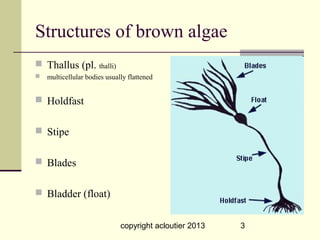
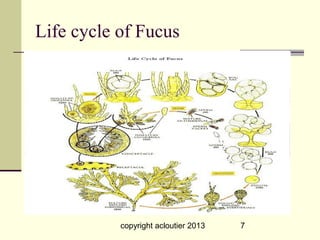
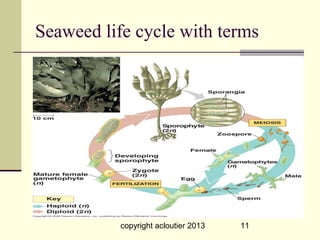
This document summarizes information about three main groups of seaweeds - brown algae, green algae, and red algae. It describes their structures and life cycles, including reproduction processes like meiosis. Some key species are described like giant kelp that can grow to 300 feet. The document also discusses the health benefits of compounds found in seaweeds and how seaweeds are used in food products and other applications.