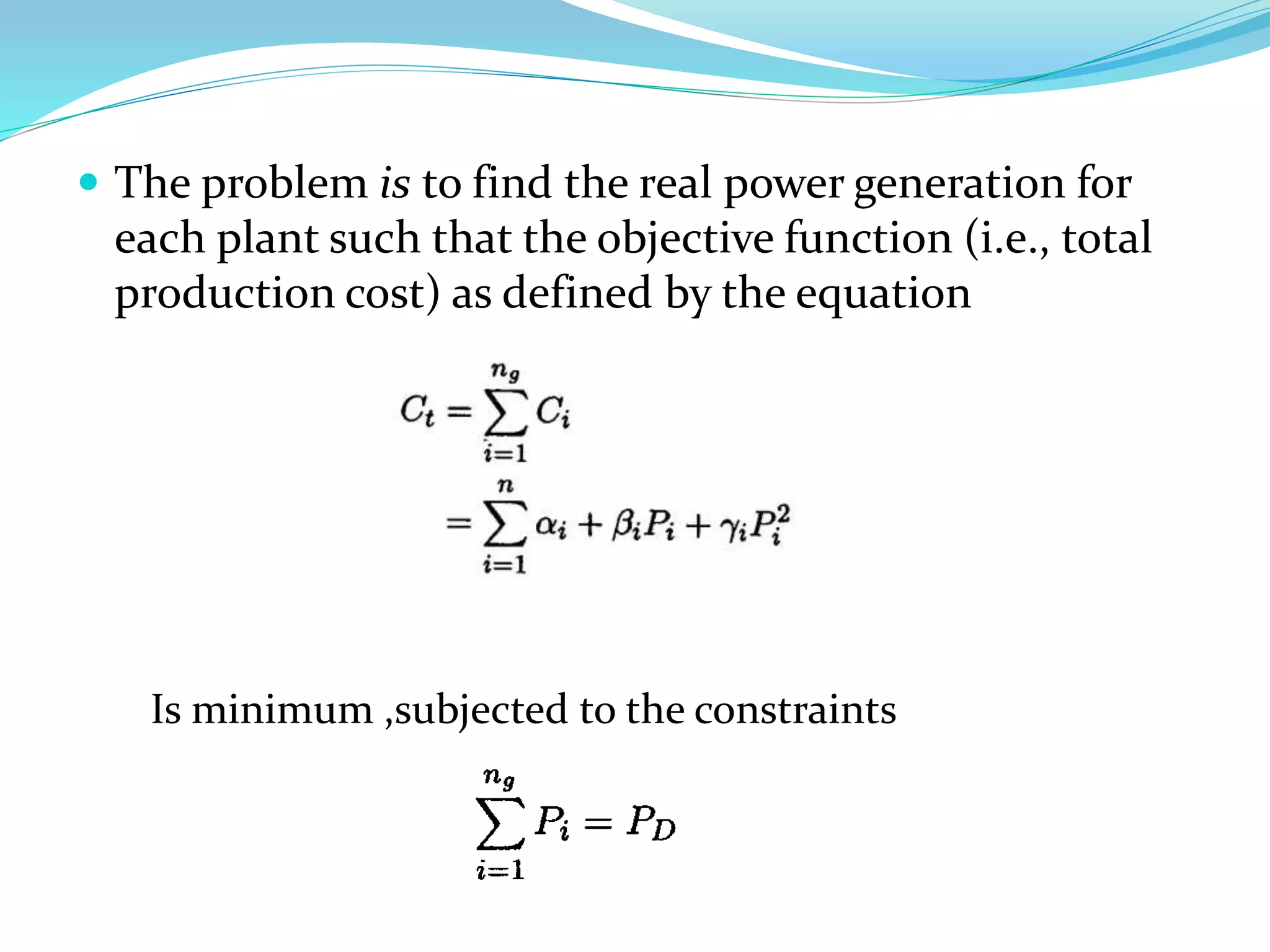
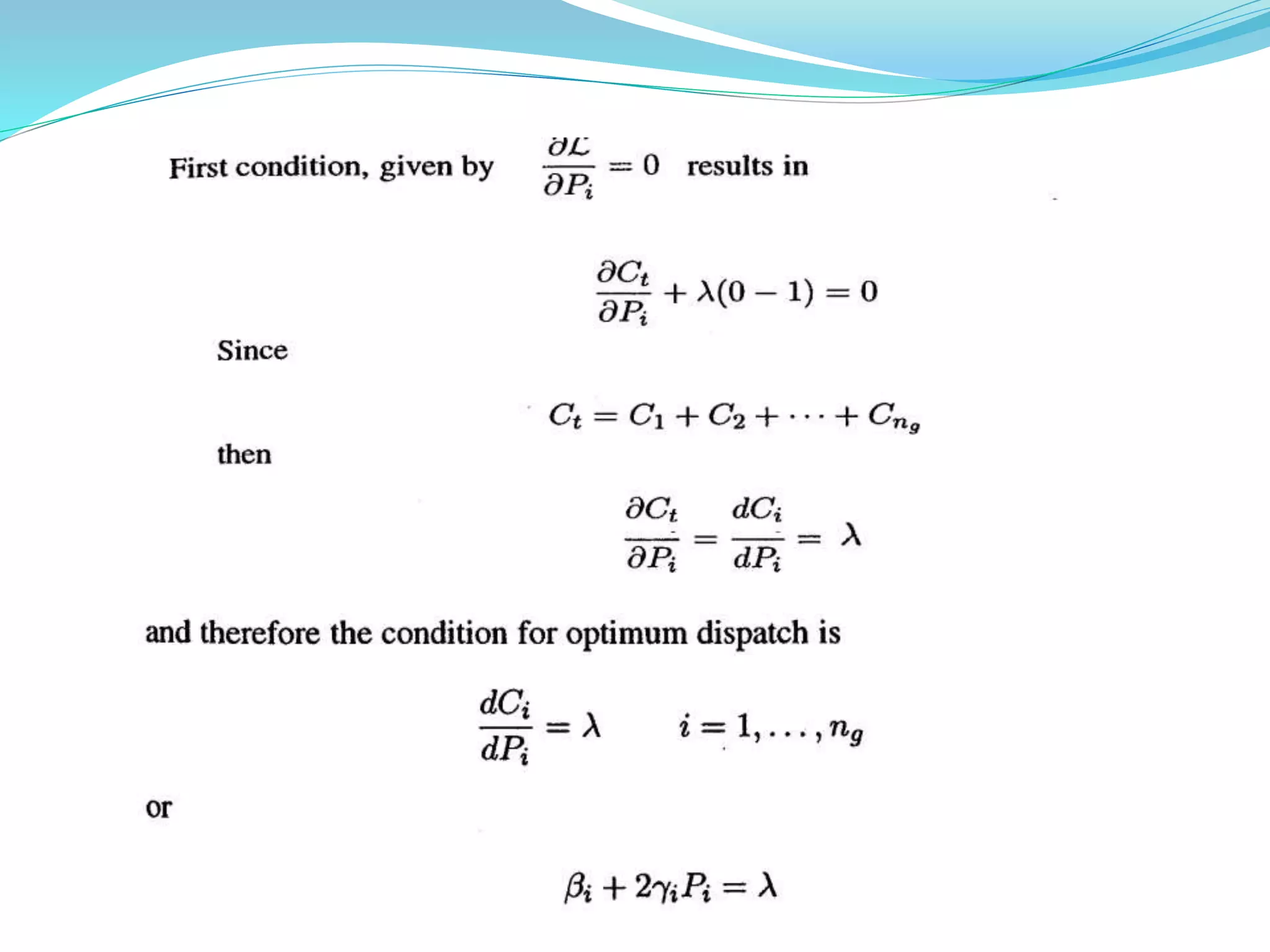
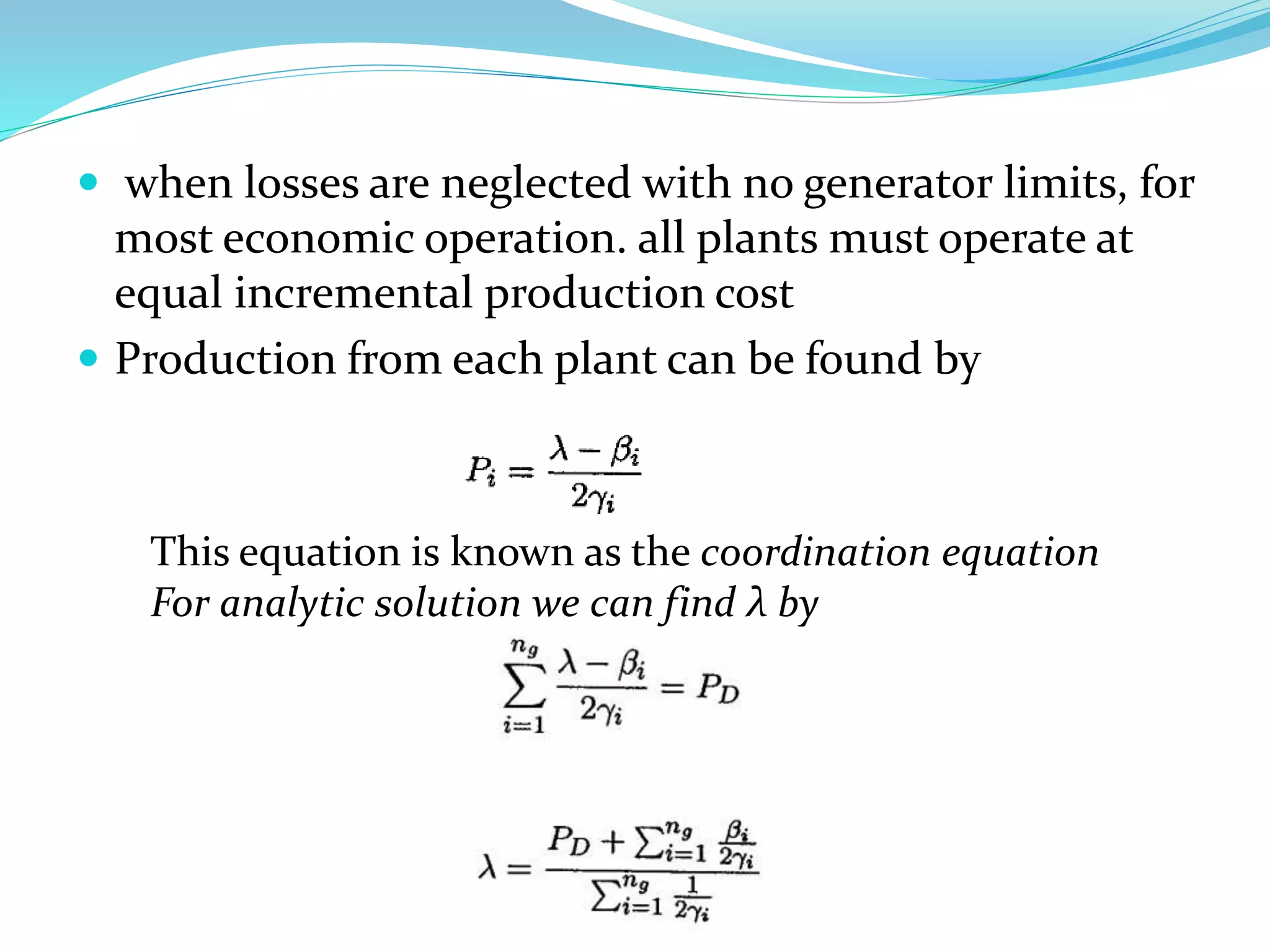
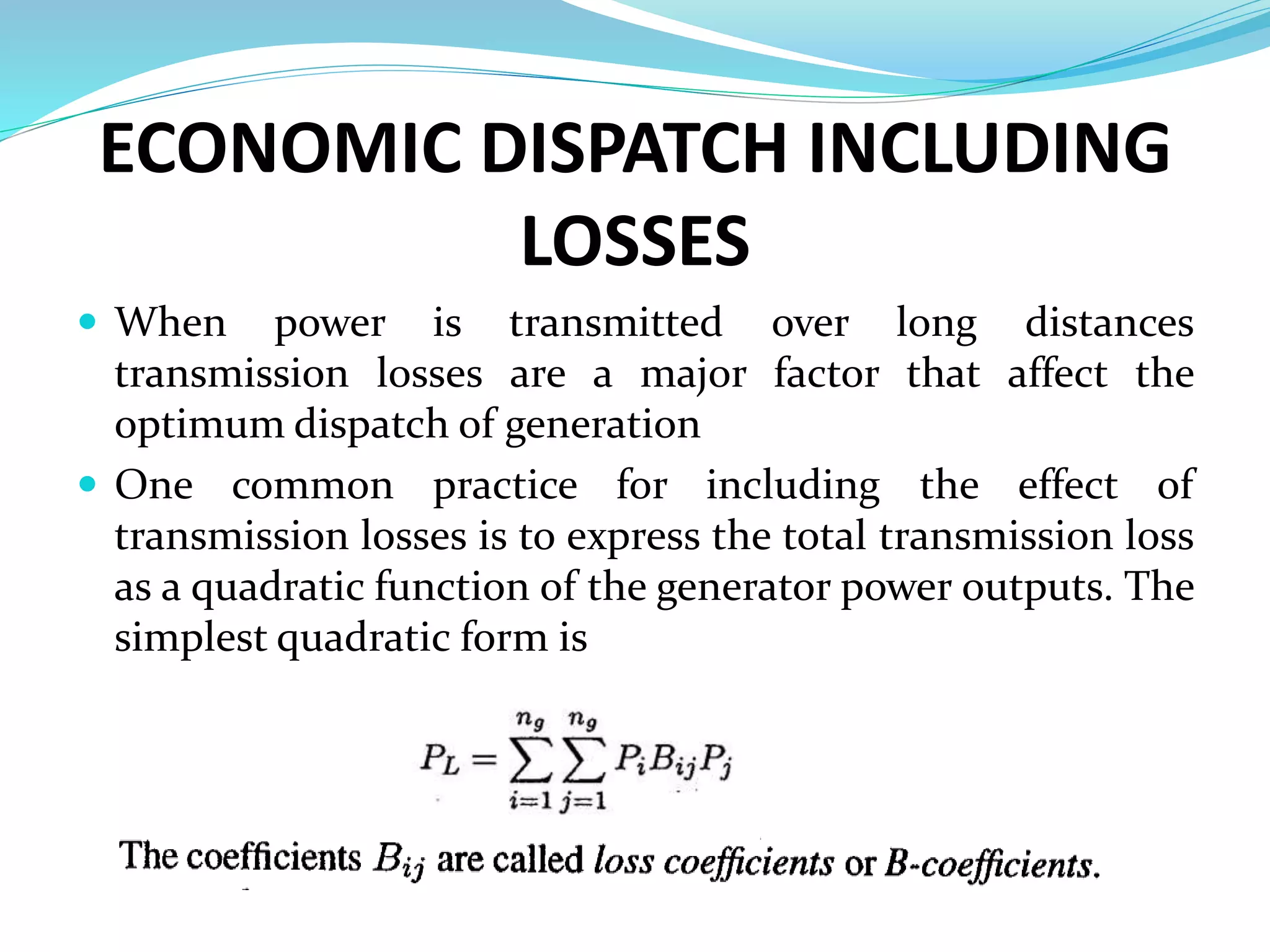
This document discusses economic load dispatch in power systems. It begins by listing the names and IDs of 5 presenters. It then outlines the contents which include introductions to economic dispatch, constraints in economic load dispatch, operating costs of thermal plants, and economic dispatch with and without losses. The document defines economic dispatch as operating generation facilities to produce energy at lowest cost while meeting demand. It describes the constraints and factors that influence minimizing generation costs such as generator efficiencies, fuel costs, and transmission losses. Equations for economic dispatch with and without losses are provided.