
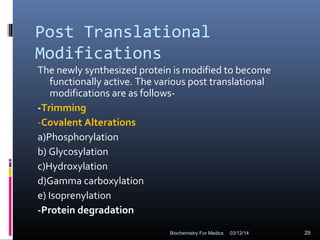
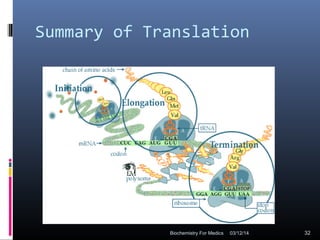
Translation is the process by which the genetic code carried by mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the small and large ribosomal subunits assemble around the mRNA along with initiator tRNA and other factors. In elongation, tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons, and peptide bonds form between them. Termination occurs when a stop codon enters the A site and causes the release of the completed protein chain.