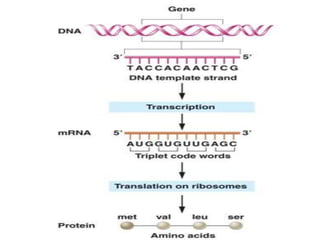
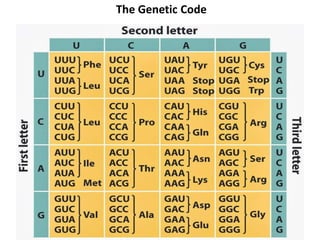
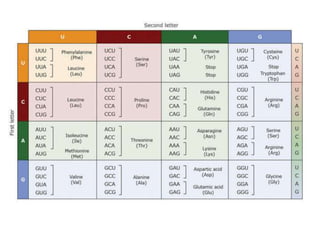
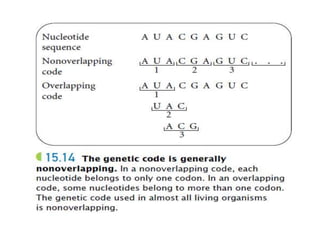
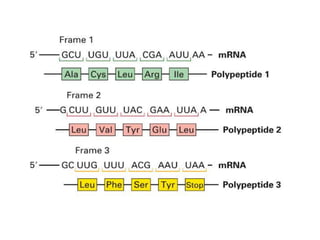
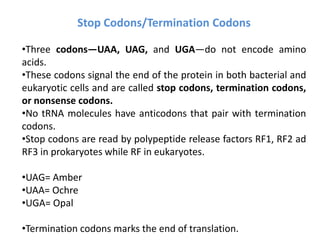
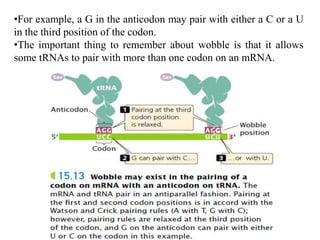
The document outlines the concept of the genetic code, emphasizing that codons, made of three nucleotides, are the basic units of this code, allowing for the encoding of amino acids. It describes properties of the genetic code, such as being degenerate, non-overlapping, comma-less, unambiguous, and nearly universal, as well as detailing the roles of initiation and stop codons. Additionally, the document covers the wobble hypothesis, which explains flexibility in base pairing at the third position of codons.