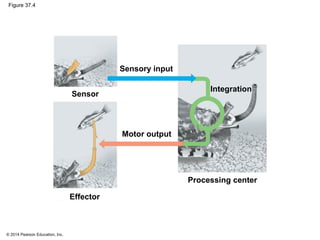
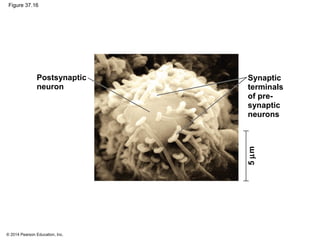
1. Neurons communicate through electrical and chemical signals to transfer information in the body. They have specialized structures like dendrites, axons, and synapses that allow them to receive and transmit signals.
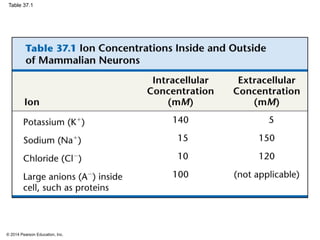
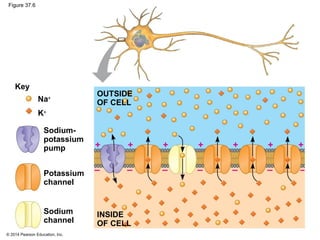
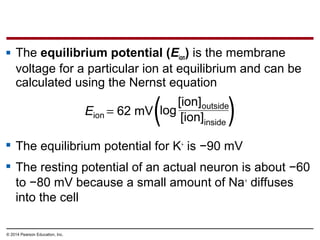
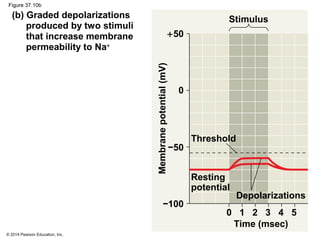
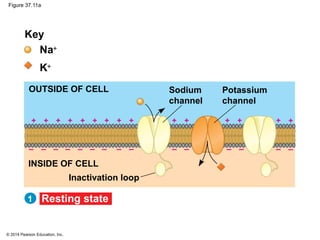
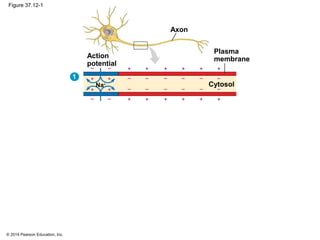
2. At rest, neurons maintain a negative membrane potential through ion pumps and selective ion channels. When stimulated, they may produce graded electrical signals or action potentials for long-distance signaling.
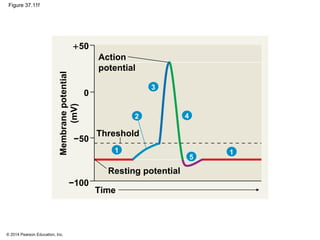
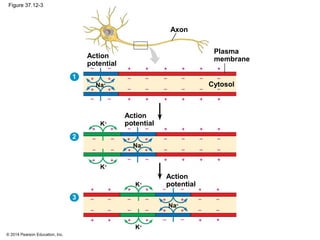
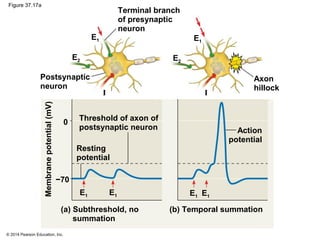
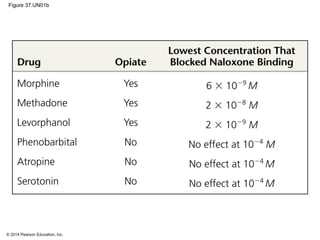
3. Action potentials are generated when the membrane potential reaches a threshold due to changing sodium and potassium concentrations inside and outside the cell. They propagate along axons to transmit signals to other neurons.