1. Unit commitment involves determining the optimal mix of generators to meet expected demand while satisfying operational constraints like minimum up and down times. It aims to minimize total costs which include start-up costs and variable running costs.
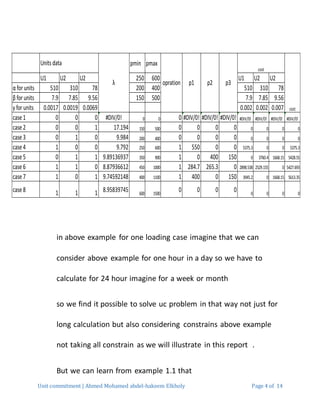
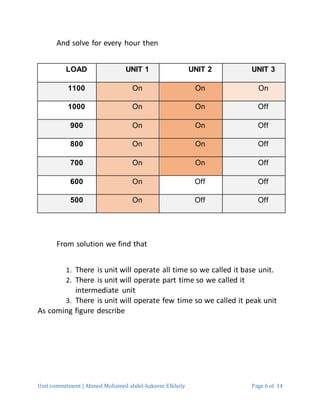
2. The example problem determines the lowest cost combination of 3 generators to produce 550MW of power. Various constraints like minimum generation levels and ramp rates must be considered.
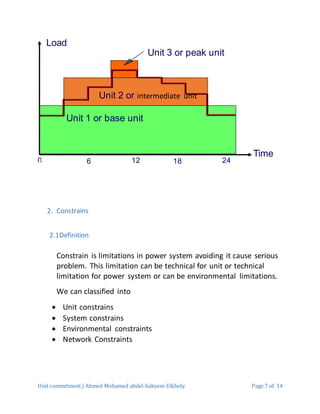
3. Key constraints in unit commitment include minimum and maximum generation limits, minimum up and down times, and ramp rates for changing output. System constraints require matching generation to load while maintaining sufficient operating reserves. Environmental and network limits also factor into the optimization.