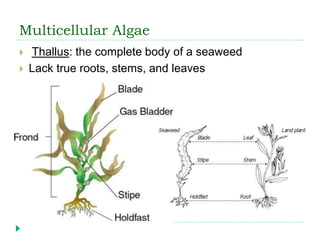
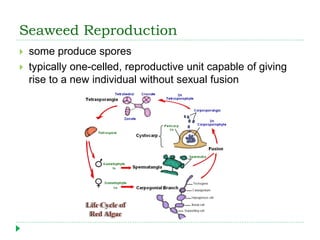
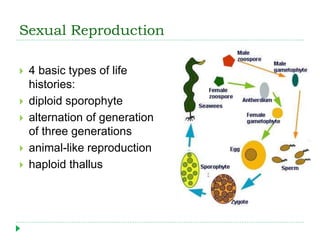
This document discusses seaweeds and plants found in marine environments. It describes seaweeds as multicellular algae that come in three main types - green, brown, and red. The document outlines the key characteristics of seaweeds like their thallus structure and lack of true roots, stems, and leaves. It also discusses economic uses of seaweeds and their role as primary producers. Finally, it briefly introduces flowering seagrasses, salt-marsh plants, and mangroves as examples of marine-adapted angiosperms.