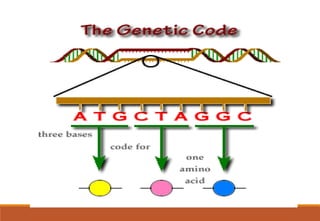
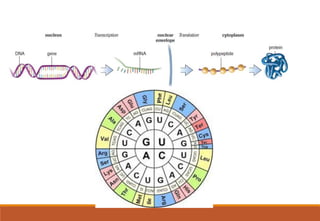
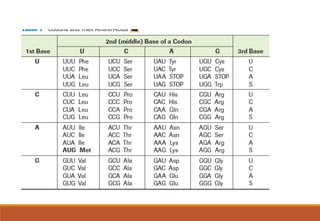
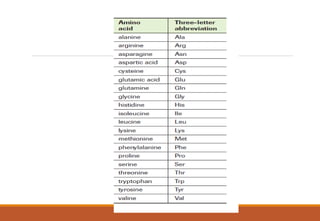
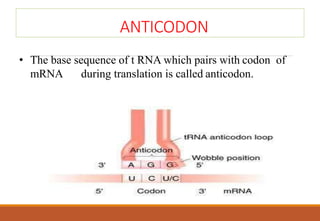
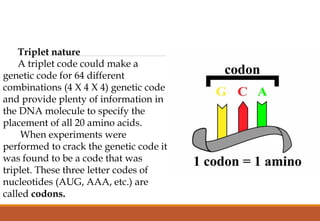
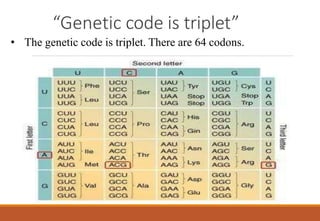
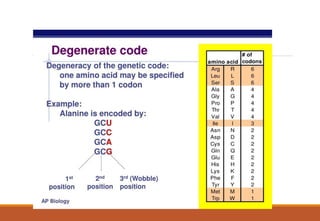
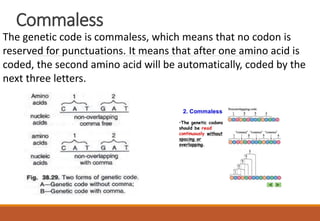
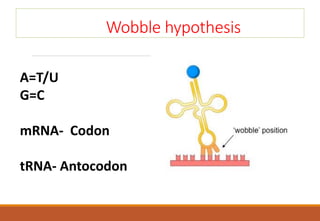
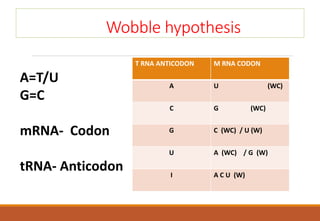
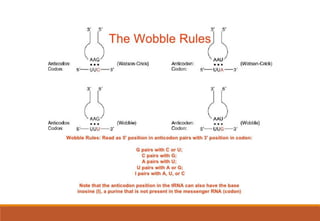
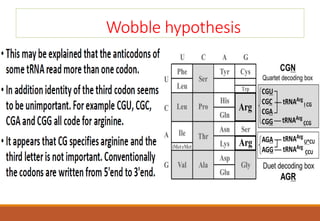
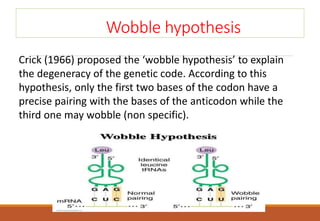
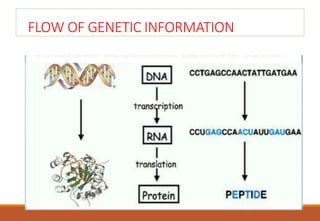
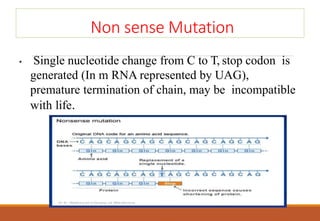
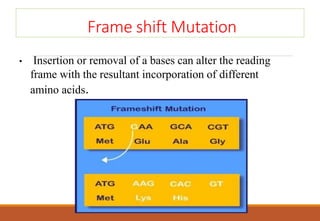
The genetic code is a system that translates nucleotide sequences in DNA and RNA into proteins, consisting of 64 codons made up of three nucleotides each, with 61 codons coding for 20 amino acids and 3 as stop codons. It has characteristics such as being triplet, comma-less, and universal, allowing for degeneration, where multiple codons can code for the same amino acid. The document also discusses mutations that can occur in this code, including silent, missense, nonsense, and frame shift mutations.